Forces of Change
... Creates soil and breaks down mountains Coasts Canyons Cliffs caverns Humans are both Builders AND Breakers of Landforms Islands and Mountains ...
... Creates soil and breaks down mountains Coasts Canyons Cliffs caverns Humans are both Builders AND Breakers of Landforms Islands and Mountains ...
& Time River the
... time capsules. Inside them is a fascinating history of Earth’s landscape and climate. Over four years, I traveled across the river basin to gather these time capsules from the free-flowing Fraser. I can open them to reveal a geochemical journey that starts in the atmosphere, moves through plants and ...
... time capsules. Inside them is a fascinating history of Earth’s landscape and climate. Over four years, I traveled across the river basin to gather these time capsules from the free-flowing Fraser. I can open them to reveal a geochemical journey that starts in the atmosphere, moves through plants and ...
lesson 4 rock cycleplus - science
... Temperature and pressure cause the rock to reform as small crystals that are much harder. This is marble. It is used as a hard and decorative stone in buildings, sculptures etc. ...
... Temperature and pressure cause the rock to reform as small crystals that are much harder. This is marble. It is used as a hard and decorative stone in buildings, sculptures etc. ...
Study Guide: Plate tectonics TEST 2/soil Rocks/Weathering and
... 5. What is a transform boundary? Plates slide or scrape past one another- also called a strikeslip fault 6. What is weathering? The breaking down of rocks and plants into smaller pieces 7. What is erosion? The movement of broken down rocks and plants by wind, water, gravity or ice 8. The lithosphere ...
... 5. What is a transform boundary? Plates slide or scrape past one another- also called a strikeslip fault 6. What is weathering? The breaking down of rocks and plants into smaller pieces 7. What is erosion? The movement of broken down rocks and plants by wind, water, gravity or ice 8. The lithosphere ...
Composition of the crust, part 1
... Continental drift is the theory that proposes that the present continents were originally connected as one or two large landmasses that have broken up and literally drifted apart over the last several million years. Plate tectonics, a descendant of continental drift, is a coherent theory of massive ...
... Continental drift is the theory that proposes that the present continents were originally connected as one or two large landmasses that have broken up and literally drifted apart over the last several million years. Plate tectonics, a descendant of continental drift, is a coherent theory of massive ...
NAME - KCSE Online
... - The surface rock and rock beneath should be thick limestone / dolomite / chalk to allow water to penetrate through the rock and react with it. - The rock / limestone / dolomite / chalk should be hard and well jointed to allow water to percolate. - The climate should be hot and humid to increase th ...
... - The surface rock and rock beneath should be thick limestone / dolomite / chalk to allow water to penetrate through the rock and react with it. - The rock / limestone / dolomite / chalk should be hard and well jointed to allow water to percolate. - The climate should be hot and humid to increase th ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Some sedimentary rocks are formed when a sea or a lake dries up, l~avil~g large amounts of mineralsF~gure 13-~0 Chemtca~ rocks form that were dissolved in the water. As you can see in tn many different places. As [ne sun bears down, evaooration forms Figure 13-30. the deposited minerals may" create ...
... Some sedimentary rocks are formed when a sea or a lake dries up, l~avil~g large amounts of mineralsF~gure 13-~0 Chemtca~ rocks form that were dissolved in the water. As you can see in tn many different places. As [ne sun bears down, evaooration forms Figure 13-30. the deposited minerals may" create ...
STRESS – is the total amount of force that is placed upon crustal
... STRESS – is the total amount of force that is placed upon crustal rocks that can cause a change in the rock’s shape or volume (volume means the amount of space that an object takes up). There are 3 main types of stress that crustal rocks can be subjected to: compression, tension, and shearing. The m ...
... STRESS – is the total amount of force that is placed upon crustal rocks that can cause a change in the rock’s shape or volume (volume means the amount of space that an object takes up). There are 3 main types of stress that crustal rocks can be subjected to: compression, tension, and shearing. The m ...
Jamies Group - Junee North Public School
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
... circles stones are 26 feet high and the outer circles stones are 10 feet high. There are two types of stones used in the construction of Stonehenge. The large outer circle is made of Sarsen which is sedimentary Sandstone and the inner circle is made of Bluestone which is a blend of Basalt and Gabbro ...
