educational resources overview - Saskatchewan Mining Association
... EC7.2 Identify locations and processes used to extract Earth’s geological resources and examine the impacts of those locations and processes on society and the environment. a) Identify questions to investigate arising from practical problems and issues related to the study of Earth’s geological reso ...
... EC7.2 Identify locations and processes used to extract Earth’s geological resources and examine the impacts of those locations and processes on society and the environment. a) Identify questions to investigate arising from practical problems and issues related to the study of Earth’s geological reso ...
Interactive Animation: Relative Geologic Dating
... GeoTutor: Constructing an Order of Sequence of Geologic Events Geologic Time Scale Geologists have divided the whole of history into units of increasing magnitude. This is called the geologic time scale. The entire time scale was originally based on relative dating, since radiometric dating was no ...
... GeoTutor: Constructing an Order of Sequence of Geologic Events Geologic Time Scale Geologists have divided the whole of history into units of increasing magnitude. This is called the geologic time scale. The entire time scale was originally based on relative dating, since radiometric dating was no ...
THE ORIGIN AND GROWTH OF CONTINENTS 1 Geophysical
... geological processes on the ocean floor will give rise to a non-uniform mixture of basic volcanic material and pelagic sediment. Poss’ibly this layer is primitive crust. The material in layer 2 is much less uniform, and there are wide variations in the seismic velocities observed. There is some .dou ...
... geological processes on the ocean floor will give rise to a non-uniform mixture of basic volcanic material and pelagic sediment. Poss’ibly this layer is primitive crust. The material in layer 2 is much less uniform, and there are wide variations in the seismic velocities observed. There is some .dou ...
5.1.4 The felsic unit
... There are three possible causes to form the linear arrays; constant sum effect, hydraulic sorting, and mixing of two end-members. The constant sum effect is rejected because elemental ratios, such as Ti/Mg and Al/Mg, also show linear arrays (Fig. 5a). Hydraulic sorting from a single source was sugge ...
... There are three possible causes to form the linear arrays; constant sum effect, hydraulic sorting, and mixing of two end-members. The constant sum effect is rejected because elemental ratios, such as Ti/Mg and Al/Mg, also show linear arrays (Fig. 5a). Hydraulic sorting from a single source was sugge ...
4 Igneous Rocks - North Coast Distance Education
... whereas silicic magmas are viscous.This is because silicic magmas have lower temperatures and greater amounts of SiO2. The viscosity of a magma is influenced by its SiO2 content because silica tetrahedra bond or link together even before crystallization occurs, and the linkages offer resistance to f ...
... whereas silicic magmas are viscous.This is because silicic magmas have lower temperatures and greater amounts of SiO2. The viscosity of a magma is influenced by its SiO2 content because silica tetrahedra bond or link together even before crystallization occurs, and the linkages offer resistance to f ...
a non-technical guide to the geology of the burren region, co
... “depressurisation” would have allowed the underlying rocks to relax and expand, forming microscopic fractures in the rocks. Such fractures are extremely abundant in the limestones of the Burren region and are visible today as fissures; unlike the fissures formed by the N-S veins, however, these youn ...
... “depressurisation” would have allowed the underlying rocks to relax and expand, forming microscopic fractures in the rocks. Such fractures are extremely abundant in the limestones of the Burren region and are visible today as fissures; unlike the fissures formed by the N-S veins, however, these youn ...
Review of the Lithium Isotope System as a Geochemical Tracer
... The Li isotopic composition of river water is not highly sensitive to that of the bedrock, in contrast to radiogenic isotopic ratios used to monitor chemical weathering (Huh et al., 1998). There is thus promise in using the evolution of the Li isotope ratio of seawater to assess past changes in the ...
... The Li isotopic composition of river water is not highly sensitive to that of the bedrock, in contrast to radiogenic isotopic ratios used to monitor chemical weathering (Huh et al., 1998). There is thus promise in using the evolution of the Li isotope ratio of seawater to assess past changes in the ...
