7th Grade Science Unit 3 Vocabulary Uniformitarianism
... the past can be explained by current geologic processes. ...
... the past can be explained by current geologic processes. ...
Background Information for Plate Tectonics Rock Formation
... – crushed to make gravel used in construction, Pumice – abrasive used for cleaning & polishing, Obsidian – heated to form perlite which is used in place of soil for starting seeds. b. Sedimentary rock forms when particles of other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented t ...
... – crushed to make gravel used in construction, Pumice – abrasive used for cleaning & polishing, Obsidian – heated to form perlite which is used in place of soil for starting seeds. b. Sedimentary rock forms when particles of other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented t ...
Phinizy Down Under - Phinizy Center for Water Sciences
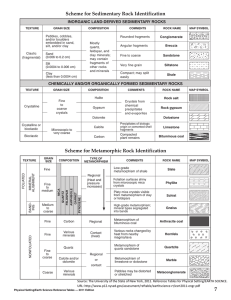
... Metamorphic rocks are rocks already formed, but change through heat and pressure. Examples include quartz, marble, slate, and schist. Sedimentary rocks form from mud, sand, clay or other minerals that are carried and deposited by weathering, and then are compressed. Examples of sedimentary rocks inc ...
... Metamorphic rocks are rocks already formed, but change through heat and pressure. Examples include quartz, marble, slate, and schist. Sedimentary rocks form from mud, sand, clay or other minerals that are carried and deposited by weathering, and then are compressed. Examples of sedimentary rocks inc ...
Semester Exam Study Guide
... with each layer. Use all three laws at least once. 21. Give an example of relative time. 22. How old is a mammoth tusk if there is only 25% of the original carbon 14 remaining in the sample? 23. What is the main cause of extinction in the last 11,000 yrs? 24. Describe the main characteristics associ ...
... with each layer. Use all three laws at least once. 21. Give an example of relative time. 22. How old is a mammoth tusk if there is only 25% of the original carbon 14 remaining in the sample? 23. What is the main cause of extinction in the last 11,000 yrs? 24. Describe the main characteristics associ ...
summary notes on minerals, rocks
... b. there are over 100 types of elements on Earth - only a few are common 1) oxygen and silicon are the most common by mass, oxygen and potassium by volume 2. Minerals are homogeneous - the same throughout - uniform 3. No 2 different minerals have completely identical mineral properties 4. Most rocks ...
... b. there are over 100 types of elements on Earth - only a few are common 1) oxygen and silicon are the most common by mass, oxygen and potassium by volume 2. Minerals are homogeneous - the same throughout - uniform 3. No 2 different minerals have completely identical mineral properties 4. Most rocks ...
Minerals, Rocks and Resources Outline
... • Organic sedimentary rock contain the accumulation of plant and animal remains – Fossils are commonly found • Chemical sedimentary rocks are deposited by the settling of materials from solution in seawater – This occurs during the evaporation of seawater and when chemical reactions in the water for ...
... • Organic sedimentary rock contain the accumulation of plant and animal remains – Fossils are commonly found • Chemical sedimentary rocks are deposited by the settling of materials from solution in seawater – This occurs during the evaporation of seawater and when chemical reactions in the water for ...
File - Earth Science Introduction
... 66 What kind of sedimentary rock can be cemented together by calcite or quartz? 67 What kind of sedimentary rock is made from dissolved minerals? 68 Besides texture, how else are rocks classified? 69 What kind of rock is formed from lava that cools on the Earth’s surface? 70 What kind of sedimentary ...
... 66 What kind of sedimentary rock can be cemented together by calcite or quartz? 67 What kind of sedimentary rock is made from dissolved minerals? 68 Besides texture, how else are rocks classified? 69 What kind of rock is formed from lava that cools on the Earth’s surface? 70 What kind of sedimentary ...
