ANPS 019 Beneyto 11-06
... The purpose of this region is to keep the eyes directed forward. The right frontal eye field forces both eyes to the left while the left frontal eye field forces both eyes to the right. In a unilateral lesion, both eyes will deviate TOWARDS the side of the lesion. ...
... The purpose of this region is to keep the eyes directed forward. The right frontal eye field forces both eyes to the left while the left frontal eye field forces both eyes to the right. In a unilateral lesion, both eyes will deviate TOWARDS the side of the lesion. ...
Graduate School Systems Neuroscience, MEDS 5371 2011 BASAL
... accumbens, olfactory tubercle, and nucleus basalis Meynert in the substantia innominata. The ventral striatum is strongly innervated by dopaminergic fibers from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) located in the mesencephalon next to SN. These DA projections are known as the mesolimbic dopamine system. ...
... accumbens, olfactory tubercle, and nucleus basalis Meynert in the substantia innominata. The ventral striatum is strongly innervated by dopaminergic fibers from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) located in the mesencephalon next to SN. These DA projections are known as the mesolimbic dopamine system. ...
File
... Multimodal Association Areas • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
... Multimodal Association Areas • Receive inputs from multiple sensory areas • Send outputs to multiple areas, including the premotor cortex • Allow us to give meaning to information received, store it as memory, compare it to previous experience, and decide on action to take ...
item[`#file`]
... unimodal association cortex, which is modality specific and directly connected to the nearby primary sensory or motor area, and multimodal association cortex, which receives input from the unimodal areas. Association cortex serves as the neural interface between sensory and motor areas in cortex, an ...
... unimodal association cortex, which is modality specific and directly connected to the nearby primary sensory or motor area, and multimodal association cortex, which receives input from the unimodal areas. Association cortex serves as the neural interface between sensory and motor areas in cortex, an ...
Deficient Fear Conditioning in Psychopathy
... [CS]) comes to predict a fear-eliciting stimulus (unconditioned stimulus [US]) after they have been paired several times.4-6 The brain circuits underlying the acquisition and maintenance of conditioned fear in humans have been the focus of major research efforts. Imaging studies using positron emiss ...
... [CS]) comes to predict a fear-eliciting stimulus (unconditioned stimulus [US]) after they have been paired several times.4-6 The brain circuits underlying the acquisition and maintenance of conditioned fear in humans have been the focus of major research efforts. Imaging studies using positron emiss ...
Lect-3-Sensory cortex-Dr.Zahoor2010-10
... Areas 1, 2, and 3, which constitute PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA I, 40 is SECONDARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA II and areas 5 and 7, which constitute the SOMATOSENSORY ASSOCIATION AREA. ...
... Areas 1, 2, and 3, which constitute PRIMARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA I, 40 is SECONDARY SOMATOSENSORY AREA II and areas 5 and 7, which constitute the SOMATOSENSORY ASSOCIATION AREA. ...
Central Nervous System
... Gnostic area or General Interpretation area • Region that encompasses parts of the temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes. Located posterior to the auditory association area and usually equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere ...
... Gnostic area or General Interpretation area • Region that encompasses parts of the temporal, parietal, and occipital lobes. Located posterior to the auditory association area and usually equated with Wernicke’s area . • Only found in one hemisphere but not the other; most often the left hemisphere ...
Glutamate-like immunoreactivity in axon terminals from the olfactory
... the piriform cortex is reduced following olfactory bulbectomy or transection of the lateral olfactory tract (Bradford and Richards, 1976). The present study was undertaken because to date there is no morphological information available regarding the neurotransmitter associated with this efferent pat ...
... the piriform cortex is reduced following olfactory bulbectomy or transection of the lateral olfactory tract (Bradford and Richards, 1976). The present study was undertaken because to date there is no morphological information available regarding the neurotransmitter associated with this efferent pat ...
The Frontal Lobes: Movement and Morality Part I
... extensive and, along with the dorsomedial eye field, differs in both input and output from Area 6. As such, it is not involved with limb movement, but is associated instead with specialized control of eye movement when a visual target is available. In the absence of a visual target, the dorsomedial ...
... extensive and, along with the dorsomedial eye field, differs in both input and output from Area 6. As such, it is not involved with limb movement, but is associated instead with specialized control of eye movement when a visual target is available. In the absence of a visual target, the dorsomedial ...
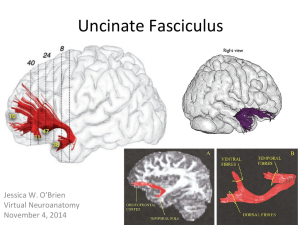
Uncinate Fasciculus
... • Some neurons in the inferior temporal cortex respond selecOvely to highly specific complex objects, including faces ...
... • Some neurons in the inferior temporal cortex respond selecOvely to highly specific complex objects, including faces ...
M&E and the Frontal Lobes
... counterfactual processing/ Regret? Counterfactual processing -The consequence of a decision/behavior can lead to feelings such as: satisfaction, relief, or regret… evaluation of the potential outcomes of alternative decisions. Testing the role of the orbito-frontal cortex in counterfactual reactions ...
... counterfactual processing/ Regret? Counterfactual processing -The consequence of a decision/behavior can lead to feelings such as: satisfaction, relief, or regret… evaluation of the potential outcomes of alternative decisions. Testing the role of the orbito-frontal cortex in counterfactual reactions ...
