Rock Cycle
... By rolling the die, determine what kind of rock you will start out being. A roll of a 1 or 2 = igneous A roll of a 3 or 4 = sedimentary A roll of a 5 or 6 = metamorphic Record your starting rock in the Data table. Use a colored pencil to circle this type of rock on your Rock Cycle diagram. ...
... By rolling the die, determine what kind of rock you will start out being. A roll of a 1 or 2 = igneous A roll of a 3 or 4 = sedimentary A roll of a 5 or 6 = metamorphic Record your starting rock in the Data table. Use a colored pencil to circle this type of rock on your Rock Cycle diagram. ...
03 Structural Control mod 4b
... • Form in jointed igneous rocks or horizontal sedimentary beds with well-developed jointing or intersecting faults. ...
... • Form in jointed igneous rocks or horizontal sedimentary beds with well-developed jointing or intersecting faults. ...
Petroleum Geology www.AssignmentPoint.com Petroleum geology
... studies of the local stratigraphy, palaeogeography and sedimentology to determine the likelihood of organic-rich sediments having been deposited in the past. ...
... studies of the local stratigraphy, palaeogeography and sedimentology to determine the likelihood of organic-rich sediments having been deposited in the past. ...
paleontological and stratigraphical studies on
... Siwa area for being a virgin, unexplored and unleased area compared with other parts of Egypt. The GPC-drilling activities in the study area started by the parametric Siwa-1 well in July 1969. This well was proceeded by all other studied wells: El Basur-1, Kohla-1&2, Gibb Afia-2, Zeitun-1, Bahrein1& ...
... Siwa area for being a virgin, unexplored and unleased area compared with other parts of Egypt. The GPC-drilling activities in the study area started by the parametric Siwa-1 well in July 1969. This well was proceeded by all other studied wells: El Basur-1, Kohla-1&2, Gibb Afia-2, Zeitun-1, Bahrein1& ...
Dating the Finer Aspect of Petroleum Systems
... Organic-rich sedimentary units are the typical source for hydrocarbons in many of the world’s sedimentary basins. By establishing the absolute age of source rocks it is possible to provide important chronologic constraints for the evolution of a petroleum system and thus permit the calibration of bi ...
... Organic-rich sedimentary units are the typical source for hydrocarbons in many of the world’s sedimentary basins. By establishing the absolute age of source rocks it is possible to provide important chronologic constraints for the evolution of a petroleum system and thus permit the calibration of bi ...
Archean
... • Seawater seeps into the crust near spreading ridges, becomes heated, rises and discharges • Black smokers – Discharge water saturated with dissolved minerals – Life may have formed near these in the past ...
... • Seawater seeps into the crust near spreading ridges, becomes heated, rises and discharges • Black smokers – Discharge water saturated with dissolved minerals – Life may have formed near these in the past ...
Mineral Resources
... resources. Renewable means it can be replaced in one human lifetime (like a tree), nonrenewable means it cannot be replaced in a lifetime (oil, coal, gold). ...
... resources. Renewable means it can be replaced in one human lifetime (like a tree), nonrenewable means it cannot be replaced in a lifetime (oil, coal, gold). ...
Earth Materials
... streak. When you write on a chalkboard, you observe the streak of the rock chalk. The streak of a mineral is usually quite consistent; thus streak color is much more useful than mineral color. For example, the iron ore mineral, hematite, can be various shades of silver-gray to red in color, but the ...
... streak. When you write on a chalkboard, you observe the streak of the rock chalk. The streak of a mineral is usually quite consistent; thus streak color is much more useful than mineral color. For example, the iron ore mineral, hematite, can be various shades of silver-gray to red in color, but the ...
PEN CAER
... The top of the chiefly basaltic Strumble Head Volcanic Formation and the base of the overlying chiefly silicic Goodwick Volcanic Formation is marked by a complex interdigitation of lavas and high-level intrusions (Figure 6.12). The various facies of a thick rhyolite flow or dome at the base of the G ...
