PPT
... •In relaxed muscle, the Z-lines are far apart and the H and I bands are wide. •When the muscle contracts, the actin and myosin bands slide over each other and the Zlines get closer. •Also, the H and I bands become much shorter. •As the units shorten, the entire muscle shortens. This is how muscles c ...
... •In relaxed muscle, the Z-lines are far apart and the H and I bands are wide. •When the muscle contracts, the actin and myosin bands slide over each other and the Zlines get closer. •Also, the H and I bands become much shorter. •As the units shorten, the entire muscle shortens. This is how muscles c ...
File - St John`s, Marlborough- GCSE PE
... (Matching the training to the requirements of an activity) (To gradually increase the amount of overload so that fitness gains occur, without injury.) ...
... (Matching the training to the requirements of an activity) (To gradually increase the amount of overload so that fitness gains occur, without injury.) ...
labmuscle
... quickly convert chemical energy into glucose to mechanical energy. Normal blood pH is 7.4. during physical a workout the pH in the blood to falls because H+ are produced during the breakdown of glucose, thus increasing the number of H+ and causing the carbonate-carbonate acid equilibrium to shift to ...
... quickly convert chemical energy into glucose to mechanical energy. Normal blood pH is 7.4. during physical a workout the pH in the blood to falls because H+ are produced during the breakdown of glucose, thus increasing the number of H+ and causing the carbonate-carbonate acid equilibrium to shift to ...
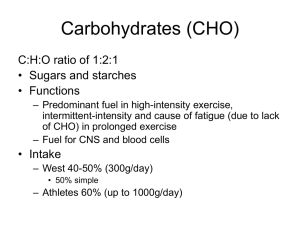
Carbohydrates (CHO)
... e.g. 50g of CHO from carrots = 750g of carrots • Glycaemic Load (GL) is more practical and takes into account GI and serving size. ...
... e.g. 50g of CHO from carrots = 750g of carrots • Glycaemic Load (GL) is more practical and takes into account GI and serving size. ...
CHRISTIAN_PECULIAR_1
... and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the c ...
... and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the c ...
Student Module_4
... – Blood Glucose - Constantly used by RBC and CNS – Liver Glycogen (1/3 is stored) - Used to maintain blood glucose – Muscle Glycogen (2/3rd is stored) • Amount of exercise and dietary carbohydrate intake determines the amount • Used to produce ATP in the muscle during exercise – Diet and exercise in ...
... – Blood Glucose - Constantly used by RBC and CNS – Liver Glycogen (1/3 is stored) - Used to maintain blood glucose – Muscle Glycogen (2/3rd is stored) • Amount of exercise and dietary carbohydrate intake determines the amount • Used to produce ATP in the muscle during exercise – Diet and exercise in ...
Document
... • Resulting elevations in G-6-P inhibited hexokinase, glucose phosphorylation and uptake • Experimental results equivocal to this point • This may work in a test tube, but it’s hard to show physio. ...
... • Resulting elevations in G-6-P inhibited hexokinase, glucose phosphorylation and uptake • Experimental results equivocal to this point • This may work in a test tube, but it’s hard to show physio. ...
Advances in Environmental Biology
... Indeed, it has been thought that HSPs provide the ability of cellular protection against a variety of stresses [1,2]. HSPs can be divided into several groups based upon their molecular masses. Of particular interest is the inducible form of the 70 kilo Dalton family of HSPs (HSP72) [3]. EC HSP 72 ha ...
... Indeed, it has been thought that HSPs provide the ability of cellular protection against a variety of stresses [1,2]. HSPs can be divided into several groups based upon their molecular masses. Of particular interest is the inducible form of the 70 kilo Dalton family of HSPs (HSP72) [3]. EC HSP 72 ha ...
Semester Exam ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY REVIEW
... 120. What is another name for the myosin heads that attach to actin molecules to move them? 121. Which type of muscle is equipped for non-rhythmical, rapid contractions? 122. Which muscle type is described as striated, with cylindrical cells, attached to the skeleton, and voluntary? 123. What name i ...
... 120. What is another name for the myosin heads that attach to actin molecules to move them? 121. Which type of muscle is equipped for non-rhythmical, rapid contractions? 122. Which muscle type is described as striated, with cylindrical cells, attached to the skeleton, and voluntary? 123. What name i ...
Lecture: Fasting and gene expression, Part 1
... Nine healthy male subjects ranging in age from 22 to 28 years, with an average height of 185 cm (range 175–192) and a mean weight of 81 kgm (range 65–110) participated in the study. The subjects were habitually physically active and maintained their normal activity pattern between the two trials. T ...
... Nine healthy male subjects ranging in age from 22 to 28 years, with an average height of 185 cm (range 175–192) and a mean weight of 81 kgm (range 65–110) participated in the study. The subjects were habitually physically active and maintained their normal activity pattern between the two trials. T ...
Consensus model for FSHD identifies opportunities
... • Activation of a germline program muscle cells – Confusion causes death and dysfunction • Immune response to germline proteins – FSHD cells express Cancer Testis Antigens • DUX4 genes can suppress muscle repair – Defensin protein blocks new muscle formation • DUX4 re-activates virus-like ele ...
... • Activation of a germline program muscle cells – Confusion causes death and dysfunction • Immune response to germline proteins – FSHD cells express Cancer Testis Antigens • DUX4 genes can suppress muscle repair – Defensin protein blocks new muscle formation • DUX4 re-activates virus-like ele ...
