Socio-cultural Aspects of Neo-nationalism in Crisis Contexts
... analysis on Austrian nationalism (2008: 171) focuses on “a taken-for-granted ‘right to survive’ serving as a standard of legitimacy (applied to the performance by political elites) and outweighing economic considerations of profit maximization”. In the context of the Greek attributions of responsibi ...
... analysis on Austrian nationalism (2008: 171) focuses on “a taken-for-granted ‘right to survive’ serving as a standard of legitimacy (applied to the performance by political elites) and outweighing economic considerations of profit maximization”. In the context of the Greek attributions of responsibi ...
Socialism as Social Empowerment
... turned out, there are a range of “perverse” unintended consequences of central planning which subvert its intended goals. Another example of the viability problem is the proposal for a generous unconditional basic income. Suppose everyone were given, with no conditions or restrictions whatsoever, a ...
... turned out, there are a range of “perverse” unintended consequences of central planning which subvert its intended goals. Another example of the viability problem is the proposal for a generous unconditional basic income. Suppose everyone were given, with no conditions or restrictions whatsoever, a ...
INTRODUCTION - Berghahn Journals
... and their distribution, these resources being vital to the existence of larger populations. For many theorists, the state, throughout history and in its numerous manifestations, was born in such processes and continues to be so. Moreover, the oppressive powers of state systems (e.g., the denial or c ...
... and their distribution, these resources being vital to the existence of larger populations. For many theorists, the state, throughout history and in its numerous manifestations, was born in such processes and continues to be so. Moreover, the oppressive powers of state systems (e.g., the denial or c ...
Paper - Saint Mary`s College
... “research in which one examines patterns of symbolic meaning within written text, audio, visual, or other communication medium.” The sample was drawn from a list of songs within five genres on Billboard.com. These five genres include Rap and Hip-Hop, Country, Modern Rock, Pop, and Rhythm & Blues (R ...
... “research in which one examines patterns of symbolic meaning within written text, audio, visual, or other communication medium.” The sample was drawn from a list of songs within five genres on Billboard.com. These five genres include Rap and Hip-Hop, Country, Modern Rock, Pop, and Rhythm & Blues (R ...
The POWERMUTT Project
... What we have described as the social science method – the effort to explain empirical phenomena by developing and testing hypotheses – could as easily be called simply “the scientific method,” without the “social” qualifier. There are, however, important differences between social sciences, includin ...
... What we have described as the social science method – the effort to explain empirical phenomena by developing and testing hypotheses – could as easily be called simply “the scientific method,” without the “social” qualifier. There are, however, important differences between social sciences, includin ...
TOPIC 1 A: Definitions of Development Topic 2 Theories of
... desirable. According to Coleman, modernized political systems have a higher capacity to deal with the function of national identity, legitimacy, penetration, participation, and distribution than traditional political systems. Finally, modernization is a lengthy process. It is an evolutionary change, ...
... desirable. According to Coleman, modernized political systems have a higher capacity to deal with the function of national identity, legitimacy, penetration, participation, and distribution than traditional political systems. Finally, modernization is a lengthy process. It is an evolutionary change, ...
Constitutional Engineering and Ethnic Conflict
... basis. Elections are contested by inter-confessional electoral alliances, which must match the pre-ordained confessional structure of each multi-member electoral district. In practice, this requires electors to engage in a degree of cross-voting by choosing candidates who hail from outside as well a ...
... basis. Elections are contested by inter-confessional electoral alliances, which must match the pre-ordained confessional structure of each multi-member electoral district. In practice, this requires electors to engage in a degree of cross-voting by choosing candidates who hail from outside as well a ...
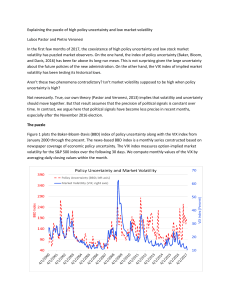
Explaining the puzzle of high policy uncertainty and low market
... We argue that the contradictory nature of the political signals in 2017 has reduced their informativeness. Political news is noisier than it used to be. Investors are becoming skeptical that politicians’ pronouncements have much to do with their future policy actions. Markets continue listening to p ...
... We argue that the contradictory nature of the political signals in 2017 has reduced their informativeness. Political news is noisier than it used to be. Investors are becoming skeptical that politicians’ pronouncements have much to do with their future policy actions. Markets continue listening to p ...
1 - Flinders University
... “Men* make their own history, but they do not make it just as they please; they do not make it under circumstances chosen by themselves, but under circumstances directly encountered, given, and transmitted from the past” (Marx cited in Feuer, 1969, p. 360). This paper provides a background against w ...
... “Men* make their own history, but they do not make it just as they please; they do not make it under circumstances chosen by themselves, but under circumstances directly encountered, given, and transmitted from the past” (Marx cited in Feuer, 1969, p. 360). This paper provides a background against w ...
social reconstruction and social movements in
... Because social movements have led to so many dramatic changes in societies around the globe, scholars have spent a great deal of time trying to understand where they come from and who participates in them. Some characteristics of social movements are that they are ―involved in conflictual relations ...
... Because social movements have led to so many dramatic changes in societies around the globe, scholars have spent a great deal of time trying to understand where they come from and who participates in them. Some characteristics of social movements are that they are ―involved in conflictual relations ...
The Normative Structures of Human Civilization. Readings in John
... What does it mean that facts endowed with deontic institutional power by declarations of validity contradict one another within the same society? What are the institutional solutions to these contradictory declarations? For example: take the declaration of repudiation, a classical example of a speec ...
... What does it mean that facts endowed with deontic institutional power by declarations of validity contradict one another within the same society? What are the institutional solutions to these contradictory declarations? For example: take the declaration of repudiation, a classical example of a speec ...
Why Federalism Matters: Implications for Tax Policy
... 3) Administrative Federalism. Under this regime, there is significant policy decentralization of taxation and spending functions to regional and large local governments, but there are no constitutionally created provinces and, by definition, no representation of provinces in the central legislature. ...
... 3) Administrative Federalism. Under this regime, there is significant policy decentralization of taxation and spending functions to regional and large local governments, but there are no constitutionally created provinces and, by definition, no representation of provinces in the central legislature. ...
State (polity)

A state is an organized political community living under a single system of government. Speakers of American English often use state and government as synonyms, with both words referring to an organized political group that exercises authority over a particular territory. States may or may not be sovereign. For instance, federated states that are members of a federal union have only partial sovereignty, but are, nonetheless, states. Some states are subject to external sovereignty or hegemony where ultimate sovereignty lies in another state. The term ""state"" can also refer to the secular branches of government within a state, often as a manner of contrasting them with churches and civilian institutions.Many human societies have been governed by states for millennia, but many have been stateless societies. The first states arose about 5,500 years ago in conjunction with the rapid growth of urban centers, the invention of writing, and the codification of new forms of religion. Over time a variety of different forms developed, employing a variety of justifications for their existence (such as divine right, the theory of the social contract, etc.). In the 21st century the modern nation-state is the predominant form of state to which people are subject.