Ch06 Sedimentary Rocks
... mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: Similar materials that are more solidified. Then: Fragments of solid rock. Cemented sand and silt. Pottery-like clay. Cemented shells. Crystalline masses of salt. ...
... mud and loose sand, silt, pebbles, and shells. Then: Similar materials that are more solidified. Then: Fragments of solid rock. Cemented sand and silt. Pottery-like clay. Cemented shells. Crystalline masses of salt. ...
millenderdale
... of 487 ± 8 Ma obtained from the flaser gabbro by Bluck et al. (1980) which is within error of most other indicators of the age of formation of the Ballantrae Complex. Geochemical data presented by Jelínek et al. (1980) for the gabbro and beerbachite dykes was interpreted in terms of a genetically re ...
... of 487 ± 8 Ma obtained from the flaser gabbro by Bluck et al. (1980) which is within error of most other indicators of the age of formation of the Ballantrae Complex. Geochemical data presented by Jelínek et al. (1980) for the gabbro and beerbachite dykes was interpreted in terms of a genetically re ...
PRESIDENTIAL ADDRESS Patterns of mineral
... Results for the contact aureole (Fig. 1) are representative of the minerals’ distribution in all three terrains. Metamorphism occurred with the emplacement of the Devonian Onawa granodiorite at P ª 3000 bars and T up to ª650 °C (Symmes and Ferry 1995). At the lowest grades of metamorphism, all pelit ...
... Results for the contact aureole (Fig. 1) are representative of the minerals’ distribution in all three terrains. Metamorphism occurred with the emplacement of the Devonian Onawa granodiorite at P ª 3000 bars and T up to ª650 °C (Symmes and Ferry 1995). At the lowest grades of metamorphism, all pelit ...
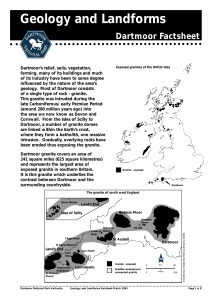
Geology and Landforms Factsheet - the Dartmoor National Park
... Weathering eventually causes the disintegration of the granite down to individual crystal level. The resultant gravel is called growan. During periglacial times it became very mobile - moving down slopes and accumulating on flat ground as head deposits. It is the parent material for a number of Dart ...
... Weathering eventually causes the disintegration of the granite down to individual crystal level. The resultant gravel is called growan. During periglacial times it became very mobile - moving down slopes and accumulating on flat ground as head deposits. It is the parent material for a number of Dart ...
Sedimentary Phosphate Deposits Mineral Deposit Profile F07
... phosphorites form in or laterally adjacent to organic-rich sediments beneath regions where upwelling, nutrient-rich, cold waters interact with a warm sunlit surface seawater layer, creating favourable conditions for intense algal bloom. Algae die, or are eaten by other life forms, then accumulate on ...
... phosphorites form in or laterally adjacent to organic-rich sediments beneath regions where upwelling, nutrient-rich, cold waters interact with a warm sunlit surface seawater layer, creating favourable conditions for intense algal bloom. Algae die, or are eaten by other life forms, then accumulate on ...
The chemical compositions of basalts and Dana tuff breccia with
... Light olive-grey sandstones are also common. Biotite increases markedly in some beds, and lamina and the rocks then become much darker, more foliated, and fissile. Quartz is the dominant mineral in all these rocks; feldspar commonly forms about 30 per cent; biotite and hornblende commonly form 10 to ...
... Light olive-grey sandstones are also common. Biotite increases markedly in some beds, and lamina and the rocks then become much darker, more foliated, and fissile. Quartz is the dominant mineral in all these rocks; feldspar commonly forms about 30 per cent; biotite and hornblende commonly form 10 to ...
Chemical Properties of Soil and Ground Waters
... Subsurface waters vary according to their location in the Earth's crust, the depth and conditions of occurrence, and their chemical composition. They impregnate the soil, fill the pores of loose sedimentary rocks, and fractures in the upper crystalline basement. Subsurface waters are conventionally ...