Earths History Presentation
... • Radioactive decay occurs when the nuclei of unstable atoms break down, changing the original atoms into atoms of another element. • The rate of radioactive decay is measured in terms of half-life. – Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half the atoms of a substance to decay into another el ...
... • Radioactive decay occurs when the nuclei of unstable atoms break down, changing the original atoms into atoms of another element. • The rate of radioactive decay is measured in terms of half-life. – Half-life is the amount of time it takes for half the atoms of a substance to decay into another el ...
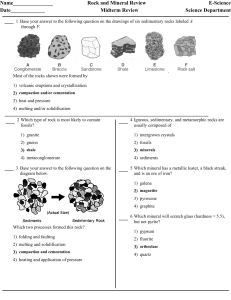
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... contains the minerals amphibole, quartz, and feldspar arranged in coarse-grained bands. ...
... contains the minerals amphibole, quartz, and feldspar arranged in coarse-grained bands. ...
Sedimentary Rocks Answers Explained
... the comments section, breccia is composed of angular fragments. 3. (3) Sediments that are 1.5 cm in size are pebble sized which when compacted and compressed turn into the sedimentary rock conglomerate. 4. (3) Sediments that are 0.05 cm in size are sand sized which when compacted and compressed turn ...
... the comments section, breccia is composed of angular fragments. 3. (3) Sediments that are 1.5 cm in size are pebble sized which when compacted and compressed turn into the sedimentary rock conglomerate. 4. (3) Sediments that are 0.05 cm in size are sand sized which when compacted and compressed turn ...
Field Trip to Ninepin Island
... water and air can easily penetrate into the rock along these joints. Chemical processes such as oxidation, hydrolysis, hydration and solution may occur. Iron-bearing minerals in the rock are oxidized to form limonite and hematite which give the weathered material the brownish colour. Sometimes, pore ...
... water and air can easily penetrate into the rock along these joints. Chemical processes such as oxidation, hydrolysis, hydration and solution may occur. Iron-bearing minerals in the rock are oxidized to form limonite and hematite which give the weathered material the brownish colour. Sometimes, pore ...
Chapter 26 - Planet Earth
... How Mineral Deposits Are Formed • Distribution of mineral resources – Earth's formation – Crust and Ocean • silicates vs. manganese oxide nodules ...
... How Mineral Deposits Are Formed • Distribution of mineral resources – Earth's formation – Crust and Ocean • silicates vs. manganese oxide nodules ...
Processes that Shape the Earth Unit Suggested Timeline
... The earth is made up of three layers, the crust the mantle and the core. The core heats the bottom of the mantle, causing convection. The convection currents in the mantle cause changes in the crust. (SC.D.1.2.4, 1.2.5) Radioactive decay in the core of earth results in energy. Evidence of the heat f ...
... The earth is made up of three layers, the crust the mantle and the core. The core heats the bottom of the mantle, causing convection. The convection currents in the mantle cause changes in the crust. (SC.D.1.2.4, 1.2.5) Radioactive decay in the core of earth results in energy. Evidence of the heat f ...
Earth Structure/Composition
... Unloading: Exfoliation – spalling – susceptible rocks Bioturbation: Animal burrowing - tree roots Chemical Weathering – What is chemical weathering? Where and how does it take place? For each of the following weathering processes – can you describe and identify each one? Can you identify the most su ...
... Unloading: Exfoliation – spalling – susceptible rocks Bioturbation: Animal burrowing - tree roots Chemical Weathering – What is chemical weathering? Where and how does it take place? For each of the following weathering processes – can you describe and identify each one? Can you identify the most su ...
Chapter 07 - Duplin County Schools
... – When the overlying rock layers are removed, the pressure on the bedrock below is reduced. – The bedrock surface, formerly buried, is then able to expand, and long, curved cracks known as joints can form that lead to exfoliation. – Exfoliation is the process by which outer rock layers are stripped ...
