PHYSICO-GEOLOGICAL PROCESSES Landslides Landslides are
... slopes, relief, physical and mechanical characteristics of rocks and soils, the availability and regime of underground waters. Landslides appear mostly along slopes consisting of clay soils. These processes are particularly typical of areas made up of Tertiary and Quaternary sediments. The geologica ...
... slopes, relief, physical and mechanical characteristics of rocks and soils, the availability and regime of underground waters. Landslides appear mostly along slopes consisting of clay soils. These processes are particularly typical of areas made up of Tertiary and Quaternary sediments. The geologica ...
1 Weathering Critical Thinking
... metal react with? In most cases, the answer is air. The oxygen in the air can react with many metals. These reactions are a kind of chemical weathering called oxidation. Rust is a common example of oxidation. Rocks can rust if they have a lot of iron in them. Many people think that rust forms only w ...
... metal react with? In most cases, the answer is air. The oxygen in the air can react with many metals. These reactions are a kind of chemical weathering called oxidation. Rust is a common example of oxidation. Rocks can rust if they have a lot of iron in them. Many people think that rust forms only w ...
Evaluating the provenance of metasedimentary rocks of the
... event in the craton (Li et al., 2000; Kusky and Li, 2003), whereas others argued that it was an amalgamation event involved in the discrete Western and Eastern Blocks to form the North China Craton (Zhao et al., 2000, 2003, 2005, 2008, Kröner et al., 2005, 2006). Particular controversy is the issue ...
... event in the craton (Li et al., 2000; Kusky and Li, 2003), whereas others argued that it was an amalgamation event involved in the discrete Western and Eastern Blocks to form the North China Craton (Zhao et al., 2000, 2003, 2005, 2008, Kröner et al., 2005, 2006). Particular controversy is the issue ...
Recommendation of a Strategy - University of South Alabama
... Greater regional dip than the major thrusts that occur between them. ...
... Greater regional dip than the major thrusts that occur between them. ...
Geology - Regional School District 13
... inorganic, luster, mica, mineralogy, native mineral, quartz, rock-forming minerals, silica tetrahedron, silicate, streak, specific gravity, Read critically. Produce quality work. Communicate effectively. Collaborate and cooperate. ...
... inorganic, luster, mica, mineralogy, native mineral, quartz, rock-forming minerals, silica tetrahedron, silicate, streak, specific gravity, Read critically. Produce quality work. Communicate effectively. Collaborate and cooperate. ...
GRANOPHILE METAL DEPOSITS - Department of Natural Resources
... The Central Mineral Belt hosts several distinct mineralization environments in a wide range of rocks types and age that form geographically distinct belts, including: i) volcanic-hosted, stratabound mineralization (possibly syngenetic) in rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs, e.g., Michelin and Burnt Lake depos ...
... The Central Mineral Belt hosts several distinct mineralization environments in a wide range of rocks types and age that form geographically distinct belts, including: i) volcanic-hosted, stratabound mineralization (possibly syngenetic) in rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs, e.g., Michelin and Burnt Lake depos ...
Petrography and illite crystallinity of the Lesser Himalayan
... muscovite+chlorite+albite+quartz. Lithic fragments (1 mm) and quartz clasts are common in this rock (Fig. 4e). Grain size is bimodal. Foliation is defined by the parallel arrangements of fine-grained muscovite and chlorite in the matrix. The modal composition shows 60% quartz, 15% muscovite, 10% lit ...
... muscovite+chlorite+albite+quartz. Lithic fragments (1 mm) and quartz clasts are common in this rock (Fig. 4e). Grain size is bimodal. Foliation is defined by the parallel arrangements of fine-grained muscovite and chlorite in the matrix. The modal composition shows 60% quartz, 15% muscovite, 10% lit ...
The Lizard
... Gondwana advanced it produced by tectonic activity topographic highs that caused slope failure with debris flows. This in turn caused older rocks (Ordovician) to fall into the Devonian marine mudstones. With erosion these are now exposed as quartzite blocks, once sandstones, and the more extensive b ...
... Gondwana advanced it produced by tectonic activity topographic highs that caused slope failure with debris flows. This in turn caused older rocks (Ordovician) to fall into the Devonian marine mudstones. With erosion these are now exposed as quartzite blocks, once sandstones, and the more extensive b ...
