MAIN IDEAS
... 2. What is the genetic makeup of the parents? AA and aa 3. Why will Aa plants have a straight hairline rather than a peaked one? Straight hairline is dominant. ...
... 2. What is the genetic makeup of the parents? AA and aa 3. Why will Aa plants have a straight hairline rather than a peaked one? Straight hairline is dominant. ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Living Things
... 3. B. They come from other living things. 4. C. The cell is both the basic unit of structure and the unit of function in living things. 5. D. Respiration 6. C. Digest TransportRespiration 7. The diagram shows the life cycle of the flies. It shows it growing and developing into an adult. 8. The chl ...
... 3. B. They come from other living things. 4. C. The cell is both the basic unit of structure and the unit of function in living things. 5. D. Respiration 6. C. Digest TransportRespiration 7. The diagram shows the life cycle of the flies. It shows it growing and developing into an adult. 8. The chl ...
Online Onion Root Tips
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/activities/cell_cycle/cell_cycle.html ...
The Cell: A Review
... including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its ...
... including bacteria have no nucleus (their single chromosome floats freely in the cytoplasm), nearly all other cells do. The nucleus contains the cell's DNA. This genetic material provides the instructions for building proteins and, thus, dictates the structure and function of the cell throughout its ...
Chapter 1: Cells
... 7. Cell Wall- a rigid outer layer that surrounds the cell membrane. 8. Cytoplasm- the thick fluid between the nucleus and the cell membrane that contains all the remaining organelles. 9. Ribosome- a type of organelle that is not surrounded by a membrane and assembles compounds called proteins. 10. L ...
... 7. Cell Wall- a rigid outer layer that surrounds the cell membrane. 8. Cytoplasm- the thick fluid between the nucleus and the cell membrane that contains all the remaining organelles. 9. Ribosome- a type of organelle that is not surrounded by a membrane and assembles compounds called proteins. 10. L ...
Job Vacancy: Postdoctoral Research Scientist in Cell Biology
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
... of Crete, Heraklion, Greece is seeking a highly motivated postdoctoral research scientist to investigate regulation of faithful chromosome segregation and cytokinesis in vertebrate somatic cells (J Cell Biol 195: 449-466, 2011; J Cell Sci 126: 12351246, 2013; J Cell Biol 205: 339-356, 2014; J Cell S ...
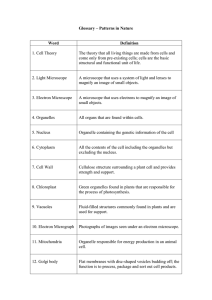
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... A microscope that uses a system of light and lenses to magnify an image of small objects. ...
... A microscope that uses a system of light and lenses to magnify an image of small objects. ...
Cells and Cell Organelles assignment
... for your answers. Do not give your answers on this page but on a separate page (or on more than one page). This assignment is due at the beginning of your lab during the week of October 19th. This assignment counts the same as a ten-point lab test, and one point will be deducted from the grade on th ...
... for your answers. Do not give your answers on this page but on a separate page (or on more than one page). This assignment is due at the beginning of your lab during the week of October 19th. This assignment counts the same as a ten-point lab test, and one point will be deducted from the grade on th ...
Document
... Protein synthesis- amino acids are joined together to make proteins like antibodies, enzymes and muscle on ribosome (B) Storage- Vacuoles store water, food and dissolved minerals Control- The nucleus contains the DNA blueprint that codes for the proteins of the cell (B) Transport- the Endoplasmic R ...
... Protein synthesis- amino acids are joined together to make proteins like antibodies, enzymes and muscle on ribosome (B) Storage- Vacuoles store water, food and dissolved minerals Control- The nucleus contains the DNA blueprint that codes for the proteins of the cell (B) Transport- the Endoplasmic R ...
kakamega south cemtral districts mock examination
... daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the diploid state of species; -May lead to variation due to crossing over; (Max = lmk) Uric acid; ...
... daughter cells; while mitosis is a type of cell division where a single parent cell divides to form two diploid daughter cells; b) Lead to formation of haploid gamete cells who through fussion maintains the diploid state of species; -May lead to variation due to crossing over; (Max = lmk) Uric acid; ...
