Cerebrum Renatus Conference (3)
... Rene Descartes associated the origin of the ‘animal spirits’ to the pineal gland. The pineal gland, to Descartes, was associated with movement and sensation. He believed that within the nerves of the body are tiny ‘valvules’ that operated to control the flow of the spirits into and out of the nerves ...
... Rene Descartes associated the origin of the ‘animal spirits’ to the pineal gland. The pineal gland, to Descartes, was associated with movement and sensation. He believed that within the nerves of the body are tiny ‘valvules’ that operated to control the flow of the spirits into and out of the nerves ...
copyright 2004 scientific american, inc.
... more nuanced understanding, relating to two of the features that music and language share: both are a means of communication, and each has a syntax, a set of rules that govern the proper combination of elements (notes and words, respectively). According to Aniruddh D. Patel of the Neurosciences Inst ...
... more nuanced understanding, relating to two of the features that music and language share: both are a means of communication, and each has a syntax, a set of rules that govern the proper combination of elements (notes and words, respectively). According to Aniruddh D. Patel of the Neurosciences Inst ...
Brain Anatomy
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
... Must be wary of using pictures of brain “hot spots” that locate complex functions in precise brain areas Parietal Lobes: enable mathematical & spatial reasoning Temporal Lobes: facial recognition ...
Using POCS Method of Problem
... Brain and Spine Protectors Meninges, Ventricles, and Cerebrospinal Fluid (Pinel p. 53): The brain and spinal cord (the CNS) are the most protected organs in the body. They are encased in bone and covered by three protective membranes, the meninges. Also protecting the CNS is cerebrospinal fluid, wh ...
... Brain and Spine Protectors Meninges, Ventricles, and Cerebrospinal Fluid (Pinel p. 53): The brain and spinal cord (the CNS) are the most protected organs in the body. They are encased in bone and covered by three protective membranes, the meninges. Also protecting the CNS is cerebrospinal fluid, wh ...
Page 1 of 4 Further reading - New Scientist 20/07/2009 http://www
... However, the Bayesian brain is not quite a general law. It is a collection of related approaches that each use Bayesian probability theory to understand one aspect of brain function, such as parsing speech, recognising objects or learning words. No one has been able to pull all these disparate appro ...
... However, the Bayesian brain is not quite a general law. It is a collection of related approaches that each use Bayesian probability theory to understand one aspect of brain function, such as parsing speech, recognising objects or learning words. No one has been able to pull all these disparate appro ...
Inhibitory postsynaptic potential
... 3-D reconstruction of part of three neurons, generated from a stack of images of the mouse cortex. R. Schalek, B. Kasthuri, K. Hayworth, J. Tapia, J. Lichtman/Harvard and D. Berger, S. Seung/MIT ...
... 3-D reconstruction of part of three neurons, generated from a stack of images of the mouse cortex. R. Schalek, B. Kasthuri, K. Hayworth, J. Tapia, J. Lichtman/Harvard and D. Berger, S. Seung/MIT ...
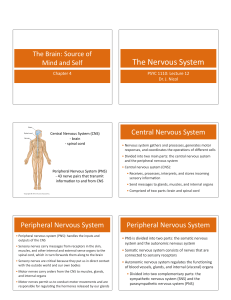
The Nervous System
... • Positron emission tomography (PET) -‐ radioacJve glucose-‐like substance injected into blood and accumulates in areas of the brain that are acJve; the radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on ...
... • Positron emission tomography (PET) -‐ radioacJve glucose-‐like substance injected into blood and accumulates in areas of the brain that are acJve; the radiaJon is read by a scanner and superimposed on ...
Nervous System 2
... • The brain stem connects the brain and the spinal cord. • The brain stem consists of two regions, the pons and the medulla oblongata. • Each of these regions acts as a neural “switchboard” regulating the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. • Blood pressure, heart rate, b ...
... • The brain stem connects the brain and the spinal cord. • The brain stem consists of two regions, the pons and the medulla oblongata. • Each of these regions acts as a neural “switchboard” regulating the flow of information between the brain and the rest of the body. • Blood pressure, heart rate, b ...
Chapter 2
... Genes are not blueprints; they are molecules. These molecules have the ability to direct the assembly of proteins that build the body. This genetic protein assembly can be turned on and off by the environment, or by other genes. Any trait we see is a result of the complex interactions of man ...