Table 1. Description of Geologic Units
... of weathering, topography, type of parent rock, well depth, and degree of fracturing and jointing encountered by the well. In Maryland, well yields overall range from 0 to 200 gallons per minute (gpm); however, greater than 70 percent of the wells have a yield of 10 gpm or less, and only 2 percent h ...
... of weathering, topography, type of parent rock, well depth, and degree of fracturing and jointing encountered by the well. In Maryland, well yields overall range from 0 to 200 gallons per minute (gpm); however, greater than 70 percent of the wells have a yield of 10 gpm or less, and only 2 percent h ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Illinois State University
... 7. Forms as a result of being near an intrusion of magma 8. Found in mountain belts 9. May have been originally been a metamorphic rock 10.Form at temperatures above 200 oC 11.May underlie several adjacent states ...
... 7. Forms as a result of being near an intrusion of magma 8. Found in mountain belts 9. May have been originally been a metamorphic rock 10.Form at temperatures above 200 oC 11.May underlie several adjacent states ...
NOTISER A pillow lava locality in the Grong District, Norway EBBE
... In the course of field work during the summer of 1963, well-preserved pillow lavas were found in the Caledonian of the Grong district (Fig. 1). Due to road-work, ice-scoured outcrops north of Solberg farm had been cleared of their moraine cover. Although no detailed mapping was carried out, exposure ...
... In the course of field work during the summer of 1963, well-preserved pillow lavas were found in the Caledonian of the Grong district (Fig. 1). Due to road-work, ice-scoured outcrops north of Solberg farm had been cleared of their moraine cover. Although no detailed mapping was carried out, exposure ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... The transition of one rock into another by temperatures and/or pressures unlike those in which it formed Metamorphic rocks are produced from • Igneous rocks- Rocks formed from cooled Lava • Sedimentary rocks –Rocks formed from sediment piling on top of more sediment and forming rocks • Other metamor ...
... The transition of one rock into another by temperatures and/or pressures unlike those in which it formed Metamorphic rocks are produced from • Igneous rocks- Rocks formed from cooled Lava • Sedimentary rocks –Rocks formed from sediment piling on top of more sediment and forming rocks • Other metamor ...
seafloorpapermodel_questions1_7
... What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the mid-ocean ridges that wind throughout all Earth’s oceans. Molten rock, called magma, from inside Earth rises to the seafloor and as it rises it cools and solidifies into new rock. In some places on ...
... What scientists found was that new seafloor has continually been forming over millions of years at the mid-ocean ridges that wind throughout all Earth’s oceans. Molten rock, called magma, from inside Earth rises to the seafloor and as it rises it cools and solidifies into new rock. In some places on ...
LIFEPAC 9th Grade Science Unit 3 Worktext - HomeSchool
... crust are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks were originally molten; then they were crystallized by cooling. Sedimentary rocks were laid in place by moving water, ice, or wind. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that were under enough pressure, or heat combined with pressure, to twist the ...
... crust are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Igneous rocks were originally molten; then they were crystallized by cooling. Sedimentary rocks were laid in place by moving water, ice, or wind. Metamorphic rocks are rocks that were under enough pressure, or heat combined with pressure, to twist the ...
Metamorphic Petrology Review
... • (T-F) All minerals show the transition from brittle to ductile under very similar conditions. • What two minerals are considered characteristic of impact metamorphism? What other material is often found in impact zones? • Describe two other features that are commonly associated with impacts. • Met ...
... • (T-F) All minerals show the transition from brittle to ductile under very similar conditions. • What two minerals are considered characteristic of impact metamorphism? What other material is often found in impact zones? • Describe two other features that are commonly associated with impacts. • Met ...
Webelos den Meeting 9 - Boy Scouts of America
... Make arrangements for a field trip to a landscaping contractor, stone quarry, concrete plant, geological site, geological laboratory, rock show, or rock shop. Arrange for drivers. This is the most interesting plan, but you can still complete the achievement using other requirements noted below. Id ...
... Make arrangements for a field trip to a landscaping contractor, stone quarry, concrete plant, geological site, geological laboratory, rock show, or rock shop. Arrange for drivers. This is the most interesting plan, but you can still complete the achievement using other requirements noted below. Id ...
