1st Semester Post Test Study Guide 2010 – 2011 KEY 1. Define
... 34.Explain the two types of weathering. Give examples of each. chemical and mechanical processes that break down the surface Mechanical weathering is the type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces. Ex. ice wedging, abrasion, plants, animals, release of pressure Chemica ...
... 34.Explain the two types of weathering. Give examples of each. chemical and mechanical processes that break down the surface Mechanical weathering is the type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces. Ex. ice wedging, abrasion, plants, animals, release of pressure Chemica ...
Title Page Photo “All things deteriorate in time.”—Virgil (Brainyquote.com)
... Physical disintegration of rock into smaller fragments No change in its chemical composition Increases surface area for chemical weathering There are 4 main types of Mechanical Weathering: frost wedging (or frost shattering), salt wedging, temperature changes, and exfoliation. ...
... Physical disintegration of rock into smaller fragments No change in its chemical composition Increases surface area for chemical weathering There are 4 main types of Mechanical Weathering: frost wedging (or frost shattering), salt wedging, temperature changes, and exfoliation. ...
Lesson 4-3 Sedimentary Rocks Outline
... b. When water travels through rock, some of the elements of the rock can dissolve and be ...
... b. When water travels through rock, some of the elements of the rock can dissolve and be ...
Name: Date
... 1. Mechanical Weathering- The breaking of rock into smaller pieces by forces due to gravity, ice, plant roots or other forces 2. Chemical Weathering- The changing of materials in a rock by chemical processes Review: Raindrops take in carbon dioxide from the air and make a chemical called carbonic ac ...
... 1. Mechanical Weathering- The breaking of rock into smaller pieces by forces due to gravity, ice, plant roots or other forces 2. Chemical Weathering- The changing of materials in a rock by chemical processes Review: Raindrops take in carbon dioxide from the air and make a chemical called carbonic ac ...
CRCT Review Packet
... 3. Scientists use a series of steps called the ____________________ _____________________ to solve problems. The scientist gathers information, makes a _________________, designs an ____________________, collects and interprets the ___________, and then draws a _______________. 4. When doing a lab, ...
... 3. Scientists use a series of steps called the ____________________ _____________________ to solve problems. The scientist gathers information, makes a _________________, designs an ____________________, collects and interprets the ___________, and then draws a _______________. 4. When doing a lab, ...
Mechanical weathering - occurs when physical forces break rock
... Weathering and Erosion Mechanical weathering - occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller and smaller pieces without changing the rock’s mineral composition. Frost wedging - the mechanical breakup of rock caused by the expansion of freezing water in cracks and crevices Talus large piles of ...
... Weathering and Erosion Mechanical weathering - occurs when physical forces break rock into smaller and smaller pieces without changing the rock’s mineral composition. Frost wedging - the mechanical breakup of rock caused by the expansion of freezing water in cracks and crevices Talus large piles of ...
Earth Revealed #10: Geologic Time
... 7. What kind of conditions exist for the formation of gold, silver and copper (in other words, how do they form)? ...
... 7. What kind of conditions exist for the formation of gold, silver and copper (in other words, how do they form)? ...
File - Boreal Agrominerals
... chiefly comprised of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite and iron minerals. High levels of base cations and low silica content characterize them. In the weathering process this group of rocks weather to very important secondary clay minerals (vermiculite, illite, montromillinite) and in the proces ...
... chiefly comprised of olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite and iron minerals. High levels of base cations and low silica content characterize them. In the weathering process this group of rocks weather to very important secondary clay minerals (vermiculite, illite, montromillinite) and in the proces ...
First Hour Exam, Fall, 2006
... d. mechanical weathering is the same as erosion, but chemical weathering is different from erosion because it involves chemistry. 20. Ice-wedging is a very effective mechanical weathering process because a. water expands as it freezes, pushing rocks apart from the inside. b. the ice grinds away at t ...
... d. mechanical weathering is the same as erosion, but chemical weathering is different from erosion because it involves chemistry. 20. Ice-wedging is a very effective mechanical weathering process because a. water expands as it freezes, pushing rocks apart from the inside. b. the ice grinds away at t ...
Name (Per____) Name (Per____) Pre-assessment--
... that farmers can conserve their soil. OR Make a 3D model that shows one way farmers can conserve soil. OR Make a brochure (or website) to educate farmers about soil conservation. ...
... that farmers can conserve their soil. OR Make a 3D model that shows one way farmers can conserve soil. OR Make a brochure (or website) to educate farmers about soil conservation. ...
Weathering - Kawameeh Middle School
... • If the speed of flowing water decreases, the water can no longer carry sediment and the sediment settles at the bottom of the water. • Floodplains form when sediment settles out of rivers that flood the areas next to ...
... • If the speed of flowing water decreases, the water can no longer carry sediment and the sediment settles at the bottom of the water. • Floodplains form when sediment settles out of rivers that flood the areas next to ...
Science
... - Soil: thin layer of loose materials that covers most of the Earth’s surface - Soil layers: o Topsoil: top layer of soil that includes rock particles mixed with the dark products of decay. Decayed parts of plants and animals are humus. Humus contains the nutrients plants need to grow. o Subsoil: un ...
