PHY 102 Lab Manual: LCR circuit
... an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. Resonance: An impo ...
... an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. Resonance: An impo ...
Chapter 8
... • This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second order differential equation. • RLC series and parallel circuits will be discussed in this context. • The step response of these circuits will be covered as well. • Finally the concept of duality will be discussed ...
... • This chapter will expand on that with second order circuits: those that need a second order differential equation. • RLC series and parallel circuits will be discussed in this context. • The step response of these circuits will be covered as well. • Finally the concept of duality will be discussed ...
SPH 3U Electricity and Magnetism Lesson 3: Kirchhoff`s Voltage and
... branches of large, complicated circuits). Kirchoff’s Laws allow us to analyze how they will behave (and then build large, complicated circuits to do things for us). Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law: In any complete path (full loop from start to finish) in an electric circuit, the total electric potential inc ...
... branches of large, complicated circuits). Kirchoff’s Laws allow us to analyze how they will behave (and then build large, complicated circuits to do things for us). Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law: In any complete path (full loop from start to finish) in an electric circuit, the total electric potential inc ...
Series & Parallel Circuits PowerPoint
... will still flow across the other legs and all other components will still work. ...
... will still flow across the other legs and all other components will still work. ...
Document
... The side connected to the input AC voltage source is called the primary and has N1 turns. The other side, called the secondary, is connected to a resistor and has N2 turns. ...
... The side connected to the input AC voltage source is called the primary and has N1 turns. The other side, called the secondary, is connected to a resistor and has N2 turns. ...
t299-3-03f
... Two straight conducting rails form a right angle where their ends are joined and lie along the +x, +y axes. An identical pair of rails moves with speed v0 m/s along a line at degrees to the +y axis, as shown, so that a rectangular circuit is formed which increases in size. At t = 0 the area enclos ...
... Two straight conducting rails form a right angle where their ends are joined and lie along the +x, +y axes. An identical pair of rails moves with speed v0 m/s along a line at degrees to the +y axis, as shown, so that a rectangular circuit is formed which increases in size. At t = 0 the area enclos ...
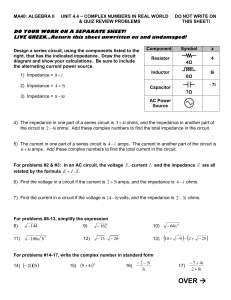
Practical Electricity 2
... 4. The circuit shown is used to control the brightness of two identical lamps. The variable resistor is adjusted until the lamps operate at their correct voltage of 3.0V ...
... 4. The circuit shown is used to control the brightness of two identical lamps. The variable resistor is adjusted until the lamps operate at their correct voltage of 3.0V ...
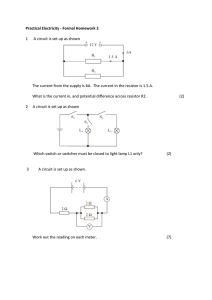
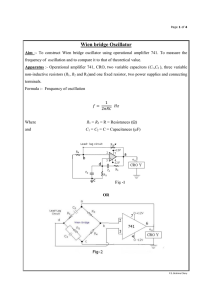
Operational amplifier 741 as Wein bridge Oscillator
... Description :- Fig-1 or Fig-2 is the circuit of the Wien bridge oscillator ( as these two circuits are same). A resistor R4 is connected to the inverting terminal (2) of the operational amplifier from the ground. Similarly a parallel combination of a resistance R2 and a capacitor C2 is connected to ...
... Description :- Fig-1 or Fig-2 is the circuit of the Wien bridge oscillator ( as these two circuits are same). A resistor R4 is connected to the inverting terminal (2) of the operational amplifier from the ground. Similarly a parallel combination of a resistance R2 and a capacitor C2 is connected to ...
CHAPTE 2 LITERATURE REVIEW 2.1 Introduction I have performed
... capacitor and self-made inductor constitute a parallel LC circuit. It is also called a tank circuit and will vibrate at a resonant frequency, which will be picked up the FM radio. In tank circuits, the underlying physics is that a capacitor stores electrical energy in the electric field between its ...
... capacitor and self-made inductor constitute a parallel LC circuit. It is also called a tank circuit and will vibrate at a resonant frequency, which will be picked up the FM radio. In tank circuits, the underlying physics is that a capacitor stores electrical energy in the electric field between its ...
Inductor Lab (RL and LC circuits)
... pushing at a different frequency, one would sometimes be working with, sometimes working against the child’s motion. The swing would not go very high. Resonance is important for tuning. Signals are placed on carrier waves and one must tune one’s receiver (change its natural frequency) to match the c ...
... pushing at a different frequency, one would sometimes be working with, sometimes working against the child’s motion. The swing would not go very high. Resonance is important for tuning. Signals are placed on carrier waves and one must tune one’s receiver (change its natural frequency) to match the c ...
Power Point
... voltage remains the same and resistance increases does the number of electrons passing a point in the circuit in one second (current, I) increase, decrease or stay the same? Decrease When the turkey baster was filled with water and held up and allowed to drain it did so rather quickly. When pa ...
... voltage remains the same and resistance increases does the number of electrons passing a point in the circuit in one second (current, I) increase, decrease or stay the same? Decrease When the turkey baster was filled with water and held up and allowed to drain it did so rather quickly. When pa ...
Lecture Notes - Resonance Circuits and Characteristics File
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
... The frequencies corresponding to 0.707 of the maximum current are called the band frequencies, cutoff frequencies, or half-power frequencies (ƒ1, ƒ2). Half-power frequencies are those frequencies at which the power delivered is onehalf that delivered at resonant frequency. The range of frequen ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.