Restless Earth - Geography @ KE Camp Hill Boys
... of an earthquake in a rich and poorer area of the world – its causes, effects and responses Understand how and why the effects and responses are different in these two areas Understand means of trying to reduce the impact of earthquakes – the three P’s ...
... of an earthquake in a rich and poorer area of the world – its causes, effects and responses Understand how and why the effects and responses are different in these two areas Understand means of trying to reduce the impact of earthquakes – the three P’s ...
Teaching About Plate Tectonics and Faulting Using Foam Models
... Use the block models to demonstrate normal faulting as the two outer blocks are moved apart as shown in Figure 1B. This procedure is best performed by holding the blocks “in the air” in front of you, supporting the model by the two outer blocks, rather than on a table. Note that as the two outer blo ...
... Use the block models to demonstrate normal faulting as the two outer blocks are moved apart as shown in Figure 1B. This procedure is best performed by holding the blocks “in the air” in front of you, supporting the model by the two outer blocks, rather than on a table. Note that as the two outer blo ...
1 Living with earthquakes and volcanoes
... moved around by currents inside the earth. Notice how in some places the plates are moving towards each other and in other places they are moving apart. Plate boundaries are the places where plates meet – this is where earthquakes and volcanoes often occur. ...
... moved around by currents inside the earth. Notice how in some places the plates are moving towards each other and in other places they are moving apart. Plate boundaries are the places where plates meet – this is where earthquakes and volcanoes often occur. ...
Geology 10 review- Test #3 Read Chapters 10, 11, 12, 15, 16 and 1
... anticline (or plunging syncline), and draw a block diagram to support your answer; Draw a picture of a normal fault (or reverse fault) and label the hanging wall and footwall; What is a strike-slip fault? ...
... anticline (or plunging syncline), and draw a block diagram to support your answer; Draw a picture of a normal fault (or reverse fault) and label the hanging wall and footwall; What is a strike-slip fault? ...
18 Earthquake Prediction
... •Some events are rather rare , they don't happen that often. For instance, car accidents are the exception rather than the rule. Still, over a period of time, we can say something about the nature of rare events. The Poisson distribution was derived by the French mathematician Poisson in 1837, and t ...
... •Some events are rather rare , they don't happen that often. For instance, car accidents are the exception rather than the rule. Still, over a period of time, we can say something about the nature of rare events. The Poisson distribution was derived by the French mathematician Poisson in 1837, and t ...
Reading Science!
... Transform boundaries occur when two plates slide horizontally past one another. Transform boundaries are different than the other boundary types. They do not usually form mountains, volcanoes, or trenches. However, movement along transform boundaries can trigger earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault in ...
... Transform boundaries occur when two plates slide horizontally past one another. Transform boundaries are different than the other boundary types. They do not usually form mountains, volcanoes, or trenches. However, movement along transform boundaries can trigger earthquakes. The San Andreas Fault in ...
ES 104 Laboratory # 4 - Western Oregon University
... The Theory of Plate Tectonics has revolutionized the science of Geology in the last 30 years. The theory states that the outer surface of the earth consists of 7 major lithospheric plates and numerous smaller ones, and these plates move around on a ductile layer referred to as the asthenosphere. The ...
... The Theory of Plate Tectonics has revolutionized the science of Geology in the last 30 years. The theory states that the outer surface of the earth consists of 7 major lithospheric plates and numerous smaller ones, and these plates move around on a ductile layer referred to as the asthenosphere. The ...
Earthquakes - DU Portfolio
... study of earthquakes. http://mbmgquake.mtech.edu/glossary.html Looking at earth, it is apparent that the various continents, especially South America and Africa, resemble pieces of a puzzle. Alfred Wegener developed the theory of continental drift back in 1912, which was not well received and for al ...
... study of earthquakes. http://mbmgquake.mtech.edu/glossary.html Looking at earth, it is apparent that the various continents, especially South America and Africa, resemble pieces of a puzzle. Alfred Wegener developed the theory of continental drift back in 1912, which was not well received and for al ...