... - Soil: thin layer of loose materials that covers most of the Earth’s surface - Soil layers: o Topsoil: top layer of soil that includes rock particles mixed with the dark products of decay. Decayed parts of plants and animals are humus. Humus contains the nutrients plants need to grow. o Subsoil: un ...
Review for Earth Science
... 18. Weathering ~ a process by which rock is broken down into smaller pieces. Weathering can be classified as either physical/mechanical or chemical weathering. 19. Physical weathering occurs when rock is broken down, but remains the same type of rock. Examples include frost action, plant and animal ...
... 18. Weathering ~ a process by which rock is broken down into smaller pieces. Weathering can be classified as either physical/mechanical or chemical weathering. 19. Physical weathering occurs when rock is broken down, but remains the same type of rock. Examples include frost action, plant and animal ...
Document
... carrying away rock components in solution. (A) Joints and bedding planes in a limestone bluff. (B) This stream has carried away less-resistant rock components, forming a cave under the ledge. ...
... carrying away rock components in solution. (A) Joints and bedding planes in a limestone bluff. (B) This stream has carried away less-resistant rock components, forming a cave under the ledge. ...
The Earth
... Objective: Describe how wind and water move and change things. (Strand VI-B5) Related Vocabulary: Weathering - the process by which rock becomes soil. Chemical weathering - such as acid rain Biological weathering - such as by growing things Erosion - the movement of weathered materials. Activity: 1 ...
... Objective: Describe how wind and water move and change things. (Strand VI-B5) Related Vocabulary: Weathering - the process by which rock becomes soil. Chemical weathering - such as acid rain Biological weathering - such as by growing things Erosion - the movement of weathered materials. Activity: 1 ...
Section Nine Earth Science Landforms and Changes to
... 1. B – when a river deposits rocks, soil, and sand as it enters a body of water, the deposited materials will most likely form a delta. 2. C – the waves are most responsible for causing the erosion that wears away the rock in the sea arch 3. B – the most common way that plants break apart rocks happ ...
... 1. B – when a river deposits rocks, soil, and sand as it enters a body of water, the deposited materials will most likely form a delta. 2. C – the waves are most responsible for causing the erosion that wears away the rock in the sea arch 3. B – the most common way that plants break apart rocks happ ...
Changing Earth`s Surface
... constant change through natural geological processes. Forces inside Earth can cause changes to occur on Earth’s surface through volcanic activity and faulting as tectonic plates move. There are other factors such as weathering, erosion and deposition that change Earth’s surface. Weathering, the brea ...
... constant change through natural geological processes. Forces inside Earth can cause changes to occur on Earth’s surface through volcanic activity and faulting as tectonic plates move. There are other factors such as weathering, erosion and deposition that change Earth’s surface. Weathering, the brea ...
Chapter 14 – Weathering and Erosion
... new mineral called a carbonate. Carbonic acid reacts with calcite, a major component of limestone, and forms calcium bicarbonate. Calcium bicarbonate dissolves easily in water, and so limestone weathers away. • Organic Acids – these are produced naturally by certain living things. Lichens and mosses ...
... new mineral called a carbonate. Carbonic acid reacts with calcite, a major component of limestone, and forms calcium bicarbonate. Calcium bicarbonate dissolves easily in water, and so limestone weathers away. • Organic Acids – these are produced naturally by certain living things. Lichens and mosses ...
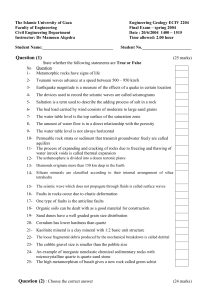
Question (1) (25 marks) State whether the following statements are
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
... 16- Faults in rocks occur due to elastic deformation 17- One type of faults is the anticline faults 18- Organic soils can be dealt with as a good material for construction 19- Sand dunes have a well graded grain size distribution 20- Corndum has lower hardness than quartz 21- Kaolinite mineral is a ...
Yr 7 Rocks and Fossils Unit Overview
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
Section 7.3 Student note
... cools -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock ...
... cools -crystal size depends on how slow it cooled -Intrusive igneous rocks formed well below the surface, ‘intruded into the rock’ -Extrusive rocks formed on the Earth’s surface (exited the Earth) -reach the surface through cracks in the crust/plates, or through erosion and uplift of layers of rock ...
File
... crumbling away. This solid rock that is crumbling to rock fragments is in the Grand Canyon, Arizona. ...
... crumbling away. This solid rock that is crumbling to rock fragments is in the Grand Canyon, Arizona. ...
crust, mantle, outer core, inner core
... Bowl-shaped part of a volcano; lava often collects here before flowing down the slope ( vent, crater, magma chamber, pipe) ...
... Bowl-shaped part of a volcano; lava often collects here before flowing down the slope ( vent, crater, magma chamber, pipe) ...
These forces are responsible for forming many of the landforms on
... 5. Arches – formed by weathering and erosion a. Sea Arches are formed by waves hitting a cliff face and weathering/eroding away a portion of the cliff. It can start as a sea cave that eventually expands through a portion of the cliff or connects with another cave on the opposite wall of the cliff. b ...
... 5. Arches – formed by weathering and erosion a. Sea Arches are formed by waves hitting a cliff face and weathering/eroding away a portion of the cliff. It can start as a sea cave that eventually expands through a portion of the cliff or connects with another cave on the opposite wall of the cliff. b ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.