DO NOW
... must go through the ammeter, so there can be only one current path. A connection with only one current path is called a series connection. ...
... must go through the ammeter, so there can be only one current path. A connection with only one current path is called a series connection. ...
Lecture 1
... 2. Kill the independent sources in circuit and determine the equivalent resistance RTH of the circuit 3. Re-activate the sources and determine the open-circuit voltage VOC across the circuit terminals 4. Place the Thévenin equivalent circuit into the original overall circuit and perform the desired ...
... 2. Kill the independent sources in circuit and determine the equivalent resistance RTH of the circuit 3. Re-activate the sources and determine the open-circuit voltage VOC across the circuit terminals 4. Place the Thévenin equivalent circuit into the original overall circuit and perform the desired ...
Electric Circuits - Bowlesphysics.com
... Electrical POWER We have already learned that POWER is the rate at which work (energy) is done. Circuits that are a prime example of this as batteries only last for a certain amount of time AND we get charged an energy bill each month based on the amount of energy we used over the course of a month ...
... Electrical POWER We have already learned that POWER is the rate at which work (energy) is done. Circuits that are a prime example of this as batteries only last for a certain amount of time AND we get charged an energy bill each month based on the amount of energy we used over the course of a month ...
ph104exp07_AC_RLC_Circuits_03
... One way to start measurements is to read Vout over a broad range of frequencies, both above and below the characteristic frequency, such as between 0.1fchar to 10fchar. Three or four measurements on each side of fchar and one at fchar ought to be enough to tell you where the interesting frequencies ...
... One way to start measurements is to read Vout over a broad range of frequencies, both above and below the characteristic frequency, such as between 0.1fchar to 10fchar. Three or four measurements on each side of fchar and one at fchar ought to be enough to tell you where the interesting frequencies ...
2 - Stephen F. Austin State University
... Function Generators are devices that can create all of these waveforms. These devices will be used in lab. Sketch the waveforms and circuit symbols for the waveforms above. ...
... Function Generators are devices that can create all of these waveforms. These devices will be used in lab. Sketch the waveforms and circuit symbols for the waveforms above. ...
up11_educue_ch31 - University of Manchester
... A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. Which graph correctly shows the instantaneous current through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? (current in purple, voltage in blue) ...
... A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. Which graph correctly shows the instantaneous current through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? (current in purple, voltage in blue) ...
lesson2
... Once the capacitor is discharged the current wants to stop flowing, but the inductor then begins to use the stored energy in the magnetic field to keep the current flowing, causing the current to diminish slowly rather than all at once. This causes the capacitor to charge back up (but with the oppos ...
... Once the capacitor is discharged the current wants to stop flowing, but the inductor then begins to use the stored energy in the magnetic field to keep the current flowing, causing the current to diminish slowly rather than all at once. This causes the capacitor to charge back up (but with the oppos ...
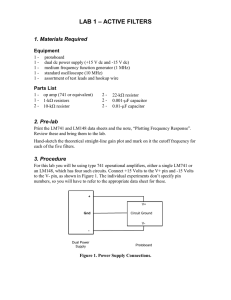
lab 1 – active filters
... Follow these steps for each of the five active filters. 1. Make a theoretical straight-line Bode plot of the filter response by using Excel as described in the memo, “Plotting Frequency Response”. 2. Construct the circuit. 3. Have the wiring checked by someone other than the person who connected it. ...
... Follow these steps for each of the five active filters. 1. Make a theoretical straight-line Bode plot of the filter response by using Excel as described in the memo, “Plotting Frequency Response”. 2. Construct the circuit. 3. Have the wiring checked by someone other than the person who connected it. ...
Electric Pickup Truck
... To restore 12 kWh back into a large battery bank in 6 minutes would require a 500 Amp charger. Or 500 x 25µF = 12,500 µF. 500 A at 240 V = 120,000 Watts. ...
... To restore 12 kWh back into a large battery bank in 6 minutes would require a 500 Amp charger. Or 500 x 25µF = 12,500 µF. 500 A at 240 V = 120,000 Watts. ...
RLC Series AC Circuits
... and forth to one another, with the resistor dissipating exactly what the voltage source puts into the circuit. This assumes no signi cant electromagnetic radiation from the inductor and capacitor, such as radio waves. Such radiation can happen and may even be desired, as we will see in the next chap ...
... and forth to one another, with the resistor dissipating exactly what the voltage source puts into the circuit. This assumes no signi cant electromagnetic radiation from the inductor and capacitor, such as radio waves. Such radiation can happen and may even be desired, as we will see in the next chap ...
Question 1: In this circuit, three resistors receive the same amount of
... Question 20: The circuit shown here is commonly referred to as a current divider. Calculate the voltage dropped across each resistor, the current drawn by each resistor, and the total amount of electrical resistance ßeen" by the 9-volt battery: ...
... Question 20: The circuit shown here is commonly referred to as a current divider. Calculate the voltage dropped across each resistor, the current drawn by each resistor, and the total amount of electrical resistance ßeen" by the 9-volt battery: ...
document
... The instantaneous voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current The instantaneous voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90° The instantaneous voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90° ...
... The instantaneous voltage across the resistor is in phase with the current The instantaneous voltage across the inductor leads the current by 90° The instantaneous voltage across the capacitor lags the current by 90° ...
Electronic glossary
... converted into direct current in order to be usable. This is called rectification. UK domestic AC is supplied at 230V. Capacitor Capacitors are components that store charge. The higher the capacitance, the more charge they store. Capacitance is measured in Farads (F). Capacitors need to charge befor ...
... converted into direct current in order to be usable. This is called rectification. UK domestic AC is supplied at 230V. Capacitor Capacitors are components that store charge. The higher the capacitance, the more charge they store. Capacitance is measured in Farads (F). Capacitors need to charge befor ...
Investigate current and bulb brightness for a series and parallel circuit
... Circuit with 1-voltage source. 2-light bulbs having the same resistance. Circuit with 1-voltage source. 3-light bulbs having the same resistance. ...
... Circuit with 1-voltage source. 2-light bulbs having the same resistance. Circuit with 1-voltage source. 3-light bulbs having the same resistance. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.