... – When the overlying rock layers are removed, the pressure on the bedrock below is reduced. – The bedrock surface, formerly buried, is then able to expand, and long, curved cracks known as joints can form that lead to exfoliation. – Exfoliation is the process by which outer rock layers are stripped ...
Rocks - earthjay science
... Carbonate rich (contain calcite/dolomite) Sedimentary Rocks These rocks can be scratched with steel and they react to acid. Dolomite needs to be powdered for acid reaction. Limestone – with or without fossils (calcite rich shells) Dolostone – similar to limestone (with or without fossils), but only ...
... Carbonate rich (contain calcite/dolomite) Sedimentary Rocks These rocks can be scratched with steel and they react to acid. Dolomite needs to be powdered for acid reaction. Limestone – with or without fossils (calcite rich shells) Dolostone – similar to limestone (with or without fossils), but only ...
To examine life in Lassen`s thermal pools we will need to dive down
... Origin of Hydrothermal Features To examine life in Lassen’s thermal pools we will need to dive down to the microscopic scale of single-celled organisms, where entire ecosystems span mere millimeters and inhabitants traffic in molecular currencies. But to understand why hot springs are hot at all, we ...
... Origin of Hydrothermal Features To examine life in Lassen’s thermal pools we will need to dive down to the microscopic scale of single-celled organisms, where entire ecosystems span mere millimeters and inhabitants traffic in molecular currencies. But to understand why hot springs are hot at all, we ...
G2S15Lesson2 SedMet
... Carbonate rich (contain calcite/dolomite) Sedimentary Rocks These rocks can be scratched with steel and they react to acid. Dolomite needs to be powdered for acid reaction. Limestone – with or without fossils (calcite rich shells) Dolostone – similar to limestone (with or without fossils), but only ...
... Carbonate rich (contain calcite/dolomite) Sedimentary Rocks These rocks can be scratched with steel and they react to acid. Dolomite needs to be powdered for acid reaction. Limestone – with or without fossils (calcite rich shells) Dolostone – similar to limestone (with or without fossils), but only ...
Our Changing Earth
... Sand dunes are large hills of sand often found in the desert. These huge features are made by wind erosion. The size and shape of dunes depend on the amount of sand, the number of plants in the area, and the strength of the winds. Winds can also blow sand dunes across the desert. The wind picks up s ...
... Sand dunes are large hills of sand often found in the desert. These huge features are made by wind erosion. The size and shape of dunes depend on the amount of sand, the number of plants in the area, and the strength of the winds. Winds can also blow sand dunes across the desert. The wind picks up s ...
ASOL SCIENCESCOPEhighschool14
... The oxide group of minerals is composed of oxygen and a metal. Some common oxides include hematite and magnetite. Minerals are important to human wealth and welfare. ...
... The oxide group of minerals is composed of oxygen and a metal. Some common oxides include hematite and magnetite. Minerals are important to human wealth and welfare. ...
A Living Planet
... - atmosphere layer of gases surrounding the earth; protects earth - lithosphere solid rock portion of earth; includes crust and upper mantle - hydrosphere bodies of water in the atmosphere as well as rain and precipitation - biosphere where plants and animals live ...
... - atmosphere layer of gases surrounding the earth; protects earth - lithosphere solid rock portion of earth; includes crust and upper mantle - hydrosphere bodies of water in the atmosphere as well as rain and precipitation - biosphere where plants and animals live ...
Soil - Cobb Learning
... They are also produced when people burn fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. Acid Precipitation The high level of acidity in acid precipitation can cause very rapid weathering of rock. ...
... They are also produced when people burn fossil fuels, such as coal and oil. Acid Precipitation The high level of acidity in acid precipitation can cause very rapid weathering of rock. ...
EPSC-201_2015final-E..
... Explain the four factors that determine whether folds or faults form during deformation. Four factors determine whether a rock will deform plastically or break: the confining pressure, temperature, time (strain-rate) and the rock composition. The higher the temperature, the weaker and less brittle a ...
... Explain the four factors that determine whether folds or faults form during deformation. Four factors determine whether a rock will deform plastically or break: the confining pressure, temperature, time (strain-rate) and the rock composition. The higher the temperature, the weaker and less brittle a ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.