MCQ - tcspgnn
... C. ? not usually porous and often shows a crystalline structure of layers of grains, sometimes contains distorted fossils due to effect of heat and pressure 18. Which is TRUE about metamorphic rocks? [8h-33] A. ? usually contain fossils B. ? very porous C. ? crystals usually jumbled D. ? formed by h ...
... C. ? not usually porous and often shows a crystalline structure of layers of grains, sometimes contains distorted fossils due to effect of heat and pressure 18. Which is TRUE about metamorphic rocks? [8h-33] A. ? usually contain fossils B. ? very porous C. ? crystals usually jumbled D. ? formed by h ...
Metamorphic Rock Metamorphic rocks have been changed over
... Metamorphic rocks have been changed over time by extreme pressure and heat. The word metamorphic literally means "changed form". Metamorphic rocks can be formed by pressure deep under the Earth's surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic pla ...
... Metamorphic rocks have been changed over time by extreme pressure and heat. The word metamorphic literally means "changed form". Metamorphic rocks can be formed by pressure deep under the Earth's surface, from the extreme heat caused by magma or by the intense collisions and friction of tectonic pla ...
Reader`s Theater Rocks, Minerals, Soil, and Fossils
... been changed from temperature and pressure. R4: That just leaves sedimentary rocks. I always think about a sandwich with sedimentary rocks. A sandwich has different layers of stuff inside of it and so does a sedimentary rock. Its layers are squeezed together until they form a rock. R1: Do rocks alwa ...
... been changed from temperature and pressure. R4: That just leaves sedimentary rocks. I always think about a sandwich with sedimentary rocks. A sandwich has different layers of stuff inside of it and so does a sedimentary rock. Its layers are squeezed together until they form a rock. R1: Do rocks alwa ...
Answers
... Metamorphic Rock Identification, the Texture can be foliated (top 4 rocks) or nonfoliated (bottom 4 rocks). Mineral alignment is found in the first three rocks, and the mineral pyroxene is found in schist and gneiss. Since the question states that the rock does not have banding it is not Gneiss and ...
... Metamorphic Rock Identification, the Texture can be foliated (top 4 rocks) or nonfoliated (bottom 4 rocks). Mineral alignment is found in the first three rocks, and the mineral pyroxene is found in schist and gneiss. Since the question states that the rock does not have banding it is not Gneiss and ...
HW # 6 - Sedimentary, Metamorphic, Rock Cycle Section: Name
... Which rock was organically formed and sometimes contains fossilized ...
... Which rock was organically formed and sometimes contains fossilized ...
W Geo Chapter 1 - Russell County Moodle
... Wind, the second major cause of erosion, can strip away exposed soil, but windblown deposits of loess, mineral-rich dust and silt, can also benefit farmers. Glaciers, huge, slow-moving sheets of ice, are also major agents of erosion, as they pick up and drag along dirt, rocks, and boulders. During t ...
... Wind, the second major cause of erosion, can strip away exposed soil, but windblown deposits of loess, mineral-rich dust and silt, can also benefit farmers. Glaciers, huge, slow-moving sheets of ice, are also major agents of erosion, as they pick up and drag along dirt, rocks, and boulders. During t ...
Chapter 1 - Plainview Schools
... Wind, the second major cause of erosion, can strip away exposed soil, but windblown deposits of loess, mineral-rich dust and silt, can also benefit farmers. Glaciers, huge, slow-moving sheets of ice, are also major agents of erosion, as they pick up and drag along dirt, rocks, and boulders. During t ...
... Wind, the second major cause of erosion, can strip away exposed soil, but windblown deposits of loess, mineral-rich dust and silt, can also benefit farmers. Glaciers, huge, slow-moving sheets of ice, are also major agents of erosion, as they pick up and drag along dirt, rocks, and boulders. During t ...