... Genes are not blueprints; they are molecules. These molecules have the ability to direct the assembly of proteins that build the body. This genetic protein assembly can be turned on and off by the environment, or by other genes. Any trait we see is a result of the complex interactions of man ...
Unit 2 The Brain
... • Of the following, which are located exclusively in the central nervous system? – A. Motor Neurons – B. Interneurons – C. Sensory Neurons – D. Glial Cells – E. Thyroid ...
... • Of the following, which are located exclusively in the central nervous system? – A. Motor Neurons – B. Interneurons – C. Sensory Neurons – D. Glial Cells – E. Thyroid ...
1. The axons of certain neurons are covered by a layer of fatty tissue
... d. Most complex activities emerge from the integrated activity of both hemispheres. ...
... d. Most complex activities emerge from the integrated activity of both hemispheres. ...
Unit Three Nervous System
... • Drugs affect the nervous system in many different ways. • Some drugs create a feeling of euphoria (well-being). • Other drugs cause a decrease in inhibitions, or an inability to stop doing something that a person would not normally do. • Using some drugs results in tolerance when they are taken co ...
... • Drugs affect the nervous system in many different ways. • Some drugs create a feeling of euphoria (well-being). • Other drugs cause a decrease in inhibitions, or an inability to stop doing something that a person would not normally do. • Using some drugs results in tolerance when they are taken co ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM
... synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
... synaptic cleft • At the postsynaptic mb. The neurotransmitter merges with receptor sites • AP starts at the postsynaptic mb • Neurotransmitters may be broken down by enzymes, washed away, or recycles ...
Nervous System Bookwork—KEY
... to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way c ...
... to enter the neuron through sodium gates. This causes local depolarization and generates the action potential, which is then self-propagating. This event is quickly followed by a second permeability change that restricts Na + entry but allows K+ to leave the neuron, causing repolarization. One way c ...
Module 1: The Brain and the Central Nervous System (CNS
... brain, the spinal cord and nerves. The brain controls everything our body does. It can be compared to a computer, as it makes sense of all the messages it receives from the spinal cord and the neurons. Our brain controls what we think, what we say, our emotions, memories, sensations, and body moveme ...
... brain, the spinal cord and nerves. The brain controls everything our body does. It can be compared to a computer, as it makes sense of all the messages it receives from the spinal cord and the neurons. Our brain controls what we think, what we say, our emotions, memories, sensations, and body moveme ...
Chapter 2: Brain and Behavior
... Deficiency in some types will cause powerful salt cravings Help body to adjust to stress Secondary source of sex hormones ...
... Deficiency in some types will cause powerful salt cravings Help body to adjust to stress Secondary source of sex hormones ...
Unit 3 Notes
... Somatic Nervous System: the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles. (Also called the skeletal nervous system.) Autonomic Nervous System: the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the ...
... Somatic Nervous System: the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body’s skeletal muscles. (Also called the skeletal nervous system.) Autonomic Nervous System: the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations
... – Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are stored within the axon terminals ...
... – Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are stored within the axon terminals ...
Chapter 24 Late Adulthood Cognitive Development
... • The most common cause of dementia, characterized by gradual deterioration of memory and personality and marked by the formation of plaques of beta-amyloid protein and tangles of tau protein in the brain. • Also called senile dementia of the Alzheimer ...
... • The most common cause of dementia, characterized by gradual deterioration of memory and personality and marked by the formation of plaques of beta-amyloid protein and tangles of tau protein in the brain. • Also called senile dementia of the Alzheimer ...
Neurolinguistics

Neurolinguistics is the study of the neural mechanisms in the human brain that control the comprehension, production, and acquisition of language. As an interdisciplinary field, neurolinguistics draws methodology and theory from fields such as neuroscience, linguistics, cognitive science, neurobiology, communication disorders, neuropsychology, and computer science. Researchers are drawn to the field from a variety of backgrounds, bringing along a variety of experimental techniques as well as widely varying theoretical perspectives. Much work in neurolinguistics is informed by models in psycholinguistics and theoretical linguistics, and is focused on investigating how the brain can implement the processes that theoretical and psycholinguistics propose are necessary in producing and comprehending language. Neurolinguists study the physiological mechanisms by which the brain processes information related to language, and evaluate linguistic and psycholinguistic theories, using aphasiology, brain imaging, electrophysiology, and computer modeling.