Chapter 1 - Cell Biology Review Extended Response Answers
... b. interphase includes G1, S and G2; c. in G1 and G2 /G phases, cell performs normal functions/protein synthesis/cell grows/organelles are replicated; d. S/synthesis phase when the DNA replicates; e. mitosis is when nucleus/genetic material divides; f. named/described stages of mitosis; g. cytokines ...
... b. interphase includes G1, S and G2; c. in G1 and G2 /G phases, cell performs normal functions/protein synthesis/cell grows/organelles are replicated; d. S/synthesis phase when the DNA replicates; e. mitosis is when nucleus/genetic material divides; f. named/described stages of mitosis; g. cytokines ...
Cells - Life Learning Cloud
... − a nucleus which controls the activities of the cell − cytoplasm in which most of the chemical reactions take place − a cell membrane which controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell − mitochondria, which is where most energy is released inrespiration − ribosomes, which is where prot ...
... − a nucleus which controls the activities of the cell − cytoplasm in which most of the chemical reactions take place − a cell membrane which controls the passage of substances in and out of the cell − mitochondria, which is where most energy is released inrespiration − ribosomes, which is where prot ...
Cellular Reproduction notes
... Chromosomes become visible Centrioles (2 tiny structures located in the cytoplasm) separate and take opposite sides of nucleus (at the poles) Condensed chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers that have started to form Each chromosome has two chromatids joined at the ...
... Chromosomes become visible Centrioles (2 tiny structures located in the cytoplasm) separate and take opposite sides of nucleus (at the poles) Condensed chromosomes attach to the spindle fibers that have started to form Each chromosome has two chromatids joined at the ...
Properties and Classification of Microorganisms
... move into a bacterial cell, they must be broken down into simpler substances. Enzymes do this by increasing the rate of biochemical reactions. Produced within the bacterial cell, enzymes move through the cell wall to break down the food on the outside into a form bacteria can use. ...
... move into a bacterial cell, they must be broken down into simpler substances. Enzymes do this by increasing the rate of biochemical reactions. Produced within the bacterial cell, enzymes move through the cell wall to break down the food on the outside into a form bacteria can use. ...
Introduction to Cytology Terminology
... PKU; an inherited disease causing brain injury and death when phenylketones build-up in the body An example of endocytosis resulting in ingestion of liquid particles into the cell; cell drinking Unicellular organisms such as protozoa that thrive on decaying matter Molecule contained in ribosomes and ...
... PKU; an inherited disease causing brain injury and death when phenylketones build-up in the body An example of endocytosis resulting in ingestion of liquid particles into the cell; cell drinking Unicellular organisms such as protozoa that thrive on decaying matter Molecule contained in ribosomes and ...
12-16-2016 life functions answer key
... single-celled organism has the same function as which organ system in humans? A) nervous C) digestive ...
... single-celled organism has the same function as which organ system in humans? A) nervous C) digestive ...
Card review
... however, the process of contact inhibition prevents mitosis when cells are in direct contact with one another. Contact inhibition occurs when proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) interact, causing them to change shape so that the growth-factor signaling proteins that normally associate wit ...
... however, the process of contact inhibition prevents mitosis when cells are in direct contact with one another. Contact inhibition occurs when proteins called cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) interact, causing them to change shape so that the growth-factor signaling proteins that normally associate wit ...
Cell Division
... called binary fission The single, circular chromosome (which is attached to the plasma membrane) replicates The cell grows & elongates, separating the two chromosomes The plasma membrane and cell wall pinch inward, eventually forming two daughter cells ...
... called binary fission The single, circular chromosome (which is attached to the plasma membrane) replicates The cell grows & elongates, separating the two chromosomes The plasma membrane and cell wall pinch inward, eventually forming two daughter cells ...
cells, cellular respiration, and heredity.
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
Nervous and endocrine systems
... a wide range of environmental conditions. • There are several key interfaces in humans between the external and internal environments including alveoli (air), villi (food) and nephrons (urine). The cellular structure of these interfaces presents a large surface area for maximum exchange. ...
... a wide range of environmental conditions. • There are several key interfaces in humans between the external and internal environments including alveoli (air), villi (food) and nephrons (urine). The cellular structure of these interfaces presents a large surface area for maximum exchange. ...
PowerPoint
... infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cells lining the nasal cavity, and why? A. Cells will lose water because this is a ...
... infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cells lining the nasal cavity, and why? A. Cells will lose water because this is a ...
PowerPoint
... infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cells lining the nasal cavity, and why? A. Cells will lose water because this is a ...
... infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cells lining the nasal cavity, and why? A. Cells will lose water because this is a ...
FOURTH GRADE ORGANISMS
... power plant that maintains all necessary functions in order to stay alive. All cells have certain components that enable them to carry out vital life processes. There are several different types of specialized cells, but emphasize to students the basic structure of the cell. A cell has several compo ...
... power plant that maintains all necessary functions in order to stay alive. All cells have certain components that enable them to carry out vital life processes. There are several different types of specialized cells, but emphasize to students the basic structure of the cell. A cell has several compo ...
Biology 2 - All Hallows Catholic High School
... Living things remove materials from the environment for growth and other processes. These materials are returned to the environment either in waste materials or when living things die and decay. Materials decay because they are broken down (digested) by micro-organisms. Microorganisms digest materia ...