Link to Lesson Notes - Mr Santowski`s Math Page
... linear graph we do this by taking the logarithm of our drug level values and then graphing time vs the logarithm of our drug ...
... linear graph we do this by taking the logarithm of our drug level values and then graphing time vs the logarithm of our drug ...
2016_Meghraoui-al_Seismotectonic of Africa
... generally considered to be a stable part of Africa, although several major historical and recent earthquakes have struck the region. The Guinea earthquake of 22nd December 1983 (Mw 6.4) is a good example as an event of intraplate seismicity which occurred on a stable West African craton (2.2-1.8 Ga) ...
... generally considered to be a stable part of Africa, although several major historical and recent earthquakes have struck the region. The Guinea earthquake of 22nd December 1983 (Mw 6.4) is a good example as an event of intraplate seismicity which occurred on a stable West African craton (2.2-1.8 Ga) ...
KEY - Belmont Secondary Home Page
... 3. Fractures in rock along which there is no movement or displacement are called __JOINTS__. 4. Fractures in rock along which movement has occurred are known as __FAULTS__. 5. When geologist talk about the __STRIKE__ of a rock layer, they refer to a compass direction measured parallel to the earth's ...
... 3. Fractures in rock along which there is no movement or displacement are called __JOINTS__. 4. Fractures in rock along which movement has occurred are known as __FAULTS__. 5. When geologist talk about the __STRIKE__ of a rock layer, they refer to a compass direction measured parallel to the earth's ...
A Model of Three Faults
... 3. What kind of fault is the San Andreas Fault? Is California likely to "fall off into the Pacific Ocean"? Why? ...
... 3. What kind of fault is the San Andreas Fault? Is California likely to "fall off into the Pacific Ocean"? Why? ...
Geology of National Parks
... E3.4C Describe the effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions on humans. E3.4d Explain how the chemical composition of magmas relates to plate tectonics and affects the geometry, structure, and explosivity of volcanoes. E3.4 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Plate motions result in potentially catastroph ...
... E3.4C Describe the effects of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions on humans. E3.4d Explain how the chemical composition of magmas relates to plate tectonics and affects the geometry, structure, and explosivity of volcanoes. E3.4 Earthquakes and Volcanoes Plate motions result in potentially catastroph ...
Chiral ratio of the compressional and shear velocity for the
... between capital Kathmandu and tourist town Pokhara. This earthquake was followed by many powerful aftershocks and an unexpected aftershock of local magnitude 6.8 on the Richter scale hit east side of Nepal in the area Dolkha on Tuesday May 12. The earthquakes caused extensive damage to buildings and ...
... between capital Kathmandu and tourist town Pokhara. This earthquake was followed by many powerful aftershocks and an unexpected aftershock of local magnitude 6.8 on the Richter scale hit east side of Nepal in the area Dolkha on Tuesday May 12. The earthquakes caused extensive damage to buildings and ...
What is an earthquake?
... forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. • Cascadia ...
... forces that squeeze rock. • If rock breaks from forces pushing from opposite directions, rock above a reverse fault surface is forced up and over the rock below the fault surface. • Cascadia ...
Earthquakes T. Perron – 12.001 – March 17, 2010 In our lab on
... Change in fault strength (rock WX, water pressure, “damage” due to previous EQs) Changes in stress state due to nearby EQs The actual EQ time series often looks like this: ...
... Change in fault strength (rock WX, water pressure, “damage” due to previous EQs) Changes in stress state due to nearby EQs The actual EQ time series often looks like this: ...
Development of the next generation Australian National Earthquake
... Most probabilistic seismic-hazard assessments (PSHAs) require an estimate of Mmax – the magnitude of the largest earthquake that is thought possible within a specified area – and are highly sensitive to the choice of Mmax (e.g., Mueller 2010). By virtue of a fortuitous combination of climatic condit ...
