Document
... Newton, who extended the concept of inertia to all bodies, realized that the moon is accelerating and is therefore subject to a centripetal force. He guessed that the force that keeps the moon in its orbit has the same origin as the force that causes the apple to fall. He recalled some thirty years ...
... Newton, who extended the concept of inertia to all bodies, realized that the moon is accelerating and is therefore subject to a centripetal force. He guessed that the force that keeps the moon in its orbit has the same origin as the force that causes the apple to fall. He recalled some thirty years ...
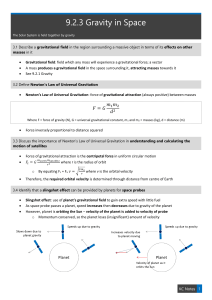
9.2.3 Gravity in Space
... o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity especially at equator o However, it is not acting as an ine ...
... o Altitude: Further away, less gravity (mountains, valleys, satellites) o Local crust density: more dense, more gravity o Oblation/shape: greater radius at equator than poles The spin of the Earth generates a centrifuge effect, less gravity especially at equator o However, it is not acting as an ine ...
ert146 lect on translational motion
... • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origin at an arbitrary point P is established. The x-y axes should not rotate and can either be fixed or translate with consta ...
... • As discussed in Chapter 16, when a body is subjected to general plane motion, it undergoes a combination of translation and rotation. • First, a coordinate system with its origin at an arbitrary point P is established. The x-y axes should not rotate and can either be fixed or translate with consta ...
C_Energy Notes PGP
... Problem: A sled loaded with bricks has a mass of 20.0 kg. It is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 25o above the horizontal, and it moves a distance of 100 m on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ground is 0.40, ...
... Problem: A sled loaded with bricks has a mass of 20.0 kg. It is pulled at constant speed by a rope inclined at 25o above the horizontal, and it moves a distance of 100 m on a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the sled and the ground is 0.40, ...
Group Problem 11 - University of St. Thomas
... Group Problem #11 Phys 112-1 F12 Page 1 of 4 Group problem #11: Capacitors, work and energy Two metal spheres are connected by a conducting wire. Sphere 1 has a radius, R1, a charge Q1, and an electric field strength at the surface of E1. Similarly Sphere 2 has a radius, R2, a charge, Q2 and an elec ...
... Group Problem #11 Phys 112-1 F12 Page 1 of 4 Group problem #11: Capacitors, work and energy Two metal spheres are connected by a conducting wire. Sphere 1 has a radius, R1, a charge Q1, and an electric field strength at the surface of E1. Similarly Sphere 2 has a radius, R2, a charge, Q2 and an elec ...
Introductory Physics
... • Speed – how fast something is moving • Velocity – speed and direction • Acceleration – change in velocity ...
... • Speed – how fast something is moving • Velocity – speed and direction • Acceleration – change in velocity ...
Set 5
... 3) A very thin circular disk with radius R and mass M lies in the xy-plane with its center at the origin. a) Assuming that the mass of the disk is distributed uniformly over its circular area, determine the elements of the inertia tensor. Note that the disk has azimuthal symmetry. b) The disk is now ...
... 3) A very thin circular disk with radius R and mass M lies in the xy-plane with its center at the origin. a) Assuming that the mass of the disk is distributed uniformly over its circular area, determine the elements of the inertia tensor. Note that the disk has azimuthal symmetry. b) The disk is now ...
WEEK 4 1/30/12 Kepler`s 3 Laws The 3 rules of planetary motion
... ■ G is calibrated to meters and must make sure other distances in equation are meters as well. Newton can explain every single motion at his time with the application of these 4 laws o Then we discovered Mercury was slightly off of where it was predicted to be § Red flag that the theory is not 100% ...
... ■ G is calibrated to meters and must make sure other distances in equation are meters as well. Newton can explain every single motion at his time with the application of these 4 laws o Then we discovered Mercury was slightly off of where it was predicted to be § Red flag that the theory is not 100% ...
Spring 2008 Qualifying Exam
... fixed point A. (See figure!) Find the angle of inclination by either finding the EulerLagrange equations of motion, or by using methods based on d’Alembert’s principle. ...
... fixed point A. (See figure!) Find the angle of inclination by either finding the EulerLagrange equations of motion, or by using methods based on d’Alembert’s principle. ...
Equilibrium of Concurrent, Coplanar Force Systems Powerpoint
... Where is a body’s mass center? We’ll study that in Module 4. But in this class, the entire body is at rest, so we know that the mass center, wherever it is, has zero acceleration. ...
... Where is a body’s mass center? We’ll study that in Module 4. But in this class, the entire body is at rest, so we know that the mass center, wherever it is, has zero acceleration. ...
Exploration of Space Lecture B
... Since the expression (42K) is a constant, the force of gravitational attraction on a planet is directly proportional to the mass of the planet and inversely proportional to the square of its distance from the sun. We saw in the previous lesson that Kepler’s constant is the same for any object circl ...
... Since the expression (42K) is a constant, the force of gravitational attraction on a planet is directly proportional to the mass of the planet and inversely proportional to the square of its distance from the sun. We saw in the previous lesson that Kepler’s constant is the same for any object circl ...