An Introduction to DNA and Genetics Directions: As you watch the
... ________________________. Mutation causes different versions (alleles) of the same ____________. Parent ______________ are shuffled – or recombined – when sex cells created in the body. Because of _______________________, sexual reproduction produces more ...
... ________________________. Mutation causes different versions (alleles) of the same ____________. Parent ______________ are shuffled – or recombined – when sex cells created in the body. Because of _______________________, sexual reproduction produces more ...
transformation mean? transcription and translation
... How is monosomy different than trisomy? How is the outcome of these conditions different when a sex chromosome is involved as opposed to an autosome? What is the primary information storage molecule in cells? How is it that DNA can store so much information, even though it only has 4 bases? What doe ...
... How is monosomy different than trisomy? How is the outcome of these conditions different when a sex chromosome is involved as opposed to an autosome? What is the primary information storage molecule in cells? How is it that DNA can store so much information, even though it only has 4 bases? What doe ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
... three fragments will be formed–a, b, and c. Which of the following gels produced by electrophoresis would represent the separation and identity of these fragments? ...
scientists and philosophers find that gene has a multitude of meanings
... closer we look, the less instructive they seem, less a “blueprint for life” than one of those disappointing two-page Basic Setup booklets that comes with your computer, tells you where to plug it in and then directs you to a Web site for more information. Scientists have learned that the canonical “ ...
... closer we look, the less instructive they seem, less a “blueprint for life” than one of those disappointing two-page Basic Setup booklets that comes with your computer, tells you where to plug it in and then directs you to a Web site for more information. Scientists have learned that the canonical “ ...
File - Biology with Radjewski
... o On vs. off o What types of cells have this? o Role of lactose (or allolactose) Lac operon vs. trp operon Genetic Engineering (5 m/c + plasmid mapping) Restriction Enyzmes Sticky ends Hydrogen bonds DNA charge Direction DNA migrates in gel electrophoresis Which sized DNA fragments mov ...
... o On vs. off o What types of cells have this? o Role of lactose (or allolactose) Lac operon vs. trp operon Genetic Engineering (5 m/c + plasmid mapping) Restriction Enyzmes Sticky ends Hydrogen bonds DNA charge Direction DNA migrates in gel electrophoresis Which sized DNA fragments mov ...
The Wild World of Biotechnology!! Applications Genetic
... We use chemicals (CaCl2) and heat shock to get recombinant plasmids into the cell. We include antibiotic resistance genes in the recombinant plasmid so that only the successfully transformed bacteria live. We make sure the gene of interest is near a known operon and we intentionally turn that operon ...
... We use chemicals (CaCl2) and heat shock to get recombinant plasmids into the cell. We include antibiotic resistance genes in the recombinant plasmid so that only the successfully transformed bacteria live. We make sure the gene of interest is near a known operon and we intentionally turn that operon ...
JF lect 5 12
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
... Arguments in favour of genes being made of DNA • All cells of a given species contain a constant amount of DNA but the types and amounts of proteins differ in different cells • The amount of DNA doubles in every cell just before it divides and an exactly equal amount is distributed to the two dau ...
IB Biology--Chromosome Review Activity
... 4. Look @ the visuals from the BioNinja site and describe what appears to be the basic difference between active and less active genes? What is preventing the less active genes from ...
... 4. Look @ the visuals from the BioNinja site and describe what appears to be the basic difference between active and less active genes? What is preventing the less active genes from ...
Syllabus Checklist
... Describe how DNA and histones are bound together in a chromosome. Illustrate this with a simple labeled diagram below. ...
... Describe how DNA and histones are bound together in a chromosome. Illustrate this with a simple labeled diagram below. ...
Genetic Engineering - ABC-MissAngelochsBiologyClass
... Cut a piece of DNA that codes for a specific gene using restriction enzymes (act like scissors). They cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence. Example: ...
... Cut a piece of DNA that codes for a specific gene using restriction enzymes (act like scissors). They cut DNA at a specific nucleotide sequence. Example: ...
Name: Block: ______ How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyz ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism? Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyz ...
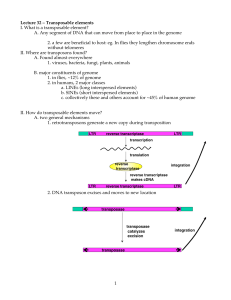
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
Assessment Builder - Printer Friendly Version Name: Date: 1 The
... This technique used to analyze DNA directly results in (1) synthesizing large fragments of DNA (2) separating DNA fragments on the basis of size (3) producing genetically engineered DNA molecules (4) removing the larger DNA fragments from the samples ...
... This technique used to analyze DNA directly results in (1) synthesizing large fragments of DNA (2) separating DNA fragments on the basis of size (3) producing genetically engineered DNA molecules (4) removing the larger DNA fragments from the samples ...