... Most probabilistic seismic-hazard assessments (PSHAs) require an estimate of Mmax – the magnitude of the largest earthquake that is thought possible within a specified area – and are highly sensitive to the choice of Mmax (e.g., Mueller 2010). By virtue of a fortuitous combination of climatic condit ...
An Alternative Analysis of the Probabilistic Seismic Hazard for Las Vegas Valley, Nevada 2014
... DEPTH Well data show that ~2/3 of the basin-fill is > ~5 Ma <5 Ma basin has less paleorelief along its base, is broader and more symmetric Shape difference and depocenter shift caused by Edipping LVFS ...
... DEPTH Well data show that ~2/3 of the basin-fill is > ~5 Ma <5 Ma basin has less paleorelief along its base, is broader and more symmetric Shape difference and depocenter shift caused by Edipping LVFS ...
Directions: Select the best answer for each item. (8.P.1A.3) Some
... d. The remains of Mesosaurus were carried across the ocean by predators. ...
... d. The remains of Mesosaurus were carried across the ocean by predators. ...
Grand Challenges for Seismology
... driving forces of plate tectonics, and the generation of the magnetic field all involve convective flow in the mantle and core. Improving the seismological resolution of deep structure as data accumulate and as new analysis methods are developed will help reveal the patterns of flow. Recent observat ...
... driving forces of plate tectonics, and the generation of the magnetic field all involve convective flow in the mantle and core. Improving the seismological resolution of deep structure as data accumulate and as new analysis methods are developed will help reveal the patterns of flow. Recent observat ...
Lab: Exploring Patterns in Regional Seismicity
... Geomorphology - the study of the physical features of the surface of the earth and their relation to its geological structures Background: Plate Tectonics The lithosphere can be divided into many large plates, which are moved around the surface of the planet over time. During this motion, plates int ...
... Geomorphology - the study of the physical features of the surface of the earth and their relation to its geological structures Background: Plate Tectonics The lithosphere can be divided into many large plates, which are moved around the surface of the planet over time. During this motion, plates int ...
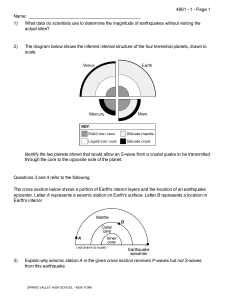
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
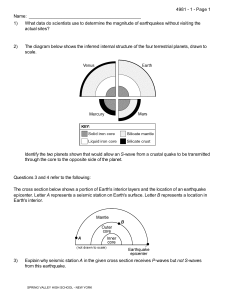
Name: 1) What data do scientists use to determine the magnitude of
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
... The Three Sisters are 10,000-foot volcanic mountain peaks in Oregon. Volcanic eruptions began building the Three Sisters from andesitic lava and cinders 700,000 years ago. The last major eruption occurred 2,000 years ago. West of the Three Sisters peaks, geologists have recently discovered that Eart ...
FOLDS AND STRUCTURES DUE TO FOLDING
... Folding generally takes place in areas of sedimentary rocks that have been laid down in horizontal layers called strata. ...
... Folding generally takes place in areas of sedimentary rocks that have been laid down in horizontal layers called strata. ...
Earthquake

An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, which can be violent enough to destroy major buildings and kill thousands of people. The severity of the shaking can range from barely felt to violent enough to toss people around. Earthquakes have destroyed whole cities. They result from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time.Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale. These two scales are numerically similar over their range of validity. Magnitude 3 or lower earthquakes are mostly almost imperceptible or weak and magnitude 7 and over potentially cause serious damage over larger areas, depending on their depth. The largest earthquakes in historic times have been of magnitude slightly over 9, although there is no limit to the possible magnitude. The most recent large earthquake of magnitude 9.0 or larger was a 9.0 magnitude earthquake in Japan in 2011 (as of March 2014), and it was the largest Japanese earthquake since records began. Intensity of shaking is measured on the modified Mercalli scale. The shallower an earthquake, the more damage to structures it causes, all else being equal.At the Earth's surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally volcanic activity.In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An earthquake's point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.