Physics_U7
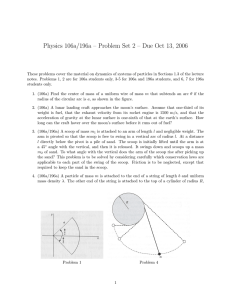
... Practice Problem #1 A honeybee with a mass of 0.150g lands on a 4.75g popsicle stick. The bee runs toward the opposite end of the stick. The stick moves with a speed of 0.120 cm/s relative to the water. Find the speed of the bee. ...
... Practice Problem #1 A honeybee with a mass of 0.150g lands on a 4.75g popsicle stick. The bee runs toward the opposite end of the stick. The stick moves with a speed of 0.120 cm/s relative to the water. Find the speed of the bee. ...
APC-Gravity - APlusPhysics
... AP-C Objectives (from College Board Learning Objectives for AP Physics 1. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation a. Determine the force that one spherically symmetrical mass exerts on another. b. Determine the strength of the gravitational field at a specified point outside a spherically symmetrical ...
... AP-C Objectives (from College Board Learning Objectives for AP Physics 1. Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation a. Determine the force that one spherically symmetrical mass exerts on another. b. Determine the strength of the gravitational field at a specified point outside a spherically symmetrical ...
95.144 Final Exam Spring 2015
... a) Determine the image position using ray tracing (draw it). Identify if the image is upright/inverted and real/virtual. b) Calculate the image position and height. ...
... a) Determine the image position using ray tracing (draw it). Identify if the image is upright/inverted and real/virtual. b) Calculate the image position and height. ...
Differentiate between a) Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and
... The etching is due to both physical and chemical processes The ions being high energy particles are able to physically knock off the material without having to react with it ...
... The etching is due to both physical and chemical processes The ions being high energy particles are able to physically knock off the material without having to react with it ...
EQUATIONS OF MOTION: RECTANGULAR COORDINATES
... Establish your coordinate system and draw the particle’s free body diagram showing only external forces. These external forces usually include the weight, normal forces, friction forces, and applied forces. Show the ‘ma’ vector (sometimes called the inertial force) on a separate diagram. Make sure a ...
... Establish your coordinate system and draw the particle’s free body diagram showing only external forces. These external forces usually include the weight, normal forces, friction forces, and applied forces. Show the ‘ma’ vector (sometimes called the inertial force) on a separate diagram. Make sure a ...
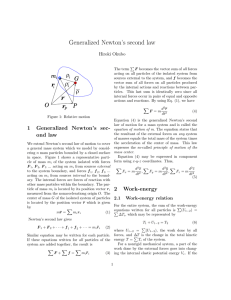
Fields and Forces Gravitational force and fields State Newton`s
... g= gravitational field strength F= Force m= mass 1.1.3. Determine the gravitational field due to one or more point masses Field lines: are drawn in the direction that a mass would accelerate if placed in the field. Field strength (g): is given by the density of the lines. 1.1.4. Device an expression ...
... g= gravitational field strength F= Force m= mass 1.1.3. Determine the gravitational field due to one or more point masses Field lines: are drawn in the direction that a mass would accelerate if placed in the field. Field strength (g): is given by the density of the lines. 1.1.4. Device an expression ...