Central Emotional Integration
... Feeling = conscious sensation mediated by cingulate & frontal cortex. ...
... Feeling = conscious sensation mediated by cingulate & frontal cortex. ...
Central Emotional System
... Feeling = conscious sensation mediated by cingulate & frontal cortex. ...
... Feeling = conscious sensation mediated by cingulate & frontal cortex. ...
Motor Cortex
... Has about 1012 neurons, each of which may receive as many as 200,000 synapses – talk about integration! Although these numbers connote a high level of complexity, the CNS is actually quite orderly. ...
... Has about 1012 neurons, each of which may receive as many as 200,000 synapses – talk about integration! Although these numbers connote a high level of complexity, the CNS is actually quite orderly. ...
Basic principles of attention and decision
... MD reciprocal connections widespread dopamine innervations Wise, 2008 ...
... MD reciprocal connections widespread dopamine innervations Wise, 2008 ...
Central Nervous System
... gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. • Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles – Allowing for voluntary motor control. – These pathways are known as the corticospinal tracts or pyramidal tracts. ...
... gyrus of each cerebral hemisphere. • Contains large neurons (pyramidal cells) which project to SC neurons which eventually synapse on skeletal muscles – Allowing for voluntary motor control. – These pathways are known as the corticospinal tracts or pyramidal tracts. ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... deficits in discrimination/reversal learning (Schoenbaum et al., 2004) and reinforcer devaluation (Setlow and Schoenbaum, 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes ...
... deficits in discrimination/reversal learning (Schoenbaum et al., 2004) and reinforcer devaluation (Setlow and Schoenbaum, 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes ...
Opposite Effects of Amphetamine Self
... deficits in discrimination/reversal learning (Schoenbaum et al., 2004) and reinforcer devaluation (Setlow and Schoenbaum, 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes ...
... deficits in discrimination/reversal learning (Schoenbaum et al., 2004) and reinforcer devaluation (Setlow and Schoenbaum, 2004) — processes dependent on OFC function (Gallagher et al., 1999; McAlonan and Brown, 2003; Schoenbaum et al., 2003). Together, these studies indicate that, apart from changes ...
DIENCEPHALON
... • Control of electrocortical activity of cerebral cortex – plays important roles in arousal, consciousness and sleep mechanisms • Integration of motor functions by providing the relays – impulses from the basal ganglia and cerebellum can reach the motor cortex ...
... • Control of electrocortical activity of cerebral cortex – plays important roles in arousal, consciousness and sleep mechanisms • Integration of motor functions by providing the relays – impulses from the basal ganglia and cerebellum can reach the motor cortex ...
cerebral cortex
... connecting Broca´s and Wernicke´s centre of speech comissural tracts: tracts connecting two places in opposite hemispheres, they provide coordinated action of both hemispheres, the largest comissure is corpus callosum projection tracts: tracts connecting cerebral cortex with lower levels of CNS (or ...
... connecting Broca´s and Wernicke´s centre of speech comissural tracts: tracts connecting two places in opposite hemispheres, they provide coordinated action of both hemispheres, the largest comissure is corpus callosum projection tracts: tracts connecting cerebral cortex with lower levels of CNS (or ...
Document
... form motor cortex Motor cortex makes two types of projections. • A direct pathway to the ventral lateral spinal cord • An indirect pathway to the reticular formation (which subsequently goes to medial spinal cord). • For example a direct pathway will move the hand and the indirect pathway will postu ...
... form motor cortex Motor cortex makes two types of projections. • A direct pathway to the ventral lateral spinal cord • An indirect pathway to the reticular formation (which subsequently goes to medial spinal cord). • For example a direct pathway will move the hand and the indirect pathway will postu ...
Cortical inputs to the CA1 field of the monkey hippocampus originate
... We conclude from these studies that the same regions of the ventral temporal lobe that project to the entorhinal cortex also project to CA1. These projections originate mainly from areas 35 and 36 of the perirhinal cortex, and areas TF and TH of the parahippocampal cortex. We observed a sharp drop i ...
... We conclude from these studies that the same regions of the ventral temporal lobe that project to the entorhinal cortex also project to CA1. These projections originate mainly from areas 35 and 36 of the perirhinal cortex, and areas TF and TH of the parahippocampal cortex. We observed a sharp drop i ...
Orbitofrontal cortex
The orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) is a prefrontal cortex region in the frontal lobes in the brain which is involved in the cognitive processing of decision-making. In non-human primates it consists of the association cortex areas Brodmann area 11, 12 and 13; in humans it consists of Brodmann area 10, 11 and 47The OFC is considered anatomically synonymous with the ventromedial prefrontal cortex. Therefore the region is distinguished due to the distinct neural connections and the distinct functions it performs. It is defined as the part of the prefrontal cortex that receives projections from the magnocellular, medial nucleus of the mediodorsal thalamus, and is thought to represent emotion and reward in decision making. It gets its name from its position immediately above the orbits in which the eyes are located. Considerable individual variability has been found in the OFC of both humans and non-human primates. A related area is found in rodents.




![item[`#file`]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017295781_1-6f859caa8971becb0e29118db742025f-300x300.png)