Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
... - Corpus Callosum – Principal commissure connecting the left and right hemisphere together - Gyrus (plural) – The bumps created by two sulci - Sulcus (plural) – The space between the folds of the cerebral cortex - Fissure – A space that is not created by a fold of the brain - The white matte ...
Synthesis Intro Workshop
... Whether or not humans are conscious of it, we process pheromones which we put out constantly. A study done by Berglund, Lindstrom and Savic suggests that the processing specific human pheromones differs based on sexual preference. 4,16‐androstadien‐3‐one (AND) and estra‐1,3,4(10),16‐tetraen‐3‐ol (E ...
... Whether or not humans are conscious of it, we process pheromones which we put out constantly. A study done by Berglund, Lindstrom and Savic suggests that the processing specific human pheromones differs based on sexual preference. 4,16‐androstadien‐3‐one (AND) and estra‐1,3,4(10),16‐tetraen‐3‐ol (E ...
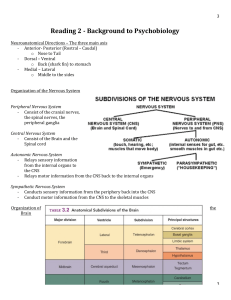
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
... • Cerebrum: largest portion; last to receive sensory input and integrate it before commanding voluntary motor response; coordinates other areas of the brain; and carries out higher thought processes, memory, language, speech, and learning. ...
vocab - sociallyconsciousbird.com
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
... cerebral cortex – the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells that covers the cerebral hemispheres; the body’s ultimate control and information processing center glial cells – cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, and protect neurons frontal lobes – the portion of the cerebral c ...
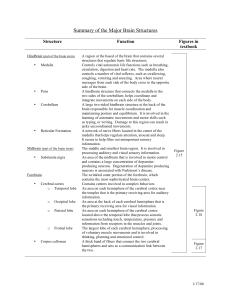
Summary of the Major Brain Structures
... A network of nerve fibers located in the center of the medulla that helps regulate attention, arousal and sleep. It seems to help filter out unimportant sensory information. The middle and smallest brain region. It is involved in processing auditory and visual sensory information. An area of the mid ...
... A network of nerve fibers located in the center of the medulla that helps regulate attention, arousal and sleep. It seems to help filter out unimportant sensory information. The middle and smallest brain region. It is involved in processing auditory and visual sensory information. An area of the mid ...
Cerebral Cortex: The 2-3 mm membrane around the cerebrum to
... the cerebrum that controls emotions, logic, memory, judgment. Contains the Motor Cortex, the part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Temporal Lobe: The section of the cerebrum that interprets messages from the ears. Right lobe right ear. Connects with the frontal and parietal lobes. ...
... the cerebrum that controls emotions, logic, memory, judgment. Contains the Motor Cortex, the part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Temporal Lobe: The section of the cerebrum that interprets messages from the ears. Right lobe right ear. Connects with the frontal and parietal lobes. ...
Step Up To: Psychology
... 20. Curare is a poison people use to paralyze animals when hunting. It is therefore an ____ which inhibits the ...
... 20. Curare is a poison people use to paralyze animals when hunting. It is therefore an ____ which inhibits the ...
Brain Notes
... functional MRI Uses magnetic field Not harmful Shows brain structure and activity ...
... functional MRI Uses magnetic field Not harmful Shows brain structure and activity ...
CS 160 * Comparative Cognition * Spring 02
... - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - Together, Colliculi coord their “maps” of motion in vis & auditory world, so thing seen = thing heard - N ...
... - e.g. “Blindsight” Human w/damage to higher visual areas is “blind” but can point to moving stim. - Inferior Colliculus = Processes auditory info (esp location), & integrate with motor output - Together, Colliculi coord their “maps” of motion in vis & auditory world, so thing seen = thing heard - N ...
The Brain and Nervous System - Mr. Conzen
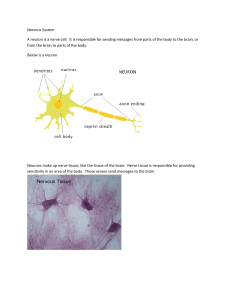
... from tissues and organs toward CNS Motor neurons - how the CNS sends instructions out to body tissues. Interneurons - processes internal commincation in the CNS ...
... from tissues and organs toward CNS Motor neurons - how the CNS sends instructions out to body tissues. Interneurons - processes internal commincation in the CNS ...
An Integrative Approach to Psychopathology - Home
... Most sensory, emotional, and cognitive processing ...
... Most sensory, emotional, and cognitive processing ...
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 378
... Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts internally Projection tracts (fibers) – connect more or less vertically Association tracts (fibers) – connect one gyrus to another in the same hemisphere ...
... Gray surface (cortex), 2-4 mm thick, is mostly neuron cell bodies with white tracts internally Projection tracts (fibers) – connect more or less vertically Association tracts (fibers) – connect one gyrus to another in the same hemisphere ...
The Promise and Peril of Tomorrow`s Neuroscience
... specifically define what the mind is. On the other hand, the book goes into great detail in explaining how human beings evolved over time with particular attention to the human brain. One of the great strengths of the human brain is its “plasticity” – its ability to assemble and disassemble neurons ...
... specifically define what the mind is. On the other hand, the book goes into great detail in explaining how human beings evolved over time with particular attention to the human brain. One of the great strengths of the human brain is its “plasticity” – its ability to assemble and disassemble neurons ...
Neurotransmitters
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
... Glutamate is used at the great majority of fast excitatory synapses in the brain and spinal cord. It is also used at most synapses that are "modifiable", i.e. capable of increasing or decreasing in strength. Modifiable synapses are thought to be the main memory-storage elements in the brain. GABA is ...
Nerves and the brain
... the brain. Information comes to this area from our senses and the brain sorts it out in the light of past experiences. As a result, motor impulses are sent along the nerves to cause an appropriate action to take place. ...
... the brain. Information comes to this area from our senses and the brain sorts it out in the light of past experiences. As a result, motor impulses are sent along the nerves to cause an appropriate action to take place. ...
Visual Cortical Dynamics Charles Gilbert The Rockefeller University
... Vision is an active and dynamic process. The strategy our brain uses to parse scenes and recognize objects depends on our previous experiences. Our interpretation of visual scenes requires an interaction between internal representations of object properties acquired through experience and the immedi ...
... Vision is an active and dynamic process. The strategy our brain uses to parse scenes and recognize objects depends on our previous experiences. Our interpretation of visual scenes requires an interaction between internal representations of object properties acquired through experience and the immedi ...
File
... a bundle of fibers called the _corpus callosum___. 3. Covering the outermost layer of the cerebrum is the _cerebral cortex_. 4. What are the functions of the four lobes? Answer: Frontal- movement, higher thinking, emotional responses. Parietal- attention, language, space perception. Occipital- visio ...
... a bundle of fibers called the _corpus callosum___. 3. Covering the outermost layer of the cerebrum is the _cerebral cortex_. 4. What are the functions of the four lobes? Answer: Frontal- movement, higher thinking, emotional responses. Parietal- attention, language, space perception. Occipital- visio ...
Brain and Cognitive Modeling and Neurocomputation
... and results of Cognitive and Brain Modeling – What is it good for? – What does it replace? ...
... and results of Cognitive and Brain Modeling – What is it good for? – What does it replace? ...