Answer
... 12. Rocks are produced when magma or lava cools and hardens are called _____? a. igneous rocks c. sedimentary rocks b. metamorphic rocks d. all of the above ...
... 12. Rocks are produced when magma or lava cools and hardens are called _____? a. igneous rocks c. sedimentary rocks b. metamorphic rocks d. all of the above ...
Metamorphic Petrology Review
... • (T-F) All minerals show the transition from brittle to ductile under very similar conditions. • What two minerals are considered characteristic of impact metamorphism? What other material is often found in impact zones? • Describe two other features that are commonly associated with impacts. • Met ...
... • (T-F) All minerals show the transition from brittle to ductile under very similar conditions. • What two minerals are considered characteristic of impact metamorphism? What other material is often found in impact zones? • Describe two other features that are commonly associated with impacts. • Met ...
Geologic Time - North Coast Distance Education
... principle of uniformitarianism. According to Hutton, past geologic events could be explained by the natural processes operating today, such as erosion by running water, volcanism, and the gradual uplift of Earth’s crust. Hutton assumed that these processes occurred in the distant past just as they o ...
... principle of uniformitarianism. According to Hutton, past geologic events could be explained by the natural processes operating today, such as erosion by running water, volcanism, and the gradual uplift of Earth’s crust. Hutton assumed that these processes occurred in the distant past just as they o ...
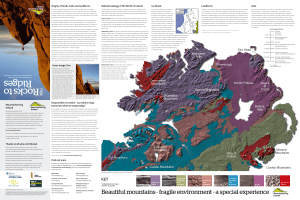
Rocks to Ridges - Mountaineering Ireland
... extended as far as 100km across the western continental shelf ...
... extended as far as 100km across the western continental shelf ...
Lecture D
... andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite. Also shown is the hydration of Al2SiO5 to pyrophyllite, which limits the occurrence of an Al2SiO5 polymorph at low grades in the presence of excess silica and water. The diagram was calculated using the program TWQ (Berman, 1988, 1990, 1991). ...
... andalusite, kyanite, and sillimanite. Also shown is the hydration of Al2SiO5 to pyrophyllite, which limits the occurrence of an Al2SiO5 polymorph at low grades in the presence of excess silica and water. The diagram was calculated using the program TWQ (Berman, 1988, 1990, 1991). ...
Chapter 21: Fossils and the Rock Record
... it. The bottom layer was eroded, and the loose material on the surface became incorporated in the newly deposited top layer. These particles, called inclusions, indicate that the rocks in the lower layer are older than those on top. As you learned in Chapter 6, once a rock has been eroded, the resul ...
... it. The bottom layer was eroded, and the loose material on the surface became incorporated in the newly deposited top layer. These particles, called inclusions, indicate that the rocks in the lower layer are older than those on top. As you learned in Chapter 6, once a rock has been eroded, the resul ...
Metamorphic Rocks Notes
... Intensity of Metamorphism Low-Grade Metamorphism Little change to rock High-Grade Metamorphism extreme change to rock ...
... Intensity of Metamorphism Low-Grade Metamorphism Little change to rock High-Grade Metamorphism extreme change to rock ...
Igneous rocks
... • How are igneous rocks formed? • How does magma differ from lava? • What two criteria are used to classify igneous rocks? • How does the rate of cooling of magma influence the crystal size of minerals in igneous rocks? • How is the mineral makeup of an igneous rock related to Bowen’s reaction serie ...
... • How are igneous rocks formed? • How does magma differ from lava? • What two criteria are used to classify igneous rocks? • How does the rate of cooling of magma influence the crystal size of minerals in igneous rocks? • How is the mineral makeup of an igneous rock related to Bowen’s reaction serie ...
Section 1
... Where U v is the volume of the voids and U is the total volume of material. It may be expressed as a decimal fraction or as a percentage. Porosity ranges from 1 percent to as much as 80 percent in some recently deposited clays, but in most granular materials it falls between about 5 and 40 percent ( ...
... Where U v is the volume of the voids and U is the total volume of material. It may be expressed as a decimal fraction or as a percentage. Porosity ranges from 1 percent to as much as 80 percent in some recently deposited clays, but in most granular materials it falls between about 5 and 40 percent ( ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.