Precambrian Crystalline Basement rocks of Eritrea
... much of the primary fabric has survived deformation; metamorphism is mostly of low grade. c) A number of ophiolite complexes are associated with volcanic rocks and sediments; some are preserved more or less complete, others highly dismembered. d) The greenschists have been invaded by abundant granit ...
... much of the primary fabric has survived deformation; metamorphism is mostly of low grade. c) A number of ophiolite complexes are associated with volcanic rocks and sediments; some are preserved more or less complete, others highly dismembered. d) The greenschists have been invaded by abundant granit ...
INFORME GEOBRASIL (www.geobrasil.net)
... organisms – blue-green bacteria – are a lot younger; around 2 Ga. Structures in sedimentary rocks back to 3.5 Ga, such as stromatolites, which do look a lot like products of living cyanobacteria and may have a biogenic origin, do not contain cellular structures that would constitute proof. So a repo ...
... organisms – blue-green bacteria – are a lot younger; around 2 Ga. Structures in sedimentary rocks back to 3.5 Ga, such as stromatolites, which do look a lot like products of living cyanobacteria and may have a biogenic origin, do not contain cellular structures that would constitute proof. So a repo ...
Geology of Caves and Rockshelters
... along a cliff. The resistant rocks form the roof of the shelter, while the less resistant rocks are removed, permitting continuous development of the shelter. As the shelter grows back into the cliff face, the roof becomes unstable; periodically, parts of the roof collapse. Thus, the shelter never c ...
... along a cliff. The resistant rocks form the roof of the shelter, while the less resistant rocks are removed, permitting continuous development of the shelter. As the shelter grows back into the cliff face, the roof becomes unstable; periodically, parts of the roof collapse. Thus, the shelter never c ...
Sinkholes and Acid Rain
... Some types of rock, especially limestone, can be dissolved by weakly acidic water. Carbon dioxide in the air and soil reacts with water to form a weak carbonic acid. Slightly acidic water can slowly dissolve limestone, especially along fractures or other weak areas. As fractures enlarge, they can be ...
... Some types of rock, especially limestone, can be dissolved by weakly acidic water. Carbon dioxide in the air and soil reacts with water to form a weak carbonic acid. Slightly acidic water can slowly dissolve limestone, especially along fractures or other weak areas. As fractures enlarge, they can be ...
Scanned PDF - Hydrogeologists Without Borders
... Flu vial materials occur in nearly all regions. In many areas aquifers of fluvial origin are important sources of water supply. Figure 4.2 illustrates the morphology and variations in deposits formed by braided rivers and by meandering rivers. Because of the shifting position of river channels and t ...
... Flu vial materials occur in nearly all regions. In many areas aquifers of fluvial origin are important sources of water supply. Figure 4.2 illustrates the morphology and variations in deposits formed by braided rivers and by meandering rivers. Because of the shifting position of river channels and t ...
Eras of Time Reading File
... Woods are parts of old Lake Agassiz. The land that was once lake bottom is now good, rich farmland. The Red River Valley is part of this rich farmland. The area along the Red River is an important place for growing crops such as potatoes, sugar beets, and grains. After a dirt dam broke at the south ...
... Woods are parts of old Lake Agassiz. The land that was once lake bottom is now good, rich farmland. The Red River Valley is part of this rich farmland. The area along the Red River is an important place for growing crops such as potatoes, sugar beets, and grains. After a dirt dam broke at the south ...
Unit II - SP College
... Organically, Sedimentary rocks are further sub-divided into many types on the basis of their chemical compositions: 1. Calcareous Rocks; these rocks contain large amounts of carbonates of Calcium and Magnesium and are derived from the skeletons and remains of those animals and plants which contain ...
... Organically, Sedimentary rocks are further sub-divided into many types on the basis of their chemical compositions: 1. Calcareous Rocks; these rocks contain large amounts of carbonates of Calcium and Magnesium and are derived from the skeletons and remains of those animals and plants which contain ...
Advertising - Science Outreach
... delta setting, and their composition indicates a different source when compared to those rocks attributed to the first phase of the Rangitata Orogeny. At the end of the Cretaceous, ‘New Zealand’ began to separate from the remains of Gondwanaland leading to the formation the proto-Tasman Sea. Between ...
