Microbiology - Imperial Valley College
... These cuts produce a DNA fragment with two stick ends. DNA from another source, perhaps a plasmid, cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
... These cuts produce a DNA fragment with two stick ends. DNA from another source, perhaps a plasmid, cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
Amplification of DNA Sequences
... can be detected simply by placing the PCR reaction mixture in agarose gel and performing electrophoresis. Because the length of the DNA target sequence is known, the presence of a distinct band in the agarose gel following ethidium bromide staining that is of the appropriate size is evidence that vi ...
... can be detected simply by placing the PCR reaction mixture in agarose gel and performing electrophoresis. Because the length of the DNA target sequence is known, the presence of a distinct band in the agarose gel following ethidium bromide staining that is of the appropriate size is evidence that vi ...
DNA: The Genetic Material
... Section 3: DNA, RNA, and Protein Section 4: Gene Regulation and Mutation ...
... Section 3: DNA, RNA, and Protein Section 4: Gene Regulation and Mutation ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... consist of megabase-scale domains of coordinated origin firing separated by large originless transition regions. Here, we report a quantitative genome-wide analysis of DNA replication kinetics in several human cell types that contradicts this view. DNA combing in HeLa cells sorted into four temporal ...
... consist of megabase-scale domains of coordinated origin firing separated by large originless transition regions. Here, we report a quantitative genome-wide analysis of DNA replication kinetics in several human cell types that contradicts this view. DNA combing in HeLa cells sorted into four temporal ...
Genetic population structure of the European anchovy
... Population structure. The marine species appear to have a lower degree of geographic differentiation than continental species. This phenomenon is typically explained by a high dispersal rate due to a planktonic egg and larval phase of many of these species, or adult history stages coupled with an a ...
... Population structure. The marine species appear to have a lower degree of geographic differentiation than continental species. This phenomenon is typically explained by a high dispersal rate due to a planktonic egg and larval phase of many of these species, or adult history stages coupled with an a ...
Transcription and translation ppt
... DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand It does this by covalently bonding ribonucleoside triphosphates that align opposite their exposed complementary partner (using the energ ...
... DNA that is transcribed into RNA is called a gene). RNA polymerase separates the DNA strands and synthesises a complementary RNA copy from the antisense DNA strand It does this by covalently bonding ribonucleoside triphosphates that align opposite their exposed complementary partner (using the energ ...
Gene Section MRE11A (MRE11 meiotic recombination 11 homolog A (S. cerevisiae))
... Mre11 participates in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks and replication errors as well as in meiotic homologous recombination. The R/M/N complex is part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC). The phosphorylation of Mre11 and NBS1 by another member of this super-complex, ATM ...
... Mre11 participates in the repair of DNA double-strand breaks and replication errors as well as in meiotic homologous recombination. The R/M/N complex is part of the BRCA1-associated genome surveillance complex (BASC). The phosphorylation of Mre11 and NBS1 by another member of this super-complex, ATM ...
Antioxidants and Vitamins in Clinical Conditions
... which are produced during normal metabolism in the body (Becker 1993). Other antioxidants are found in the diet. Although about 4000 antioxidants have been identified, the best known are vitamin E (Halliwel et al. 2005), vitamin C (Vatassery et al. 1989) and the carotenoids (Burton and Ingold 1984). ...
... which are produced during normal metabolism in the body (Becker 1993). Other antioxidants are found in the diet. Although about 4000 antioxidants have been identified, the best known are vitamin E (Halliwel et al. 2005), vitamin C (Vatassery et al. 1989) and the carotenoids (Burton and Ingold 1984). ...
DNA CLONING
... Since only about 10% of host cells accept and propagate a plasmid under available transformation conditions, drug selection is used to kill host cells that lack the plasmid after transformation; usually ampicillin and/or tetracylin resistance genes are used in plasmid vectors Should be small in si ...
... Since only about 10% of host cells accept and propagate a plasmid under available transformation conditions, drug selection is used to kill host cells that lack the plasmid after transformation; usually ampicillin and/or tetracylin resistance genes are used in plasmid vectors Should be small in si ...
DNA THIS ONE
... How many AA’ AA ’ s are there: How can DNA code for the production of our traits if there are only four different nucleotides: If given a strand of DNA you should be able to: - Identify the other strand of DNA - Determine the mRNA - Determine the amino acids the mRNA will code for Problem: If you ar ...
... How many AA’ AA ’ s are there: How can DNA code for the production of our traits if there are only four different nucleotides: If given a strand of DNA you should be able to: - Identify the other strand of DNA - Determine the mRNA - Determine the amino acids the mRNA will code for Problem: If you ar ...
PGC-1α: a key regulator of energy metabolism
... because rapidly growing evidence strongly suggests that it is a powerful regulator of energy metabolism under conditions of both health and disease (12). PGC-1␣ and Adaptive Thermogenesis PGC-1␣ was originally discovered as a cold-inducible transcription coactivator of adaptive thermogenesis, a phys ...
... because rapidly growing evidence strongly suggests that it is a powerful regulator of energy metabolism under conditions of both health and disease (12). PGC-1␣ and Adaptive Thermogenesis PGC-1␣ was originally discovered as a cold-inducible transcription coactivator of adaptive thermogenesis, a phys ...
Consalez, GG, Stayton, CL, Freimer, NB, Goonewardena, Brown, WT, Gilliam, TC and Warren, ST: Isolation and characterization of a highly polymorphic human locus (DXS 455) in proximal Xq28. Genomics 12:710-714 (1992).
... One region of the human genome where genetic mapping of disease loci has been particularly fruitful is the terminal band of the human X chromosome long arm. Band Xq28 is one of the more gene-dense regions of the human genome yet recognized, with over 27 loci identified (Davies et at., 1990). Many of ...
