LM386 Audio Amplifier - Cornerstone Robotics
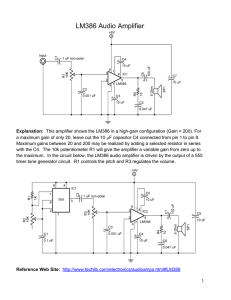
... Explanation: This amplifier shows the LM386 in a high-gain configuration (Gain = 200). For a maximum gain of only 20, leave out the 10 F capacitor C4 connected from pin 1 to pin 8. Maximum gains between 20 and 200 may be realized by adding a selected resistor in series with the C4. The 10k potentio ...
... Explanation: This amplifier shows the LM386 in a high-gain configuration (Gain = 200). For a maximum gain of only 20, leave out the 10 F capacitor C4 connected from pin 1 to pin 8. Maximum gains between 20 and 200 may be realized by adding a selected resistor in series with the C4. The 10k potentio ...
for immediate release
... design engineers using relays and circuit breakers (or relays and fuses) can replace those two devices with a single compact unit, plus get the benefits of emerging “smart” circuit protection technology. The new device saves space, saves time, increases reliability, and provides unprecedented protec ...
... design engineers using relays and circuit breakers (or relays and fuses) can replace those two devices with a single compact unit, plus get the benefits of emerging “smart” circuit protection technology. The new device saves space, saves time, increases reliability, and provides unprecedented protec ...
Resistor Inductor Capacitor Series Circuits
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
... icon below channel A. Click on the rescale icon and a graph of the resistor voltage versus time is shown. Click on the Input selection box at the lower left of the graph window (second row, second icon), click on Analog B and click on Voltage to display the inductor voltage graph. Repeat this to se ...
V 1 = V 2 = V 3
... • Current is the same between junctions. • Assign direction to current arbitrarily. • If result is a negative current, it means that the current actually flows in the opposite direction. Don’t change direction, just give negative answer. • Branches with a capacitor have zero current. ...
... • Current is the same between junctions. • Assign direction to current arbitrarily. • If result is a negative current, it means that the current actually flows in the opposite direction. Don’t change direction, just give negative answer. • Branches with a capacitor have zero current. ...
Ch 2 PPt 2 Basic Theories
... • Voltage applied to each leg is the same • Voltage dropped across each leg will be the same – If more that one resistor in a leg, voltage drop will depend on the resistance of each resistor in that leg ...
... • Voltage applied to each leg is the same • Voltage dropped across each leg will be the same – If more that one resistor in a leg, voltage drop will depend on the resistance of each resistor in that leg ...
project 1
... The use of design and simulation tools such as ORCAD is recommended at early stage of design process. Frequency modulation is a form of angle modulation where the message signal is used to vary the carrier frequency. In this project, you will choose to design an FM modulator using phase-locked loop ...
... The use of design and simulation tools such as ORCAD is recommended at early stage of design process. Frequency modulation is a form of angle modulation where the message signal is used to vary the carrier frequency. In this project, you will choose to design an FM modulator using phase-locked loop ...
Checkpoint Tasks
... This means the hair becomes positively charged overall. This means the comb becomes negatively charged. 2 Predict how two charged objects will behave when placed next to each other. Fill in the grid below. (Tick = attract, cross = repel) ...
... This means the hair becomes positively charged overall. This means the comb becomes negatively charged. 2 Predict how two charged objects will behave when placed next to each other. Fill in the grid below. (Tick = attract, cross = repel) ...
V - Wappingers Central School District
... To go from the top to the bottom floor, all people must take the same path. So, by definition, the staircases are in series. With each flight people lose some of the potential energy given to them by the elevator, expending all of it by the time they reach the ground floor. So the sum of the V drops ...
... To go from the top to the bottom floor, all people must take the same path. So, by definition, the staircases are in series. With each flight people lose some of the potential energy given to them by the elevator, expending all of it by the time they reach the ground floor. So the sum of the V drops ...
Resistors in Parallel and Series 2 Series and Parallel Circuits
... the current and voltage. Calculate the resistance using V=IR. Record this in the “powered” column. Repeat with each of the other two resistors. V ...
... the current and voltage. Calculate the resistance using V=IR. Record this in the “powered” column. Repeat with each of the other two resistors. V ...
Example 1: Consider the circuit shown in Figure 1
... independent source. When the independent source is a current source, the current source current is equal to the current in the capacitor or inductor. Similarly, when the independent source is a voltage source, the voltage source voltage is equal to the voltage across the capacitor or inductor. These ...
... independent source. When the independent source is a current source, the current source current is equal to the current in the capacitor or inductor. Similarly, when the independent source is a voltage source, the voltage source voltage is equal to the voltage across the capacitor or inductor. These ...
Review PPT game.
... the voltage across one resistor will be _________the voltage across the second resistor. A: Equal to ► Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be __________ the current through the other resistor. A: Different from ...
... the voltage across one resistor will be _________the voltage across the second resistor. A: Equal to ► Two different resistors are connected in parallel. The current through one of the resistors will be __________ the current through the other resistor. A: Different from ...
DTC P0350: IGNITION COIL PRIMARY/SECONDARY CIRCUIT P0350
... POWERTRAIN DTC CHARTS & DESCRIPTIONS -- GASOLINE MODELS -2006 For... Page 1 of 1 ...
... POWERTRAIN DTC CHARTS & DESCRIPTIONS -- GASOLINE MODELS -2006 For... Page 1 of 1 ...
Amateur Radio Technician Class Element 2 Course Presentation
... incorporate “crowbar protection” to provide overvoltage protection. ...
... incorporate “crowbar protection” to provide overvoltage protection. ...
Chemical Bonds
... currents through each path. • The equivalent resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. ...
... currents through each path. • The equivalent resistance is the sum of the individual resistances. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.