... delta setting, and their composition indicates a different source when compared to those rocks attributed to the first phase of the Rangitata Orogeny. At the end of the Cretaceous, ‘New Zealand’ began to separate from the remains of Gondwanaland leading to the formation the proto-Tasman Sea. Between ...
Castle Hill Field Guide (Teacher version)
... delta setting, and their composition indicates a different source when compared to those rocks attributed to the first phase of the Rangitata Orogeny. At the end of the Cretaceous, ‘New Zealand’ began to separate from the remains of Gondwanaland leading to the formation the proto-Tasman Sea. Between ...
... delta setting, and their composition indicates a different source when compared to those rocks attributed to the first phase of the Rangitata Orogeny. At the end of the Cretaceous, ‘New Zealand’ began to separate from the remains of Gondwanaland leading to the formation the proto-Tasman Sea. Between ...
Alkaline rocks in the Kuboos-Bremen Igneous Province, southern
... alkali-granite. Quartz-feldspar porphyries also occur, found in topographically higher parts of the granite body where they are virtually devoid of mafic minerals and associated with hypidiomorphic granular varieties that are similarly leucocratic. Additionally, in the northeast corner of the body a ...
... alkali-granite. Quartz-feldspar porphyries also occur, found in topographically higher parts of the granite body where they are virtually devoid of mafic minerals and associated with hypidiomorphic granular varieties that are similarly leucocratic. Additionally, in the northeast corner of the body a ...
Relative and Absolute Dating 2013
... This may not seem very accurate, but compared to the 4,500 million years the earth has been around it gives us a lot more information than we had before ...
... This may not seem very accurate, but compared to the 4,500 million years the earth has been around it gives us a lot more information than we had before ...
Fossils - Blountstown Middle School
... nonconformity, occurs when metamorphic or igneous rocks are uplifted and eroded. • Sedimentary rocks are then deposited on top of this erosion surface. ...
... nonconformity, occurs when metamorphic or igneous rocks are uplifted and eroded. • Sedimentary rocks are then deposited on top of this erosion surface. ...
Geology - Bradford Woods
... Sedimentary rocks are formed over time as layers of pebbles, sand and silt are deposited in an area and compressed. Often sedimentary rocks are formed under water. Metamorphic rocks are formed when heat from magma and/or pressure from plate movement change one kind of rock into another. Metamorp ...
... Sedimentary rocks are formed over time as layers of pebbles, sand and silt are deposited in an area and compressed. Often sedimentary rocks are formed under water. Metamorphic rocks are formed when heat from magma and/or pressure from plate movement change one kind of rock into another. Metamorp ...
Planet Earth Notes
... The place deep in the crust where the earthquake begins is called the focus of the earthquake. The primary and secondary waves come from the focus of the earthquake. The surface location directly above the focus is called the epicentre. Surface waves travel out from the epicentre. ...
... The place deep in the crust where the earthquake begins is called the focus of the earthquake. The primary and secondary waves come from the focus of the earthquake. The surface location directly above the focus is called the epicentre. Surface waves travel out from the epicentre. ...
Fossils
... 2. Presence of Hard Body Parts Fossils of organisms that contained hard parts are abundant in the fossil record, but only rare traces of soft tissue organisms are seen as fossils. Soft-bodied organisms could get buried by volcanic ash. 3. Low Oxygen Environment In a low oxygen environment, there is ...
... 2. Presence of Hard Body Parts Fossils of organisms that contained hard parts are abundant in the fossil record, but only rare traces of soft tissue organisms are seen as fossils. Soft-bodied organisms could get buried by volcanic ash. 3. Low Oxygen Environment In a low oxygen environment, there is ...
EarthComm_c3s7
... geologic events can occur. Many kinds of geologic processes can shape the geologic history of an area. You have read about many of these in previous sections. Here are some important ones: deposition, erosion, folding, faulting, uplift, subsidence, igneous intrusion, volcanism, metamorphism, changes ...
... geologic events can occur. Many kinds of geologic processes can shape the geologic history of an area. You have read about many of these in previous sections. Here are some important ones: deposition, erosion, folding, faulting, uplift, subsidence, igneous intrusion, volcanism, metamorphism, changes ...