... One region of the human genome where genetic mapping of disease loci has been particularly fruitful is the terminal band of the human X chromosome long arm. Band Xq28 is one of the more gene-dense regions of the human genome yet recognized, with over 27 loci identified (Davies et at., 1990). Many of ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... – Which will carry fragments of DNA into a host cell – Vector DNA functions to insert and amplify the DNA of intersite. • Vectors should contain an origin of replication – Enables the vector, together with the foreign DNA fragment inserted into it, to replicate • they contain one or more single (uni ...
... – Which will carry fragments of DNA into a host cell – Vector DNA functions to insert and amplify the DNA of intersite. • Vectors should contain an origin of replication – Enables the vector, together with the foreign DNA fragment inserted into it, to replicate • they contain one or more single (uni ...
MICRO-MANIPULATION OF CHICKEN CHROM OSOMES AND
... Microscraping. With the help of an inverted microscope and hydraulic micro manipulator, chromosomes are scraped from the surface of coverslips. After scraping is completed the scraped chromosome is picked up with a micro needle and transported to a siliconized coverslip. For each experiment ten copi ...
... Microscraping. With the help of an inverted microscope and hydraulic micro manipulator, chromosomes are scraped from the surface of coverslips. After scraping is completed the scraped chromosome is picked up with a micro needle and transported to a siliconized coverslip. For each experiment ten copi ...
File
... 1. Newcombe spread E. coli cells on an agar base. After several generations of growth, he respread the cells and sprayed them with streptomycin, thus killing all cells except those that were resistant mutants. More mutants were observed after spreading than if they had not been respread. The experim ...
... 1. Newcombe spread E. coli cells on an agar base. After several generations of growth, he respread the cells and sprayed them with streptomycin, thus killing all cells except those that were resistant mutants. More mutants were observed after spreading than if they had not been respread. The experim ...
Characteristic Features of the Nucleotide Sequences of Yeast
... have recently become available. In addition, the data for indicated. All four genes were predicted to be likely genes chromosomes III and V were extracted from the Gen- when the sc_cul.5 (order 5) matrix was used (Fig. la). In Bank database and analyzed. In the annotation lines contrast, when the MR ...
... have recently become available. In addition, the data for indicated. All four genes were predicted to be likely genes chromosomes III and V were extracted from the Gen- when the sc_cul.5 (order 5) matrix was used (Fig. la). In Bank database and analyzed. In the annotation lines contrast, when the MR ...
DNA Technology Notes
... – Isolate donor cells (from who you will be cloning) – Remove nucleus from donor egg – Transfer nucleus from donor cells into donor egg – Stimulate cell division – Implant embryo into surrogate mother – New organism will be born ...
... – Isolate donor cells (from who you will be cloning) – Remove nucleus from donor egg – Transfer nucleus from donor cells into donor egg – Stimulate cell division – Implant embryo into surrogate mother – New organism will be born ...
7 Genetics - Life Sciences
... enetics is the study of inheritance, the transmission of traits from parent to offspring and the expression of these traits. From earliest times, people have realized that certain traits in both plants and animals are passed on from parents to offspring. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers ...
... enetics is the study of inheritance, the transmission of traits from parent to offspring and the expression of these traits. From earliest times, people have realized that certain traits in both plants and animals are passed on from parents to offspring. Artificial selection was practiced by farmers ...
No Origin, No Problem for Yeast DNA Replication
... To ensure proper transmission of genetic information, cells must accurately replicate their genome during each cell cycle. In budding yeast, DNA replication initiates from well-defined origins called autonomously replicating sequences (ARSs), while in multicellular organisms replication it is though ...
... To ensure proper transmission of genetic information, cells must accurately replicate their genome during each cell cycle. In budding yeast, DNA replication initiates from well-defined origins called autonomously replicating sequences (ARSs), while in multicellular organisms replication it is though ...
DNA Technology Notes (13.1 &13.2)
... – Isolate donor cells (from who you will be cloning) – Remove nucleus from donor egg – Transfer nucleus from donor cells into donor egg – Stimulate cell division – Implant embryo into surrogate mother – New organism will be born ...
... – Isolate donor cells (from who you will be cloning) – Remove nucleus from donor egg – Transfer nucleus from donor cells into donor egg – Stimulate cell division – Implant embryo into surrogate mother – New organism will be born ...
BI:4224
... Answer: The cells copy DNA to provide instructions for constructing proteins & regulating their synthesis (transcription). Replications involves chain separation & formation of complementary molecules of DNA on each free single chain, which attracts to itself the very sequences of nucleotides needed ...
... Answer: The cells copy DNA to provide instructions for constructing proteins & regulating their synthesis (transcription). Replications involves chain separation & formation of complementary molecules of DNA on each free single chain, which attracts to itself the very sequences of nucleotides needed ...
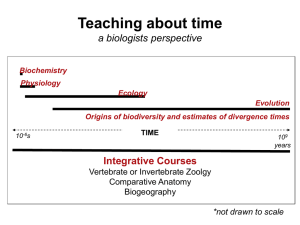
Teaching deep time through macroevolution and
... robust hypothesis (and why), and what are the reasons why the two genes resolved different hypotheses?” ….but that’s it. ...
... robust hypothesis (and why), and what are the reasons why the two genes resolved different hypotheses?” ….but that’s it. ...
Ch 07 Overview - Northwest ISD Moodle
... evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatically improved over the past 25 years due to impr ...
... evidence can be used to solve crimes. DNA contains within its noncoding regions many repeated sequences, including STRs, which vary in number among individuals; these differences are used to produce a DNA profile of a person. DNA profiling has dramatically improved over the past 25 years due to impr ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.