Chapter 3 - HCC Learning Web
... – Current draw: determined for each part of the circuit • Depends on resistance of that portion ...
... – Current draw: determined for each part of the circuit • Depends on resistance of that portion ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... By the end of this course, seventy percent of the students will be able to: Course Objectives (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES) 1. Determine the value of the four currents present in a two transistor current source circuit containing a reference resistor. 2. Determine the transcondutance (gm) and the ...
... By the end of this course, seventy percent of the students will be able to: Course Objectives (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES) 1. Determine the value of the four currents present in a two transistor current source circuit containing a reference resistor. 2. Determine the transcondutance (gm) and the ...
Second Order Linear Equations
... That being said, I need to emphasize that this is the hard way and that these formulae should only be used as a last resort. I say this because it is always possible to verify proposed solutions to differential equations by direct substitution. This means that if there exists a regimented system of ...
... That being said, I need to emphasize that this is the hard way and that these formulae should only be used as a last resort. I say this because it is always possible to verify proposed solutions to differential equations by direct substitution. This means that if there exists a regimented system of ...
electrical circuits
... • Resistors “resist” the flow of electrons in the circuit. Electrons strike a lot of particles and emit as heat. When electronics get warm, it’s the resistance in the circuit heating up. • Without them, the current would flow uncontrolled and short the circuit. • As resistance gets bigger, current g ...
... • Resistors “resist” the flow of electrons in the circuit. Electrons strike a lot of particles and emit as heat. When electronics get warm, it’s the resistance in the circuit heating up. • Without them, the current would flow uncontrolled and short the circuit. • As resistance gets bigger, current g ...
3 Input/ 2 Output Current-Mode Universal Biquad Filter Using Single DO-CCCDTA
... Current Differencing Transconductance Amplifier (DOCCCDTA). The features of the circuit are that: the quality factor and pole frequency can be tuned orthogonally via the input bias currents: the circuit description is very simple, consisting of merely one DO-CCCDTA, one voltage buffer and 2 grounded ...
... Current Differencing Transconductance Amplifier (DOCCCDTA). The features of the circuit are that: the quality factor and pole frequency can be tuned orthogonally via the input bias currents: the circuit description is very simple, consisting of merely one DO-CCCDTA, one voltage buffer and 2 grounded ...
Part III
... closed, the capacitor will begin to charge. As it does, the voltage across it increases, and the current through the resistor decreases. ...
... closed, the capacitor will begin to charge. As it does, the voltage across it increases, and the current through the resistor decreases. ...
Chap 2 Circuit Elements
... Resistors are sensitive to temperature change from an assumed ambient temperature of 27 oC. The sensitivity is defined as k = 1/R (dR/dT) where R is resistance in ohms, T is temperature in degrees Celsius, and k is ppm/ oC. color codes for resistors A system of standard colors adopted for identifi ...
... Resistors are sensitive to temperature change from an assumed ambient temperature of 27 oC. The sensitivity is defined as k = 1/R (dR/dT) where R is resistance in ohms, T is temperature in degrees Celsius, and k is ppm/ oC. color codes for resistors A system of standard colors adopted for identifi ...
Series Circuits
... Series Circuits A series circuit is a circuit where there is only one path from the source through all of the loads and back to the source. This means that all of the current in the circuit must flow through all of the loads. One example of a series circuit is a string of old Christmas lights. There ...
... Series Circuits A series circuit is a circuit where there is only one path from the source through all of the loads and back to the source. This means that all of the current in the circuit must flow through all of the loads. One example of a series circuit is a string of old Christmas lights. There ...
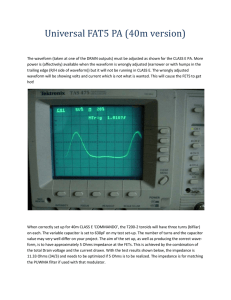
must be adjusted as shown for the CLASS E PA. More power is
... When correctly set up for 40m CLASS E 'COMMANDO', the T200-2 toroids will have three turns (bifilar) on each. The variable capacitor is set to 630pF on my test set-up. The number of turns and the capacitor value may very well differ on your project. The aim of the set up, as well as producing the co ...
... When correctly set up for 40m CLASS E 'COMMANDO', the T200-2 toroids will have three turns (bifilar) on each. The variable capacitor is set to 630pF on my test set-up. The number of turns and the capacitor value may very well differ on your project. The aim of the set up, as well as producing the co ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.