... The top of the chiefly basaltic Strumble Head Volcanic Formation and the base of the overlying chiefly silicic Goodwick Volcanic Formation is marked by a complex interdigitation of lavas and high-level intrusions (Figure 6.12). The various facies of a thick rhyolite flow or dome at the base of the G ...
DOWNLOAD A5 40 pages
... Minerals grow into crystals as they freeze, or as they precipitate from liquids. If they have space, these crystals may grow freely into the fine shapes seen in reference books, which are rare here (Euhedral); but most often their shape is dictated by the minerals around them (Anhedral). Some minera ...
... Minerals grow into crystals as they freeze, or as they precipitate from liquids. If they have space, these crystals may grow freely into the fine shapes seen in reference books, which are rare here (Euhedral); but most often their shape is dictated by the minerals around them (Anhedral). Some minera ...
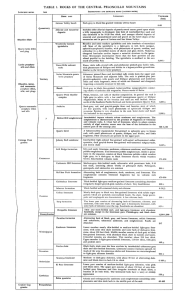
TABLE I. ROCKS OF THE CENTRAL PELON CILLO MOUNTAINS
... conglomerate is characterized by the presence of fragments of limestone and volcanic rocks. A I -foot bed of limestone, which in places consists entirely of algal remains, occurs near the base of the formation in the eastern part of the outcrop area ...
... conglomerate is characterized by the presence of fragments of limestone and volcanic rocks. A I -foot bed of limestone, which in places consists entirely of algal remains, occurs near the base of the formation in the eastern part of the outcrop area ...
cornell rock parks - Cornell`s Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
... The Cornell Rock Parks, now four in number, beautify and enrich the University’s campus and stand as a memorial to the generosity and foresight of the Bender family. The first two are located on the Engineering Quadrangle: in the early 1970s, Rock Park East was installed in front of Kimball and Thur ...
... The Cornell Rock Parks, now four in number, beautify and enrich the University’s campus and stand as a memorial to the generosity and foresight of the Bender family. The first two are located on the Engineering Quadrangle: in the early 1970s, Rock Park East was installed in front of Kimball and Thur ...
Answer Key
... removed from its source. Deposition is the process by which sediment moved by erosion is laid down. Uplift is the process by which rock within the Earth moves to Earth’s surface. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Fine grains in an igneous rock indicate that the rock cooled quickly, which means it was ...
... removed from its source. Deposition is the process by which sediment moved by erosion is laid down. Uplift is the process by which rock within the Earth moves to Earth’s surface. Answers may vary. Sample answer: Fine grains in an igneous rock indicate that the rock cooled quickly, which means it was ...
Rock cycle
... plate tectonics, the rock cycle changed from endlessly repetitive to a gradually evolving process. The Wilson cycle (a plate tectonics based rock cycle) was developed by J. Tuzo Wilson during the 1950s and 1960s. The rock cycle is a general model that describes how various geological processes creat ...
... plate tectonics, the rock cycle changed from endlessly repetitive to a gradually evolving process. The Wilson cycle (a plate tectonics based rock cycle) was developed by J. Tuzo Wilson during the 1950s and 1960s. The rock cycle is a general model that describes how various geological processes creat ...
Oldest rocks, earliest life, heaviest impacts, and the Hadean
... dates as old as 3.82 Ga, which is regarded as their true age of emplacement (Nutman et al., 1999; Crowley, 2003). These orthogneisses are rich in man-to-mountain sized enclaves which include mafic/ultramafic metamorphosed magmatic rocks, varied amphibolitic gneisses, and chemical sediments, such as ba ...
... dates as old as 3.82 Ga, which is regarded as their true age of emplacement (Nutman et al., 1999; Crowley, 2003). These orthogneisses are rich in man-to-mountain sized enclaves which include mafic/ultramafic metamorphosed magmatic rocks, varied amphibolitic gneisses, and chemical sediments, such as ba ...