BUILDING BETTER BRAINS 101
... Acetyl L Carnitine: nutrient that stimulates brain cells to improve thought processes and connections across synapses. Maintains BDNF Sources are: red meat and dairy ...
... Acetyl L Carnitine: nutrient that stimulates brain cells to improve thought processes and connections across synapses. Maintains BDNF Sources are: red meat and dairy ...
Significant Invasion of the Pharyngeal Constrictor Muscle in Early
... Figure 1. Relationship between squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil and the pharyngeal constrictor muscle. A, No invasion (normal tissue remained between the tumor and the pharyngeal constrictor muscle). B, Attachment (no normal tissue remained between the tumor and the medial surface of the pharyn ...
... Figure 1. Relationship between squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil and the pharyngeal constrictor muscle. A, No invasion (normal tissue remained between the tumor and the pharyngeal constrictor muscle). B, Attachment (no normal tissue remained between the tumor and the medial surface of the pharyn ...
pptx
... physician's office with a 2 week history of pain and numbness in her left hand A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician with a recent history of decreased activity A 63-year-old woman is brought to the physician for evaluation of her “parkinsonism” ...
... physician's office with a 2 week history of pain and numbness in her left hand A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician with a recent history of decreased activity A 63-year-old woman is brought to the physician for evaluation of her “parkinsonism” ...
Nutrition and Athletic Performance
... Key Points Low energy intakes can result in: loss of muscle mass; menstrual dysfunction; loss of or failure to gain bone density; an increased risk of fatigue, injury, and illness; and a prolonged recovery process. ...
... Key Points Low energy intakes can result in: loss of muscle mass; menstrual dysfunction; loss of or failure to gain bone density; an increased risk of fatigue, injury, and illness; and a prolonged recovery process. ...
MUSCLE PROTEINS
... How does the system work? The sliding filament model of skeletal muscle contraction. The decrease in sarcomere length is due to decreases in the width of the I band and H zone, with no change in the width of the A band. These observations mean that the lengths of both the thick and thin filaments d ...
... How does the system work? The sliding filament model of skeletal muscle contraction. The decrease in sarcomere length is due to decreases in the width of the I band and H zone, with no change in the width of the A band. These observations mean that the lengths of both the thick and thin filaments d ...
Cellular Respiration Scenarios – Teacher Answers
... Arrive at solutions for the following by always taking an energy focus and looking at how your metabolic pathways would be affected. 1) A person has just experienced a stroke cutting off oxygen to certain parts of the brain. Describe the events that would occur leading to the death of brain cells. B ...
... Arrive at solutions for the following by always taking an energy focus and looking at how your metabolic pathways would be affected. 1) A person has just experienced a stroke cutting off oxygen to certain parts of the brain. Describe the events that would occur leading to the death of brain cells. B ...
action potential
... her eyelids "droop" and that she tires easily, even when completing ordinary daily tasks such as brushing her hair. She has fallen several times while climbing a flight of stairs. These symptoms improve with rest. The physician orders blood studies, which reveal elevated levels of antibodies to ACh ...
... her eyelids "droop" and that she tires easily, even when completing ordinary daily tasks such as brushing her hair. She has fallen several times while climbing a flight of stairs. These symptoms improve with rest. The physician orders blood studies, which reveal elevated levels of antibodies to ACh ...
smooth muscle - MBBS Students Club
... about -50 to -60 mv. • The AP of visceral smooth muscle is of 2 types: 1. Typical spike potentials: (similar to skeletal muscles) mostly seen in the unitary smooth muscles 2. AP with Plateaus: Starts like a typical spike potential but repolarization delayed for several hundred to as many as 1000 mse ...
... about -50 to -60 mv. • The AP of visceral smooth muscle is of 2 types: 1. Typical spike potentials: (similar to skeletal muscles) mostly seen in the unitary smooth muscles 2. AP with Plateaus: Starts like a typical spike potential but repolarization delayed for several hundred to as many as 1000 mse ...
SMOOTH MUSCLE
... about -50 to -60 mv. • The AP of visceral smooth muscle is of 2 types: 1. Typical spike potentials: (similar to skeletal muscles) mostly seen in the unitary smooth muscles 2. AP with Plateaus: Starts like a typical spike potential but repolarization delayed for several hundred to as many as 1000 mse ...
... about -50 to -60 mv. • The AP of visceral smooth muscle is of 2 types: 1. Typical spike potentials: (similar to skeletal muscles) mostly seen in the unitary smooth muscles 2. AP with Plateaus: Starts like a typical spike potential but repolarization delayed for several hundred to as many as 1000 mse ...
Muscle System PowerPoint
... D. List the Three Types of Muscles In addition to skeletal muscles, other types of ...
... D. List the Three Types of Muscles In addition to skeletal muscles, other types of ...
To your Chair Based Exercise Leadership Course Tutor Simon Hanna
... Reduction in muscle mass Reduction in number of muscle fibres Increased connective tissue Increased size of motor units Reduced elasticity of tendons ...
... Reduction in muscle mass Reduction in number of muscle fibres Increased connective tissue Increased size of motor units Reduced elasticity of tendons ...
Tissue Mechanics II – Soft Tissue Cartilage Muscle Ligaments
... Ligament collagen more randomly oriented, lower collagen ...
... Ligament collagen more randomly oriented, lower collagen ...