... Subsurface waters vary according to their location in the Earth's crust, the depth and conditions of occurrence, and their chemical composition. They impregnate the soil, fill the pores of loose sedimentary rocks, and fractures in the upper crystalline basement. Subsurface waters are conventionally ...
CHAPTER 4 PRE-TERTIARY GEOLOGY OF NEVADA
... and most contacts within outcrops are taken from it. In some places, new contacts have been drawn, based on more recent studies. Methods This map and accompanying text is not a stratigraphic or sedimentologic summary, nor is it a geologic history of Nevada. The map portrays the known and inferred su ...
... and most contacts within outcrops are taken from it. In some places, new contacts have been drawn, based on more recent studies. Methods This map and accompanying text is not a stratigraphic or sedimentologic summary, nor is it a geologic history of Nevada. The map portrays the known and inferred su ...
Pacific Beach San Diego
... During the last 150 million years, Southern California has undergone vast geological land sculpturing. Volcanoes, earthquakes, landslides, weathering, and tectonic movement have all contributed to the present day face of Southern California. This paper will visit a few of the geologic timestamps tha ...
... During the last 150 million years, Southern California has undergone vast geological land sculpturing. Volcanoes, earthquakes, landslides, weathering, and tectonic movement have all contributed to the present day face of Southern California. This paper will visit a few of the geologic timestamps tha ...
1 I-68/I-70: A WINDOW TO THE APPALACHIANS by Dr. John J
... are nearly all Cambrian and Ordovician limestones. Because of the water soluble nature of calcium carbonate, the rocks have been dissolved down to the mean level of the streams, resulting in a broad, flat valley. The few low ridges observed within the valley are in large part due to the occasional n ...
... are nearly all Cambrian and Ordovician limestones. Because of the water soluble nature of calcium carbonate, the rocks have been dissolved down to the mean level of the streams, resulting in a broad, flat valley. The few low ridges observed within the valley are in large part due to the occasional n ...
Diversity in Nature
... Geological diversity has had a big impact on the economic basis and settlement patterns of the Nordic countries. Stone age hunters used flint and medieval people built stone houses in many places, and in modern times mineral and ore deposits have provided the economic basis for some settlements. Tod ...
... Geological diversity has had a big impact on the economic basis and settlement patterns of the Nordic countries. Stone age hunters used flint and medieval people built stone houses in many places, and in modern times mineral and ore deposits have provided the economic basis for some settlements. Tod ...
Terra Nova 2012 Jagoutz
... the occurrences of Fe-oxides or Feoxyhydroxides (FeO(OH)) indicate more oxidizing conditions during alteration. Clay mineralogy varies consistently with the presence of pyrite or Fe-oxides: During more oxidizing alteration conditions celadonite (a K-Fe3+rich mica) forms, in addition to saponite and ...
... the occurrences of Fe-oxides or Feoxyhydroxides (FeO(OH)) indicate more oxidizing conditions during alteration. Clay mineralogy varies consistently with the presence of pyrite or Fe-oxides: During more oxidizing alteration conditions celadonite (a K-Fe3+rich mica) forms, in addition to saponite and ...
Guide to Epithermal Gold and Silver in NL
... systems can be separated based on the presence of several key ore and alteration minerals related to the formation of the mineralization (See tables below). LS is also called the adularia-sericite system and HS is also called the alunitekaolinite or the acid sulphate system. (Note: The following r ...
... systems can be separated based on the presence of several key ore and alteration minerals related to the formation of the mineralization (See tables below). LS is also called the adularia-sericite system and HS is also called the alunitekaolinite or the acid sulphate system. (Note: The following r ...
guidelines on the description and classification of rocks
... Tuen Mun Valley between Castle Peak Bay in the south, and Ha Tsuen in the north. Location: Type area is located on the low hills which overlook northwestern Tuen Mun where the best exposures of fresh rock are found. Eastern outcrops are concealed by superficial deposits. Description: Consists mostly ...