PETLAB3-14
... along which volatile bubbles have concentrated during lamellar flow. These volatiles aided the crystallisation of the magma in these layers, which tend to be lighter coloured than the darker layers that are depleted in such bubbles and quenched to glass. This banding is frequently preserved even whe ...
... along which volatile bubbles have concentrated during lamellar flow. These volatiles aided the crystallisation of the magma in these layers, which tend to be lighter coloured than the darker layers that are depleted in such bubbles and quenched to glass. This banding is frequently preserved even whe ...
IM_chapter7 Metamorphic Rocks
... A metamorphic facies is a group of metamorphic rocks whose minerals all formed under a particular range of temperatures and pressures. Each facies is named after its most characteristic rock or mineral. ...
... A metamorphic facies is a group of metamorphic rocks whose minerals all formed under a particular range of temperatures and pressures. Each facies is named after its most characteristic rock or mineral. ...
Sulfur in weathering and sedimentary processes
... Iodine in magmatic and sedimentary processes Iodine content appears to be uniform and less than 1 mg/kg in common rock-forming minerals. Sedimentary rocks generally contain more iodine than igneous rocks, and over a broader range of concentrations. Two types of deposit are particularly rich in iodi ...
... Iodine in magmatic and sedimentary processes Iodine content appears to be uniform and less than 1 mg/kg in common rock-forming minerals. Sedimentary rocks generally contain more iodine than igneous rocks, and over a broader range of concentrations. Two types of deposit are particularly rich in iodi ...
What is the rock cycle?
... • Igneous rock forms from molten rock that cools. • As molten rock cools, crystals form. The longer the cooling takes, the more time the crystals have to grow. • Igneous rocks that form when magma cools beneath Earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous rock. • Igneous rocks that form when lava co ...
... • Igneous rock forms from molten rock that cools. • As molten rock cools, crystals form. The longer the cooling takes, the more time the crystals have to grow. • Igneous rocks that form when magma cools beneath Earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous rock. • Igneous rocks that form when lava co ...
Review of the Earth Science Curriculum FROM McGUIRE Equations
... *The most common igneous rocks are classified using crystal size and color. *Most sedimentary rocks are composed primarily of weathered remains of other rocks. *Sedimentary rocks usually form by the compression and cementing of sediment particles or grains. *Sedimentary rocks are common at the surf ...
... *The most common igneous rocks are classified using crystal size and color. *Most sedimentary rocks are composed primarily of weathered remains of other rocks. *Sedimentary rocks usually form by the compression and cementing of sediment particles or grains. *Sedimentary rocks are common at the surf ...
Resources and ore
... resources. Renewable means it can be replaced in one human lifetime (like a tree), nonrenewable means it cannot be replaced in a lifetime (oil, coal, gold). ...
... resources. Renewable means it can be replaced in one human lifetime (like a tree), nonrenewable means it cannot be replaced in a lifetime (oil, coal, gold). ...
Rocks and Denudation Revision Test
... 3rd Year Revision Test: Rocks and Denudation Name: _____________________ (1) Name the 3 different rock types. (5 marks) _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (2) Write in detail about the formation ...
... 3rd Year Revision Test: Rocks and Denudation Name: _____________________ (1) Name the 3 different rock types. (5 marks) _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ (2) Write in detail about the formation ...
What is happening in the rock cycle - 2010
... Over time, wind and water break down a metamorphic rock to form fine particles. Compaction and deposition compress these particles to form a new layer of rock. In time, this layer is pushed down, into the asthenosphere. Which type of rock will be formed next if the rock undergoes chemical changes bu ...
... Over time, wind and water break down a metamorphic rock to form fine particles. Compaction and deposition compress these particles to form a new layer of rock. In time, this layer is pushed down, into the asthenosphere. Which type of rock will be formed next if the rock undergoes chemical changes bu ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.