Earth Science Quiz-1
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
... a. A tentative explanation of a body of data is called a hypothesis b. A theory is less likely to be correct than hypotheses. c. A hypothesis is strengthened if it successfully predicts the outcomes of new experiments. d. If new evidence indicates that a theory is wrong, the theory may be modified d ...
1. Glass is chemically related to what mineral? Fluorite Quartz Pyrite
... chemically formed sedimentary rock extrusive igneous rock ...
... chemically formed sedimentary rock extrusive igneous rock ...
Erosion, Transport, Deposition Key Words
... power and drops off the rocks, pebbles and mud it is carrying. ...
... power and drops off the rocks, pebbles and mud it is carrying. ...
Unit 3 Test - Problem
... The diagram below shows some of the layers of rocks found in the Grand Canyon. Scientists nd these layers of rock useful for studying fossils. ...
... The diagram below shows some of the layers of rocks found in the Grand Canyon. Scientists nd these layers of rock useful for studying fossils. ...
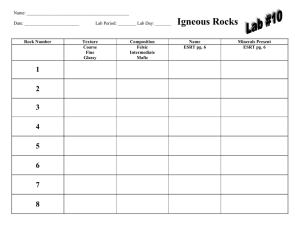
Igneous Rocks
... has a specific temperature/pressure/chemical environment stability range • Remember, these changes occur while the rock is still solid ...
... has a specific temperature/pressure/chemical environment stability range • Remember, these changes occur while the rock is still solid ...
Rocks and Minerals - National Science Teachers Association
... compressed beneath the weight of overlying sediments. They also form by chemical precipitation of minerals dissolved by water. Sedimentary rocks form at low temperatures at or very close to Earth’s surface. Common sedimentary rocks are sandstone, limestone, and shale. Metamorphic rocks are those in ...
... compressed beneath the weight of overlying sediments. They also form by chemical precipitation of minerals dissolved by water. Sedimentary rocks form at low temperatures at or very close to Earth’s surface. Common sedimentary rocks are sandstone, limestone, and shale. Metamorphic rocks are those in ...
Sedimentology and Sedimentary Processes
... http://csmres.jmu.edu/geollab/fichter/SedRx/SimpModl.html ...
... http://csmres.jmu.edu/geollab/fichter/SedRx/SimpModl.html ...
Mineral Composition
... pink, reddish-brown, buff color, angular grains buff, white, brown color, scratches glass ...
... pink, reddish-brown, buff color, angular grains buff, white, brown color, scratches glass ...
Iron Hill Museum Middle School Geology Program Teachers: This
... Vocabulary to know: organic, inorganic, mineral, rock, igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary, intrusive, extrusive, luster, cleavage/fracture, convection, process Major understandings: 1. All processes that affect rocks and minerals are a result of energy from the Sun or Earth’s interior. 2. Rocks cycle ...
... Vocabulary to know: organic, inorganic, mineral, rock, igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary, intrusive, extrusive, luster, cleavage/fracture, convection, process Major understandings: 1. All processes that affect rocks and minerals are a result of energy from the Sun or Earth’s interior. 2. Rocks cycle ...
document
... Summation/synthesis of the entire poster or project. No more than five or so sentences at the most. ...
... Summation/synthesis of the entire poster or project. No more than five or so sentences at the most. ...
Exam review questions 2008 2
... With a distinctive color-_________________________________________ 33. Why are diamonds used as gemstones? 34. Name the ore mined for aluminum. _____________________ Why is this mineral called an ore? 35. List Moh’s scale of hardness. ...
... With a distinctive color-_________________________________________ 33. Why are diamonds used as gemstones? 34. Name the ore mined for aluminum. _____________________ Why is this mineral called an ore? 35. List Moh’s scale of hardness. ...
Igneous Rocks
... allows crystals of individual minerals to form, producing a coarse texture (individual minerals can be seen). These coarse-textured, slowly cooled rocks are called intrusive or plutonic igneous rocks. Rocks that form near the earth's surface cool quickly. This fast cooling does not allow large cryst ...
... allows crystals of individual minerals to form, producing a coarse texture (individual minerals can be seen). These coarse-textured, slowly cooled rocks are called intrusive or plutonic igneous rocks. Rocks that form near the earth's surface cool quickly. This fast cooling does not allow large cryst ...
Geologic Time
... the time eruption. What else indicates one specific time? Do not copy This layer is 65 million years old. Below this layer, scientists find fossils of dinosaurs. Above this layer, there are no dinosaur fossils. What does this layer tell us? ...
... the time eruption. What else indicates one specific time? Do not copy This layer is 65 million years old. Below this layer, scientists find fossils of dinosaurs. Above this layer, there are no dinosaur fossils. What does this layer tell us? ...
The evolution of Life in the History of Earth
... with a crystalline structure and a specific chemical composition ...
... with a crystalline structure and a specific chemical composition ...
Happy Tuesday! Pull out a ½ sheet of paper or share a whole with
... PRINCIPLE OF INCLUSIONS: Igneous and sedimentary rocks that contain inclusions of other rocks must be younger than the rocks they include ...
... PRINCIPLE OF INCLUSIONS: Igneous and sedimentary rocks that contain inclusions of other rocks must be younger than the rocks they include ...
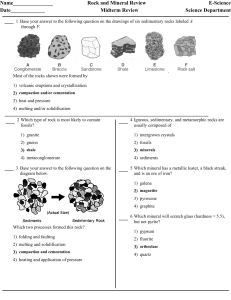
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... 4 Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks are usually composed of ...
... 4 Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks are usually composed of ...
part – i (mcq) (compulsory)
... (xii) Which of the following is associated with continent-continent convergent plate boundaries? (a) explosive volcanism (b) andesite volcanism (c) large, damaging earthquakes (d) volcanic mountain chain (e) All of these (xiii) An example of a convergent plate boundary is: (a) the Ouachita Mountains ...
... (xii) Which of the following is associated with continent-continent convergent plate boundaries? (a) explosive volcanism (b) andesite volcanism (c) large, damaging earthquakes (d) volcanic mountain chain (e) All of these (xiii) An example of a convergent plate boundary is: (a) the Ouachita Mountains ...
Types of Rock and the Rock Cycle
... Examples of extrusive igneous rocks are basalt, obsidian, and felsite. Rock that is formed from volcanic debris thrown out during an eruption is also classified as an extrusive, and is called pyroclastic. Examples of pyroclastic rock include pumice and volcanic ash. ...
... Examples of extrusive igneous rocks are basalt, obsidian, and felsite. Rock that is formed from volcanic debris thrown out during an eruption is also classified as an extrusive, and is called pyroclastic. Examples of pyroclastic rock include pumice and volcanic ash. ...
2. Geologic History Agenda Physical Geographers Intro to Calif
... Bonded elements with a crystalline structure The building blocks of rocks ...
... Bonded elements with a crystalline structure The building blocks of rocks ...
How Do Geologists Classify Rocks?
... tectonics in the rock cycle? • Plate movements start the rock cycle by help to form magma (the source of igneous rocks) and cause faulting, folding, and other motions of the crust that help to form sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. ...
... tectonics in the rock cycle? • Plate movements start the rock cycle by help to form magma (the source of igneous rocks) and cause faulting, folding, and other motions of the crust that help to form sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. ...
Clastic rock

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic with reference to sedimentary rocks as well as to particles in sediment transport whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.