... Living things remove materials from the environment for growth and other processes. These materials are returned to the environment either in waste materials or when living things die and decay. Materials decay because they are broken down (digested) by micro-organisms. Microorganisms digest materia ...
7-2 Science Support Document
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
... Previous/Future knowledge: In 5th grade (5-2.1), students recalled that the smallest unit of life was the cell and identified its major structures (including cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and vacuole). In 6th grade (6-2.1), students summarized the characteristics that all organisms share (inclu ...
ANSWERS Performance Final Study
... e. Decomposers: Break down and absorb dead and decaying organisms. Ex: mushrooms and bacteria f. Niche: Job or role. g. Food web: Realistic food chain h. Pioneer species: mosses, lichens i. Climax community: stable, mature community in which there is little change in the number of species. j. Carryi ...
... e. Decomposers: Break down and absorb dead and decaying organisms. Ex: mushrooms and bacteria f. Niche: Job or role. g. Food web: Realistic food chain h. Pioneer species: mosses, lichens i. Climax community: stable, mature community in which there is little change in the number of species. j. Carryi ...
Cell Membrane Proteins
... away from the surface of the cell, forming a pinocytotic vesicle inside the cytoplasm of the cell. This process requires energy from within the cell; this is supplied by ATP. Also, it requires the presence of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid, which probably react with contractile protein fila ...
... away from the surface of the cell, forming a pinocytotic vesicle inside the cytoplasm of the cell. This process requires energy from within the cell; this is supplied by ATP. Also, it requires the presence of calcium ions in the extracellular fluid, which probably react with contractile protein fila ...
10AB grade 2nd quarter
... C) It is a passive process. D) It occurs when molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. E) It requires integral proteins of the cell membrane. 4. Explain the following terms: ...
... C) It is a passive process. D) It occurs when molecules move from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. E) It requires integral proteins of the cell membrane. 4. Explain the following terms: ...
Chapter 3 The Basic Structure of a Cell - Otterville R
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
... • Unicellular organisms are made of one cell only • The cells of multicellular organisms are specialized to perform different functions ...
Ch. 27 - ltcconline.net
... 1. About .5 of all prokaryotes are capable of directional movement a. some can move up to 50x own body length per second b. flagella - may be scattered, at one end, or 2 ends 1. rotary 2. .1 as wide as euk. flagella 3. not covered by plasma membrane 4. may move randomly, or exhibit taxis if heteroge ...
... 1. About .5 of all prokaryotes are capable of directional movement a. some can move up to 50x own body length per second b. flagella - may be scattered, at one end, or 2 ends 1. rotary 2. .1 as wide as euk. flagella 3. not covered by plasma membrane 4. may move randomly, or exhibit taxis if heteroge ...
m5zn_2ab2252f39932cd
... 77) Which of the following statements regarding prokaryotes is false? A) Prokaryotic chromosomes are more complex than those of eukaryotes. 78) Eukaryotic chromosomes differ from prokaryotic chromosomes in that they E) are housed in a membrane-enclosed nucleus. 79) Which of the following helps maint ...
... 77) Which of the following statements regarding prokaryotes is false? A) Prokaryotic chromosomes are more complex than those of eukaryotes. 78) Eukaryotic chromosomes differ from prokaryotic chromosomes in that they E) are housed in a membrane-enclosed nucleus. 79) Which of the following helps maint ...
CDT Test - Dallastown Area School District Moodle
... Rice cultivation, cattle ranching, the filling of landfills, and coal mining are some of the activities that lead to increased levels of methane gas in the atmosphere. Which statement describes how increased levels of methane gas will most likely affect the global environment? A. It can cause ozone ...
... Rice cultivation, cattle ranching, the filling of landfills, and coal mining are some of the activities that lead to increased levels of methane gas in the atmosphere. Which statement describes how increased levels of methane gas will most likely affect the global environment? A. It can cause ozone ...
33835_CellsBldgBlcks TG
... osmosis: Term given for the diffusion of water through a membrane. photosynthesis: Process by which organisms use energy from sunlight to make their own food. protein: Substance used to build and repair cells, made up of amino acids. respiration: Process in which simple food substances such as gluco ...
... osmosis: Term given for the diffusion of water through a membrane. photosynthesis: Process by which organisms use energy from sunlight to make their own food. protein: Substance used to build and repair cells, made up of amino acids. respiration: Process in which simple food substances such as gluco ...
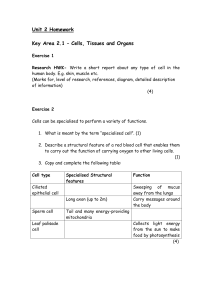
Unit 2 Homework
... (Marks available for, quality of research, references, detailed description of information and ethical issues considered) ...
... (Marks available for, quality of research, references, detailed description of information and ethical issues considered) ...
meiosis - astone
... Can be taken from an adult and then reintroduced without risk of rejection Several types: Hematopoietic – forms blood cells Stromal cells – forms bone cartilage, fat Some types of brain stem cells ...
... Can be taken from an adult and then reintroduced without risk of rejection Several types: Hematopoietic – forms blood cells Stromal cells – forms bone cartilage, fat Some types of brain stem cells ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.