Newton`s Laws Online
... Newton’s Law of Inertia QUESTION: If both teams pull the tag with equal force, what would the net force be? Section 3: Newton’s Second Law State Newton’s Second Law and write the equation. QUESTION: How much net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 5.00 m/s2? QUESTION: If you apply a net ...
... Newton’s Law of Inertia QUESTION: If both teams pull the tag with equal force, what would the net force be? Section 3: Newton’s Second Law State Newton’s Second Law and write the equation. QUESTION: How much net force is required to accelerate a 1000 kg car at 5.00 m/s2? QUESTION: If you apply a net ...
Activity - Newtons First Law File
... Answer the following questions and take good notes when necessary. This assignment will work well as a study guide if done neatly and properly. The solutions to this assignment will be posted on Moodle later – be sure to check your answers to the ...
... Answer the following questions and take good notes when necessary. This assignment will work well as a study guide if done neatly and properly. The solutions to this assignment will be posted on Moodle later – be sure to check your answers to the ...
01 - Fairfield Public Schools
... slide across the room? _______________________________________________________________ 6. According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will happen to the motion of objects moving with a certain velocity unless an unbalanced force acts on them? _____________________________________________________ ...
... slide across the room? _______________________________________________________________ 6. According to Newton’s first law of motion, what will happen to the motion of objects moving with a certain velocity unless an unbalanced force acts on them? _____________________________________________________ ...
Models ODE initial problem
... Systems which are described by a system of ordinary differential equations and their solutions are fully described by the initial state, are for example integral models of mass and enthalpy balances elementary units ("lumped parameter" or "compartment" models). The aim is to determine the evolution ...
... Systems which are described by a system of ordinary differential equations and their solutions are fully described by the initial state, are for example integral models of mass and enthalpy balances elementary units ("lumped parameter" or "compartment" models). The aim is to determine the evolution ...
Chapter 4-5 Review Ideas and Concepts You Are Responsible For
... Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System Define net force, external force, and system. Understand Newton’s second law of motion. Apply Newton’s second law to determine the weight of an o ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion: Inertia Define mass and inertia. Understand Newton's first law of motion. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a System Define net force, external force, and system. Understand Newton’s second law of motion. Apply Newton’s second law to determine the weight of an o ...
Equation Sheet – Physics 105
... 1. (2 Points) If we know an object is moving at constant velocity, we may assume: a. the net force acting on the object is zero. b. there are no forces acting on the object. c. the object is accelerating. d. the object is losing mass. 2. (2 Points) If the only forces action on a 2.0 kg mass are F1 ...
... 1. (2 Points) If we know an object is moving at constant velocity, we may assume: a. the net force acting on the object is zero. b. there are no forces acting on the object. c. the object is accelerating. d. the object is losing mass. 2. (2 Points) If the only forces action on a 2.0 kg mass are F1 ...
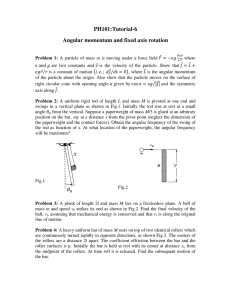
orbital motion in an inverse-square-law force field
... force exerted by the sun and acting on a planet is a central force, i.e., at all times directed along the radius vector and pointing toward the sun, and not having at any time a component, however small, perpendicular to the radius. A force of this nature cannot change the angular momentum of the pl ...
... force exerted by the sun and acting on a planet is a central force, i.e., at all times directed along the radius vector and pointing toward the sun, and not having at any time a component, however small, perpendicular to the radius. A force of this nature cannot change the angular momentum of the pl ...
2010 Spring - Jonathan Whitmore
... PROBLEM: Consider a 2-level system with energy states ( and ( + δ (δ ≥ 0). Compute the partition function and the free energy of the system. Derive an expression for the specific heat C(T ). Obtain the low-T and high-T limits of this expression. Make a sketch of your result. SOLUTION: ...
... PROBLEM: Consider a 2-level system with energy states ( and ( + δ (δ ≥ 0). Compute the partition function and the free energy of the system. Derive an expression for the specific heat C(T ). Obtain the low-T and high-T limits of this expression. Make a sketch of your result. SOLUTION: ...
Problem 1 - University of Rochester
... Imagine two electrically charged particles are separated by a distance of 0.5 meters. Particle A has a mass of 2 kg and carries a positive electrical charge of +1 Coulombs. Particle B has a mass of 4 kg and carries a charge -1.5 Coulombs. a) On the sketch below, indicate with a little arrow the dire ...
... Imagine two electrically charged particles are separated by a distance of 0.5 meters. Particle A has a mass of 2 kg and carries a positive electrical charge of +1 Coulombs. Particle B has a mass of 4 kg and carries a charge -1.5 Coulombs. a) On the sketch below, indicate with a little arrow the dire ...
Chapter6
... There are three common formulations of classical mechanics: the Newtonian, Lagrangian, and Halmiltonian formulations. A very useful property of the Lagrangian and Halmiltonian formulations is that they have the same form in any coordinate system. We will only discuss Halmiltonian mechanics that uses ...
... There are three common formulations of classical mechanics: the Newtonian, Lagrangian, and Halmiltonian formulations. A very useful property of the Lagrangian and Halmiltonian formulations is that they have the same form in any coordinate system. We will only discuss Halmiltonian mechanics that uses ...