SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
... τ = r × F , τ is perpendicular to the plane containing r and F, and its direction is given by the right handed screw rule. ...
... τ = r × F , τ is perpendicular to the plane containing r and F, and its direction is given by the right handed screw rule. ...
Newtonian Mechanics * Momentum, Energy, Collisions
... 1) Write an Excel program that has the following input fields: m1, m2 , v1 , v2 , u1 , u2 . 2) Create (and label) fields that calculate p1initial , p2initial , p1final , p2final . 3) Create (and label) fields that calculate ptotal initial , ptotal final. 4) Create (and label) fields that calculate p ...
... 1) Write an Excel program that has the following input fields: m1, m2 , v1 , v2 , u1 , u2 . 2) Create (and label) fields that calculate p1initial , p2initial , p1final , p2final . 3) Create (and label) fields that calculate ptotal initial , ptotal final. 4) Create (and label) fields that calculate p ...
I. Newton`s Laws of Motion - Old Saybrook Public Schools
... Balanced Forces forces acting on an object that are opposite in direction and equal in size no change in velocity ...
... Balanced Forces forces acting on an object that are opposite in direction and equal in size no change in velocity ...
DYNAMICS 10th solutions
... A section of track for a roller coaster consists of two circular arcs AB and CD joined by a straight portion BC. The radius of AB is 27 m and the radius of CD is 72 m. The car and its occupants, of total mass 250 kg, reach Point A with practically no velocity and then drop freely along the track. De ...
... A section of track for a roller coaster consists of two circular arcs AB and CD joined by a straight portion BC. The radius of AB is 27 m and the radius of CD is 72 m. The car and its occupants, of total mass 250 kg, reach Point A with practically no velocity and then drop freely along the track. De ...
Math 1302, Week 3 Polar coordinates and orbital motion 1
... Kepler’s Laws of motion First Law Planets move in ellipses with the sun at a focus;; Second Law The area swept out per unit time by the radius vector joining a planet and the sun is constant; Third Law The ratio of the square of the period of orbit to the cube of the semi-major axis is constant. The ...
... Kepler’s Laws of motion First Law Planets move in ellipses with the sun at a focus;; Second Law The area swept out per unit time by the radius vector joining a planet and the sun is constant; Third Law The ratio of the square of the period of orbit to the cube of the semi-major axis is constant. The ...
Problem 1. (5 points) A number of point charges with values Qi are
... A number of point charges with values Qi are fixed at positions ri. If we double the value of each and every charge, but keep the positions the same, the following quantities also double (list all that apply): (A) the total potential energy of system, (B) the force between particles one and two, (C) ...
... A number of point charges with values Qi are fixed at positions ri. If we double the value of each and every charge, but keep the positions the same, the following quantities also double (list all that apply): (A) the total potential energy of system, (B) the force between particles one and two, (C) ...
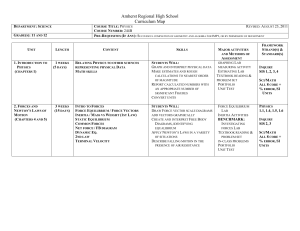
Curriculum Map for Physics - Amherst
... Amherst Regional High School Curriculum Map COURSE TITLE: PHYSICS REVISED: AUGUST 23, 2011 COURSE NUMBER: 244B PRE-REQUISITES (IF ANY): SUCCESSFUL COMPLETION OF GEOMETRY AND ALGEBRA I OR IMP I, OR BY PERMISSION OF DEPARTMENT ...
... Amherst Regional High School Curriculum Map COURSE TITLE: PHYSICS REVISED: AUGUST 23, 2011 COURSE NUMBER: 244B PRE-REQUISITES (IF ANY): SUCCESSFUL COMPLETION OF GEOMETRY AND ALGEBRA I OR IMP I, OR BY PERMISSION OF DEPARTMENT ...
Take-Home Packet to Accompany In
... ______________________ in a straight line, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: ___________ = ___________ times Acceleration. Newton’s Third Law of Motion: For every _______________, there is an ____________ and ________________________ reaction. ...
... ______________________ in a straight line, unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law of Motion: ___________ = ___________ times Acceleration. Newton’s Third Law of Motion: For every _______________, there is an ____________ and ________________________ reaction. ...
Lecture 8
... b) Now the safe is at constant speed of 1m/s. How does this change the problem? Well, in the y-direction it is immediately clear that ay = 0 because there’s no motion in that direction. So that is the same as the first problem. What about ax? Well if velocity isn’t changing, then Δv = 0 and ax = 0. ...
... b) Now the safe is at constant speed of 1m/s. How does this change the problem? Well, in the y-direction it is immediately clear that ay = 0 because there’s no motion in that direction. So that is the same as the first problem. What about ax? Well if velocity isn’t changing, then Δv = 0 and ax = 0. ...
Learning material
... We can make the dumbbells equal in mass and neglect mass of the joining section – or neglect the mass of the dumbbells and consider the mass to reside in the linear section It doesn’t matter which model we use to understand the problem and illustrate the principles involved. Certainly we would not w ...
... We can make the dumbbells equal in mass and neglect mass of the joining section – or neglect the mass of the dumbbells and consider the mass to reside in the linear section It doesn’t matter which model we use to understand the problem and illustrate the principles involved. Certainly we would not w ...