... Tuen Mun Valley between Castle Peak Bay in the south, and Ha Tsuen in the north. Location: Type area is located on the low hills which overlook northwestern Tuen Mun where the best exposures of fresh rock are found. Eastern outcrops are concealed by superficial deposits. Description: Consists mostly ...
Cr – Chromium
... organic matter. Its adsorption by clay is also highly dependent on pH; Cr6+ adsorption decreases with increasing pH, and Cr3+ adsorption increases with increasing pH. The dominant effect of organic matter is the stimulation of the reduction of Cr6+ to Cr3+, the rate of which increases with soil acid ...
... organic matter. Its adsorption by clay is also highly dependent on pH; Cr6+ adsorption decreases with increasing pH, and Cr3+ adsorption increases with increasing pH. The dominant effect of organic matter is the stimulation of the reduction of Cr6+ to Cr3+, the rate of which increases with soil acid ...
PHSC 3004 Test 3 Take Home Name__________________
... 25. ______________.is the downslope movement of surface materials as a result of gravity and the agents that cause such movement. 26. A(n) ______________.is defined by geologists as any flow of water occurring between well-defined banks. 27. At the end and along the sides of a glacier, the sediment ...
... 25. ______________.is the downslope movement of surface materials as a result of gravity and the agents that cause such movement. 26. A(n) ______________.is defined by geologists as any flow of water occurring between well-defined banks. 27. At the end and along the sides of a glacier, the sediment ...
The stratigraphic succession of Ghana
... weakness near the borders of depositional basins, so that some greenstones are older than the metasediments, others more or less of the same age, and the Tarkwaian rocks are simply lateral facies variants within Birimian metasediments. Outcrops and communications are generally poor throughout much o ...
... weakness near the borders of depositional basins, so that some greenstones are older than the metasediments, others more or less of the same age, and the Tarkwaian rocks are simply lateral facies variants within Birimian metasediments. Outcrops and communications are generally poor throughout much o ...
Metamorphic evolution of high-pressure, low
... In general, these units are composed of 40% glaucophane, 5-20% garnet, 10-15% epidote, 10-15% chlorite, 10% rutile, 5-10% phengite, 5% titanite, 5% apatite and 5% albite. Although not apparent in all grains, 20% of the glaucophane crystals display color variations in the individual grains, indicatin ...
... In general, these units are composed of 40% glaucophane, 5-20% garnet, 10-15% epidote, 10-15% chlorite, 10% rutile, 5-10% phengite, 5% titanite, 5% apatite and 5% albite. Although not apparent in all grains, 20% of the glaucophane crystals display color variations in the individual grains, indicatin ...
Weathering

Weathering is the breaking down of rocks, soil and minerals as well as artificial materials through contact with the Earth's atmosphere, biota and waters. Weathering occurs in situ, roughly translated to: ""with no movement"" , and thus should not be confused with erosion, which involves the movement of rocks and minerals by agents such as water, ice, snow, wind, waves and gravity and then being transported and deposited in other locations.Two important classifications of weathering processes exist – physical and chemical weathering; each sometimes involves a biological component. Mechanical or physical weathering involves the breakdown of rocks and soils through direct contact with atmospheric conditions, such as heat, water, ice and pressure. The second classification, chemical weathering, involves the direct effect of atmospheric chemicals or biologically produced chemicals also known as biological weathering in the breakdown of rocks, soils and minerals. While physical weathering is accentuated in very cold or very dry environments, chemical reactions are most intense where the climate is wet and hot. However, both types of weathering occur together, and each tends to accelerate the other. For example, physical abrasion (rubbing together) decreases the size of particles and therefore increases their surface area, making them more susceptible to rapid chemical reactions. The various agents act in concert to convert primary minerals (feldspars and micas) to secondary minerals (clays and carbonates) and release plant nutrient elements in soluble forms.The materials left over after the rock breaks down combined with organic material creates soil. The mineral content of the soil is determined by the parent material, thus a soil derived from a single rock type can often be deficient in one or more minerals for good fertility, while a soil weathered from a mix of rock types (as in glacial, aeolian or alluvial sediments) often makes more fertile soil. In addition, many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.