MINERAL COMPOSITION OF IGNEOUS ROCKS
... Color is often an indicator of the composition of a rock or mineral and can be effectively used to identify the composition of most igneous rocks. Light colors, including white, light gray, tan and pink, indicate a felsic composition. Felsic compositions are rich in silica (SiO2). Dark colors, such ...
... Color is often an indicator of the composition of a rock or mineral and can be effectively used to identify the composition of most igneous rocks. Light colors, including white, light gray, tan and pink, indicate a felsic composition. Felsic compositions are rich in silica (SiO2). Dark colors, such ...
The Rock Cycle
... This is called deposition. As deposition continues, layers of sediments continue to pile up, and they compact the layers on the bottom. This is called compaction. Once compaction occurs, the sediments begin to “glue” together which is called cementation. (like the word cement) ...
... This is called deposition. As deposition continues, layers of sediments continue to pile up, and they compact the layers on the bottom. This is called compaction. Once compaction occurs, the sediments begin to “glue” together which is called cementation. (like the word cement) ...
Topic 1 –MINERALS – p. 354 Term Text Book Definition Definition in
... A process in which water moving through rich soil, removes nutrients and minerals; can make soil infertile Topic 3 – EROSION – p. 373 Text Book Definition Definition in my own words The movement of rock and mineral grains from one place to another ...
... A process in which water moving through rich soil, removes nutrients and minerals; can make soil infertile Topic 3 – EROSION – p. 373 Text Book Definition Definition in my own words The movement of rock and mineral grains from one place to another ...
Rock Identification and stories lab
... characteristics: Quartzite is a non-foliated metamorphic rock composed almost entirely of quartz. It forms when a quartz-rich sandstone is altered by the heat, pressure, and chemical activity of metamorphism. These conditions recrystallize the sand grains and the silica cement that binds them togeth ...
... characteristics: Quartzite is a non-foliated metamorphic rock composed almost entirely of quartz. It forms when a quartz-rich sandstone is altered by the heat, pressure, and chemical activity of metamorphism. These conditions recrystallize the sand grains and the silica cement that binds them togeth ...
Soils - TeacherWeb
... Formed when older rocks are broken apart by plant roots, ice wedges, and earth movements Transported by glaciers, waves, currents, and wind The transported particles then become bound together (cemented) as secondary minerals grow in the spaces between the loose particles and create a new, solid ...
... Formed when older rocks are broken apart by plant roots, ice wedges, and earth movements Transported by glaciers, waves, currents, and wind The transported particles then become bound together (cemented) as secondary minerals grow in the spaces between the loose particles and create a new, solid ...
topic13pptpart1
... the rock column with trilobites, they had to come from the same time period. 3.) If an older index fossil is on TOP of a younger one: Then the Law of Superposition has been disturbed ...
... the rock column with trilobites, they had to come from the same time period. 3.) If an older index fossil is on TOP of a younger one: Then the Law of Superposition has been disturbed ...
Weathering and Soil Formation Uniformitarianism The principal that
... Soil that has developed three layers is called mature soil. It takes thousands of years and the proper conditions for soil to develop three layers. The uppermost layer of mature soil is called the A horizon. The A horizon is a dark-colored soil layer in which much activity by living organisms takes ...
... Soil that has developed three layers is called mature soil. It takes thousands of years and the proper conditions for soil to develop three layers. The uppermost layer of mature soil is called the A horizon. The A horizon is a dark-colored soil layer in which much activity by living organisms takes ...
Overview of the Big Questions in Physical Geology
... metamorphic rocks) or particles of other rocks (sedimentary rocks). A mineral is a naturally occurring solid, with a specific chemical composition, and, most importantly, a repeating structure of atoms. How do the structure and composition of silicate minerals relate to pressure and temperature cond ...
... metamorphic rocks) or particles of other rocks (sedimentary rocks). A mineral is a naturally occurring solid, with a specific chemical composition, and, most importantly, a repeating structure of atoms. How do the structure and composition of silicate minerals relate to pressure and temperature cond ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.