Diagnosing Mitochondrial Disorder
... Both parents are carriers of the genetic disorder, which appears on any of the 22 chromosome pairs other than the sex chromosomes. In other words, each parent has one affected chromosome and one unaffected in his/her individual pair. Because each parent contributes only one chromosome to the child, ...
... Both parents are carriers of the genetic disorder, which appears on any of the 22 chromosome pairs other than the sex chromosomes. In other words, each parent has one affected chromosome and one unaffected in his/her individual pair. Because each parent contributes only one chromosome to the child, ...
Plant Nuclear Genome Size Variation
... among organisms with similar levels of cellular and developmental complexity? Hypotheses: 1)Selfish DNA – most non-coding DNA consists for selfish elements capable of proliferating until the cost to host fitness becomes prohibitive. 2)Bulk DNA – genome size has a direct effect on nuclear volume, cel ...
... among organisms with similar levels of cellular and developmental complexity? Hypotheses: 1)Selfish DNA – most non-coding DNA consists for selfish elements capable of proliferating until the cost to host fitness becomes prohibitive. 2)Bulk DNA – genome size has a direct effect on nuclear volume, cel ...
Microbial Genetics - DrMinkovskyScienceWiki
... • Classify mutations by type, define mutagen. • Discuss two ways mutations can be repaired • Outline the methods of direct and indirect selection of mutants • Identify the purpose and outline the procedure for Ames test • Compare the mechanisms of genetic recombination in bacteria: transformation, c ...
... • Classify mutations by type, define mutagen. • Discuss two ways mutations can be repaired • Outline the methods of direct and indirect selection of mutants • Identify the purpose and outline the procedure for Ames test • Compare the mechanisms of genetic recombination in bacteria: transformation, c ...
SBI4U: Molecular Genetics Unit Review
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
... 3. What is the difference between the 5’ end of nucleic acids and the 3’ end? Draw a diagram to show this. 4. When new DNA or RNA is synthesized, in which direction does it grow? 5. What are two different kinds of bonds that hold nucleic acids together? 6. Write the complementary DNA strand: 5’- A A ...
They are the offspring of these two people They are the
... Ulna and radius are always side by side. ...
... Ulna and radius are always side by side. ...
An Aside: X Inactivation in Female Mammals
... If an entire organism has more than two complete chromosome sets it is POLYPLOID (triploid=3n, tetraploid=4n, etc.) Red viscacha rat from Argentina = 4n ...
... If an entire organism has more than two complete chromosome sets it is POLYPLOID (triploid=3n, tetraploid=4n, etc.) Red viscacha rat from Argentina = 4n ...
Genetic Engineering
... organism to another: Restriction enzymes were used naturally to cut out viral DNA from their own DNA and destroy it 1. Cut the DNA containing the gene of interest (GOI) away from the genes surrounding it ...
... organism to another: Restriction enzymes were used naturally to cut out viral DNA from their own DNA and destroy it 1. Cut the DNA containing the gene of interest (GOI) away from the genes surrounding it ...
Genomics - University of Missouri
... The study of the entire DNA complement of an individual. The term genome refers to all of the DNA contained in one copy of the chromosomes of an organism. It contains both coding (genes) and non-coding DNA sequences. ...
... The study of the entire DNA complement of an individual. The term genome refers to all of the DNA contained in one copy of the chromosomes of an organism. It contains both coding (genes) and non-coding DNA sequences. ...
LECTURE 4 Atypical Patterns of Inheritance
... Somatic New mutation 4-Unusual inheritance patterns due to Genomic Imprinting ...
... Somatic New mutation 4-Unusual inheritance patterns due to Genomic Imprinting ...
Meiosis Part 1 Outline
... variation!) This caused the Irish Potato Famine. Potatoes are originally from South America. One species of potato plant was taken to Ireland. This became the only species that the farmers could plant, as no new species were brought over afterwards. A pathogenic fungus, called Potato Blight, began a ...
... variation!) This caused the Irish Potato Famine. Potatoes are originally from South America. One species of potato plant was taken to Ireland. This became the only species that the farmers could plant, as no new species were brought over afterwards. A pathogenic fungus, called Potato Blight, began a ...
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial DNA is only a small portion of the DNA in a eukaryotic cell; most of the DNA can be found in the cell nucleus and, in plants, in the chloroplast.In humans, mitochondrial DNA can be assessed as the smallest chromosome coding for 37 genes and containing approximately 16,600 base pairs. Human mitochondrial DNA was the first significant part of the human genome to be sequenced. In most species, including humans, mtDNA is inherited solely from the mother.The DNA sequence of mtDNA has been determined from a large number of organisms and individuals (including some organisms that are extinct), and the comparison of those DNA sequences represents a mainstay of phylogenetics, in that it allows biologists to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among species. It also permits an examination of the relatedness of populations, and so has become important in anthropology and field biology.