File
... Section 11.4 Technology: Before Pangaea, Rodinia Scientists studying rock types and structures in Antarctica use computer models to show how new evidence supports the formation of a super-continent long before Pangaea Super-continent called Rodinia, formed more than 750 million years ago In th ...
... Section 11.4 Technology: Before Pangaea, Rodinia Scientists studying rock types and structures in Antarctica use computer models to show how new evidence supports the formation of a super-continent long before Pangaea Super-continent called Rodinia, formed more than 750 million years ago In th ...
chapter in perspective
... volcanic islands. The processes of plate tectonics, erosion, and sediment deposition have shaped the continental margins and ocean basins. In the next chapter you will learn that nearly all the ocean floor is blanketed with sediment. Except for the spreading centers themselves, the broad shoulders o ...
... volcanic islands. The processes of plate tectonics, erosion, and sediment deposition have shaped the continental margins and ocean basins. In the next chapter you will learn that nearly all the ocean floor is blanketed with sediment. Except for the spreading centers themselves, the broad shoulders o ...
Take Home 11 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... A. Earthquakes are evidence of changes in the ocean floor. B. The measurement of the weight of the ocean gave evidence of sea floor spreading. C. The ocean floor was mapped and studied using sonar and magnetometers. D. Scientists used computer measurements of volcanic activity to give details of the ...
... A. Earthquakes are evidence of changes in the ocean floor. B. The measurement of the weight of the ocean gave evidence of sea floor spreading. C. The ocean floor was mapped and studied using sonar and magnetometers. D. Scientists used computer measurements of volcanic activity to give details of the ...
How the Continents Move (910L)
... lands." There are several clues that led to the theory of Pangaea. Sir Francis Bacon noticed the first clue: the close fit of Africa and South America. But it is also interesting to see how Canada, Greenland, and northern Europe could be squeezed together into one big land mass. This idea of a huge ...
... lands." There are several clues that led to the theory of Pangaea. Sir Francis Bacon noticed the first clue: the close fit of Africa and South America. But it is also interesting to see how Canada, Greenland, and northern Europe could be squeezed together into one big land mass. This idea of a huge ...
Geology :: 7. Plate interiors
... continents, where the oceanic rocks are compressed, folded and lifted up. The rock composition of these belts is variable; fragments of oceanic and continental crust may occur as well as thick, deformed sedimentary sequences, volcanic and intrusive bodies. ...
... continents, where the oceanic rocks are compressed, folded and lifted up. The rock composition of these belts is variable; fragments of oceanic and continental crust may occur as well as thick, deformed sedimentary sequences, volcanic and intrusive bodies. ...
Development of the Theory of Plate Tectonics
... The rising convection current below the oceanic plate lifts the lithosphere producing a mid-ocean ridge. The lithosphere becomes stretched and fractured. The open fracture allows magma to flow into the fracture, solidify and repeat. ...
... The rising convection current below the oceanic plate lifts the lithosphere producing a mid-ocean ridge. The lithosphere becomes stretched and fractured. The open fracture allows magma to flow into the fracture, solidify and repeat. ...
geo-4840 tectonics-s04
... (Mediterranean See area) 3) Vaning stage: Intra-oceanic subduction and island arcs transition to Andean margins. (SE Asia and Western Passific) 2) Mature stage Passive margins with large shelf-areas (Atlantic Ocean) 1) Embryonic to Young stage. Rifts to small ocean basin with sea-floor spreading. (E ...
... (Mediterranean See area) 3) Vaning stage: Intra-oceanic subduction and island arcs transition to Andean margins. (SE Asia and Western Passific) 2) Mature stage Passive margins with large shelf-areas (Atlantic Ocean) 1) Embryonic to Young stage. Rifts to small ocean basin with sea-floor spreading. (E ...
The Paleozoic/Mesozoic tectonic evolution of Eastern Australia
... Relationships between metal deposits and both divergent and convergent margin processes have been known for many decades. However, the challenge still remains to understand the way in which "geodynamic niches" such as slab windows, rapid convergence, or phases of flatslab subduction, control the for ...
... Relationships between metal deposits and both divergent and convergent margin processes have been known for many decades. However, the challenge still remains to understand the way in which "geodynamic niches" such as slab windows, rapid convergence, or phases of flatslab subduction, control the for ...
19.4 Continental United States Geology
... ever closer to Laurasia. Gondwanaland collided just below where Laurentia and Baltica collided with each other. This new collision raised another set of mountains that continued the northern Appalachians into what are now the southern Appalachians. The combined Appalachians were as high as the Himal ...
... ever closer to Laurasia. Gondwanaland collided just below where Laurentia and Baltica collided with each other. This new collision raised another set of mountains that continued the northern Appalachians into what are now the southern Appalachians. The combined Appalachians were as high as the Himal ...
First Theory – 1880`s
... similar rocks, geologic structures and fossils on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean ...
... similar rocks, geologic structures and fossils on opposite sides of the Atlantic Ocean ...
Plate Tectonics Review Worksheet
... 6. What is the lithosphere – Solid outer layer of the earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper portion of the mantle. What is the Asthenosphere - the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move. What is the Mesosphere – the strong lower part of the mantle between the asthe ...
... 6. What is the lithosphere – Solid outer layer of the earth that consists of the crust and the rigid upper portion of the mantle. What is the Asthenosphere - the soft layer of the mantle on which the tectonic plates move. What is the Mesosphere – the strong lower part of the mantle between the asthe ...
Word - LEARNZ
... Antarctica and Gondwanaland Science History Scientists had noticed that the coast lines of Africa and South America could fit together. In the 1920’s Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift; that there was one super continent, Pangaea, ( meaning all lands ), and that this broke up, f ...