Cell Theory - Teacher Pages
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
... biology • Credit for the formulation of this theory is given to: – Theodor Schwann – Matthias Schleiden – Rudolph Virchow ...
Chapter 4 – Structure + Function of the Cell
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...
... Anton van Leeuwenhoek – identified the first living cell using a microscope ...
Bell Ringer: (pp.1-15) copy the outline. Leave space to add
... The cell is the basic unit of living things. Characteristics of life Needs of living things All living things are made of cells. The microscope led to the discovery of cells. C. Cells come from other cells D. The cell theory is important to the study of biology. ...
... The cell is the basic unit of living things. Characteristics of life Needs of living things All living things are made of cells. The microscope led to the discovery of cells. C. Cells come from other cells D. The cell theory is important to the study of biology. ...
File
... 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each cell to do its job. Mitochondria produce energy by processing oxygen and food. The cell membrane holds p ...
... 4) List five parts of all cells and their jobs (Mr. Gross’s Note: more than 5 are listed below). The cell’s nucleus contains chromosomes made of DNA, which contain instructions necessary for each cell to do its job. Mitochondria produce energy by processing oxygen and food. The cell membrane holds p ...
Cell Theory
... The three main parts of the Cell theory are: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by th ...
... The three main parts of the Cell theory are: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of the organization of living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. The cell theory was originally developed by Theodor Schwann, and fully accepted by th ...
Chapter review p 83-84 Model answers Cell Function Organelles
... 5. Tissue 6. Cell wall 7. C 8. D 9. A 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. Cells must be small in order to have a large enough surface area-to-volume ratio to get sufficient nutrients to survive and to get rid of wastes. 14. Cells are the smallest unit of all living things. Cells combine to make tissues. Different ...
... 5. Tissue 6. Cell wall 7. C 8. D 9. A 10. B 11. B 12. C 13. Cells must be small in order to have a large enough surface area-to-volume ratio to get sufficient nutrients to survive and to get rid of wastes. 14. Cells are the smallest unit of all living things. Cells combine to make tissues. Different ...
General Biology Bozeman Cell Membrane video 1. Describe what
... 9. Identify what characteristics a substance must have in order to move through the membrane, give 2 examples of these substances. ...
... 9. Identify what characteristics a substance must have in order to move through the membrane, give 2 examples of these substances. ...
Science Chapter 1 Test Notes
... 5. The bones that give the body structure make up the skeletal system. 6. The muscles and tendons that move bones make up the muscular system. 7. The system that directs activities of all other body systems is called the nervous system. 8. A group of cells that work together to perform a certain fun ...
... 5. The bones that give the body structure make up the skeletal system. 6. The muscles and tendons that move bones make up the muscular system. 7. The system that directs activities of all other body systems is called the nervous system. 8. A group of cells that work together to perform a certain fun ...
Studying Life
... population (of the same species… can reproduce) – Groups of populations make up a community (interacting or affecting each other) – The community and its non-living surrounding make up the ecosystem – All living things on the Earth form the biosphere ...
... population (of the same species… can reproduce) – Groups of populations make up a community (interacting or affecting each other) – The community and its non-living surrounding make up the ecosystem – All living things on the Earth form the biosphere ...
Cett5 frLluZ * c4tv1
... Name the light related chemical reaction that occurs in the chloroplasts. ...
... Name the light related chemical reaction that occurs in the chloroplasts. ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
Cell Processes
... from one generation to another. PROKARYOTIC cells such as bacteria have no nucleus but still possess DNA to direct cellular functions. EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus which housed the DNA. EUKARYOTIC cells also have ORGANELLES (individual structures that carry out specific functions within the cell) ...
... from one generation to another. PROKARYOTIC cells such as bacteria have no nucleus but still possess DNA to direct cellular functions. EUKARYOTIC cells have a nucleus which housed the DNA. EUKARYOTIC cells also have ORGANELLES (individual structures that carry out specific functions within the cell) ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.