Geologic Time - Tulane University
... the relative ages of rocks. Once these age relations were worked out, another principle fell into place - the principle of fossil succession. We discuss the 7 principles of stratigraphy first and then see how these apply to fossils. Principle of Uniformitarianism The principle of Uniformitarianism w ...
... the relative ages of rocks. Once these age relations were worked out, another principle fell into place - the principle of fossil succession. We discuss the 7 principles of stratigraphy first and then see how these apply to fossils. Principle of Uniformitarianism The principle of Uniformitarianism w ...
The Rock Cycle
... dense, dark-colored rocks. They form from magma that is rich in iron and magnesium and poor in silica, which is the compound SiO2. The presence of iron and magnesium in minerals in basalt gives basalt its dark color. Basaltic lava is fluid and flows freely from volcanoes in Hawaii, such as Kilauea. ...
... dense, dark-colored rocks. They form from magma that is rich in iron and magnesium and poor in silica, which is the compound SiO2. The presence of iron and magnesium in minerals in basalt gives basalt its dark color. Basaltic lava is fluid and flows freely from volcanoes in Hawaii, such as Kilauea. ...
Mineral Environments of Formation
... locate mineral resources. You can also use this to differentiate between similar appearing minerals ...
... locate mineral resources. You can also use this to differentiate between similar appearing minerals ...
Proterozoic Rocks
... Crystallization Conditions • Anhydrous mafic assemblage suggests low water pressure Hbld + Biot + Qtz = Hyper + K-spar + Plag + H20 ...
... Crystallization Conditions • Anhydrous mafic assemblage suggests low water pressure Hbld + Biot + Qtz = Hyper + K-spar + Plag + H20 ...
10-13 Sand
... • The oldest rock layer in the Grand Canyon, found far under the Muav Limestone, is at least 1.7 billion years old. ...
... • The oldest rock layer in the Grand Canyon, found far under the Muav Limestone, is at least 1.7 billion years old. ...
Minerals
... • Covalent bonding holds people and other organisms together • Metallic bonding holds civilization together • Hydrogen bonding gives water its heatretaining and solvent properties 2. Atoms bond by sharing electrons ...
... • Covalent bonding holds people and other organisms together • Metallic bonding holds civilization together • Hydrogen bonding gives water its heatretaining and solvent properties 2. Atoms bond by sharing electrons ...
Weathering and Erosion
... Wind Erosion • As the wind blows it picks up small particles of sand/sediment and blasts large rocks with the abrasive particles, cutting and shaping the rock. • The intensity of wind erosion is determined by: ...
... Wind Erosion • As the wind blows it picks up small particles of sand/sediment and blasts large rocks with the abrasive particles, cutting and shaping the rock. • The intensity of wind erosion is determined by: ...
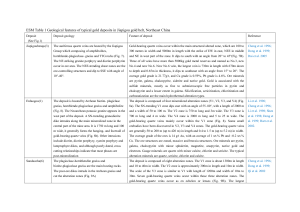
126_2013_475_MOESM1_ESM - Springer Static Content Server
... northwest (280~305) at depth with an angle from 60 to 80 (Fig. 9B). The gold grade ranges from 3 g/t to 88.5 g/t with an average of 18.98 g/t. The ore structures are zoned, disseminated, massive and breccia structures. Ore minerals are mainly pyrite with minor galena, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, p ...
... northwest (280~305) at depth with an angle from 60 to 80 (Fig. 9B). The gold grade ranges from 3 g/t to 88.5 g/t with an average of 18.98 g/t. The ore structures are zoned, disseminated, massive and breccia structures. Ore minerals are mainly pyrite with minor galena, chalcopyrite, sphalerite, p ...
GEOL3025, Section 096 Lecture #7 30 August 2007
... are related to the variations in the degree of metamorphism Changes in mineralogy occur from regions of low-grade metamorphism to regions of highgrade metamorphism ...
... are related to the variations in the degree of metamorphism Changes in mineralogy occur from regions of low-grade metamorphism to regions of highgrade metamorphism ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.