... Antarctica and Gondwanaland Science History Scientists had noticed that the coast lines of Africa and South America could fit together. In the 1920’s Alfred Wegener proposed the theory of continental drift; that there was one super continent, Pangaea, ( meaning all lands ), and that this broke up, f ...
Plates on the Move
... once joined together in a single large land mass he called Pangea (meaning “all land” in Greek). • He proposed that Pangea split apart & the continents moved gradually to their present positions - a process that became known as continental drift. ...
... once joined together in a single large land mass he called Pangea (meaning “all land” in Greek). • He proposed that Pangea split apart & the continents moved gradually to their present positions - a process that became known as continental drift. ...
File
... • The plates consist of two types of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. • The theory explains the movement of the earth’s plates and the cause of earthquakes, volcanoes, oceanic trenches, mountain ranges and many other ...
... • The plates consist of two types of crust: continental crust and oceanic crust. • The theory explains the movement of the earth’s plates and the cause of earthquakes, volcanoes, oceanic trenches, mountain ranges and many other ...
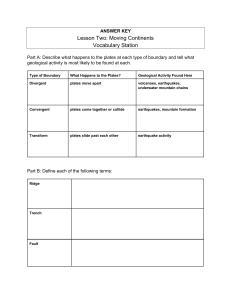
Lesson Two: Moving Continents Vocabulary Station
... According to the Continental Drift Theory, the continents once formed a giant landmass named Pangaea. It wasn’t until the 1950s and 1960s that scientists began to explain how the continents were able to move with their discovery of the midocean ridges and sea-floor spreading. According to this new t ...
... According to the Continental Drift Theory, the continents once formed a giant landmass named Pangaea. It wasn’t until the 1950s and 1960s that scientists began to explain how the continents were able to move with their discovery of the midocean ridges and sea-floor spreading. According to this new t ...
Plate Tectonics and Continental Drift
... b. When it split apart it separated into two parts with the proto-Atlantic between them (called Tethys Sea). ...
... b. When it split apart it separated into two parts with the proto-Atlantic between them (called Tethys Sea). ...
$doc.title
... • Continental slope: steep, boundary between continental and oceanic crust. Submarine canyons. To 3,000 - 4,000 M depth. • Continental rise: sediment accumulation. Turbidity currents. Mud and sand. • Abyssal plain: 4,500 - 6,000 M depth. Oceanic crust below. Mostly flat and soft sediment. Mangane ...
... • Continental slope: steep, boundary between continental and oceanic crust. Submarine canyons. To 3,000 - 4,000 M depth. • Continental rise: sediment accumulation. Turbidity currents. Mud and sand. • Abyssal plain: 4,500 - 6,000 M depth. Oceanic crust below. Mostly flat and soft sediment. Mangane ...
Physical Geology 1330 Dr. Mike Murphy
... Magnetic Stripes – parallel stripes of normally and reversely magnetized rock present on the seafloor and symmetric about mid-ocean ridges. Paleomagnetic Time Scale – established by measuring the magnetic polarity of lava flows of known age. ...
... Magnetic Stripes – parallel stripes of normally and reversely magnetized rock present on the seafloor and symmetric about mid-ocean ridges. Paleomagnetic Time Scale – established by measuring the magnetic polarity of lava flows of known age. ...
The Active Earth
... plates causing them to move small distances over long periods of time in relation to each other. ...
... plates causing them to move small distances over long periods of time in relation to each other. ...
Earth Science Library wk 8.cwk
... 1. No one could explain what forced the continents to move: Wegener’s original thought was that the continents somehow plow through the oceanic crust. Did not seem plausible given what was known about the strength of rocks. ...
... 1. No one could explain what forced the continents to move: Wegener’s original thought was that the continents somehow plow through the oceanic crust. Did not seem plausible given what was known about the strength of rocks. ...
Answers to the study guide
... 1. What are the 5 layers of the Earth a. Crust, Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core 2. Which layer of the Earth is liquid? a. Outer core 3. What makes up the lithosphere? a. The crust and the very upper portion of the mantle 4. Where is the asthenosphere located? a. Just below ...
... 1. What are the 5 layers of the Earth a. Crust, Lithosphere, asthenosphere, mantle, outer core, inner core 2. Which layer of the Earth is liquid? a. Outer core 3. What makes up the lithosphere? a. The crust and the very upper portion of the mantle 4. Where is the asthenosphere located? a. Just below ...
Plates on the Move
... together in a single large land mass he called Pangea (meaning “all land” in Greek). • He proposed that Pangea had split apart and the continents had moved gradually to their present positions - a process that became known as continental drift. ...
... together in a single large land mass he called Pangea (meaning “all land” in Greek). • He proposed that Pangea had split apart and the continents had moved gradually to their present positions - a process that became known as continental drift. ...
Supercontinent

In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of the Earth's continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, the definition of a supercontinent can be ambiguous. Many tectonicists such as P.F. Hoffman (1999) use the term ""supercontinent"" to mean ""a clustering of nearly all continents"". This definition leaves room for interpretation when labeling a continental body and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. Using the first definition provided here, Gondwana (aka Gondwanaland) is not considered a supercontinent, because the landmasses of Baltica, Laurentia and Siberia also existed at the same time but physically separate from each other. The landmass of Pangaea is the collective name describing all of these continental masses when they were in a close proximity to one another. This would classify Pangaea as a supercontinent. According to the definition by Rogers and Santosh (2004), a supercontinent does not exist today. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). The positions of continents have been accurately determined back to the early Jurassic. However, beyond 200 Ma, continental positions are much less certain.