Radio Shack HTX-100 Microphone Amplifier
... refering actually to the so-called 'ideal' operational amplifier with infinite open-loop gain, input resistance, bandwidth and a zero output resistance. However, in practice no op-amp can meet these ideal characteristics. And as you will see, a little later on, there is no such thing as an ideal op- ...
... refering actually to the so-called 'ideal' operational amplifier with infinite open-loop gain, input resistance, bandwidth and a zero output resistance. However, in practice no op-amp can meet these ideal characteristics. And as you will see, a little later on, there is no such thing as an ideal op- ...
Electrical Circuits and Circuit Diagrams
... Electricity In Series Circuits • The current must be the same through all resistors when the resistors are in series Req = R1 + R2 + R3 Veq = V1 + V2 + V3 Ieq = I1 = I2 = I3 ...
... Electricity In Series Circuits • The current must be the same through all resistors when the resistors are in series Req = R1 + R2 + R3 Veq = V1 + V2 + V3 Ieq = I1 = I2 = I3 ...
File
... Parallel Circuits • Sometimes these paths are called branches. • The current through a branch is also called the branch current. • When analyzing a parallel circuit, remember that the current always has to go somewhere. • The total current in the circuit is the sum of the currents in all the branch ...
... Parallel Circuits • Sometimes these paths are called branches. • The current through a branch is also called the branch current. • When analyzing a parallel circuit, remember that the current always has to go somewhere. • The total current in the circuit is the sum of the currents in all the branch ...
doc - Rutgers Engineering
... the capacitive voltage sinwave and slowly reduce the frequency of the wave generator until you find that the capacitive voltage p-p has reduced to 0.707 volt p-p. Note that you may need to change the frequency Multiplier control to achieve low enough frequencies Record the frequency at which this oc ...
... the capacitive voltage sinwave and slowly reduce the frequency of the wave generator until you find that the capacitive voltage p-p has reduced to 0.707 volt p-p. Note that you may need to change the frequency Multiplier control to achieve low enough frequencies Record the frequency at which this oc ...
Lecture 6
... the first resistor that you place in the circuit and then copy the resistor to place the other resistors into the circuit, you only need to modify the TOLERANCE of the resistors once. • If you place all of the resistors into the circuit before changing the properties, you will need to click on each ...
... the first resistor that you place in the circuit and then copy the resistor to place the other resistors into the circuit, you only need to modify the TOLERANCE of the resistors once. • If you place all of the resistors into the circuit before changing the properties, you will need to click on each ...
Chapter 6 Electricity: Electrical Circuit
... one load. It then moves to another load. It returns through a wire to the power source. 4. A circuit is a series circuit as long as all of the parts are connects one after another. 5. If any part of a series circuit is removed or broken, the circuit is open and no current can flow through it. What i ...
... one load. It then moves to another load. It returns through a wire to the power source. 4. A circuit is a series circuit as long as all of the parts are connects one after another. 5. If any part of a series circuit is removed or broken, the circuit is open and no current can flow through it. What i ...
FE Exam Review Electrical Circuits
... • At the instant the switch is in position a the charge on the capacitor is zero, the capacitor starts to charge. The capacitor continues to charge until it reaches its maximum charge (Q = Cε) • Once the capacitor is fully charged, the current in the circuit is zero. • Once the maximum charge is rea ...
... • At the instant the switch is in position a the charge on the capacitor is zero, the capacitor starts to charge. The capacitor continues to charge until it reaches its maximum charge (Q = Cε) • Once the capacitor is fully charged, the current in the circuit is zero. • Once the maximum charge is rea ...
Series and Parallel Circuits - WESTWOODPHYSICSIG2-2010
... UEENEEE004A Solve Problems in multiple path dc circuits Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheet STUDENT NAME: ............................................. DATE: ............................. RESULT: CY / CN OBJECTIVE: To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistanc ...
... UEENEEE004A Solve Problems in multiple path dc circuits Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheet STUDENT NAME: ............................................. DATE: ............................. RESULT: CY / CN OBJECTIVE: To gain an understanding of the circuit quantities, voltage, current and resistanc ...
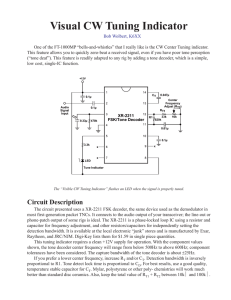
Visual CW Tuning Indicator
... Raytheon, and JRC/NJM. Digi-Key lists them for $1.59 in single piece quantities. This tuning indicator requires a clean +12V supply for operation. With the component values shown, the tone decoder center frequency will range from below 500Hz to above 600Hz; component tolerances have been considered. ...
... Raytheon, and JRC/NJM. Digi-Key lists them for $1.59 in single piece quantities. This tuning indicator requires a clean +12V supply for operation. With the component values shown, the tone decoder center frequency will range from below 500Hz to above 600Hz; component tolerances have been considered. ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.