SuperPosition - people.csail.mit.edu
... composed of resistors, inductors and capacitors are sinusoidal (sines or cosines), then all the voltages and currents in the circuit are sinusoids of the same frequency. The only changes that occur to the signals are scaling and delays. Delays are measured as “phase differences”- the original and re ...
... composed of resistors, inductors and capacitors are sinusoidal (sines or cosines), then all the voltages and currents in the circuit are sinusoids of the same frequency. The only changes that occur to the signals are scaling and delays. Delays are measured as “phase differences”- the original and re ...
Capacitor Applications - HolyStone International
... tasks, such as smoothing, filtering, bypassing etc…. One type of capacitor may not be suitable for all applications. Ceramic capacitors are generally superior than other types and therefore can be used in a vast ranges of application. The following is the typical capacitor applications in electronic ...
... tasks, such as smoothing, filtering, bypassing etc…. One type of capacitor may not be suitable for all applications. Ceramic capacitors are generally superior than other types and therefore can be used in a vast ranges of application. The following is the typical capacitor applications in electronic ...
Lecture 7 Overview - Welcome to the University of Delaware
... Time constant τ=RC. Time needed to charge capacitor to 63% of full charge Larger RC means the capacitor takes longer to charge Larger R implies smaller current flow The larger C is, the more charge the capacitor can hold. Solution is only true for simple circuit with resistor and capacitor in series ...
... Time constant τ=RC. Time needed to charge capacitor to 63% of full charge Larger RC means the capacitor takes longer to charge Larger R implies smaller current flow The larger C is, the more charge the capacitor can hold. Solution is only true for simple circuit with resistor and capacitor in series ...
BS7671 Formula and Tips
... Resistance of copper and aluminium conductors Uo = the normal voltage to earth Zs = the earth fault loop impedance and : Zs = Ze + (R1 + R2) Ze = the external earth fault loop impedance of the supply cable Zs = the earth fault loop impendence of the Internal current carrying circuit. R1+R2 = the su ...
... Resistance of copper and aluminium conductors Uo = the normal voltage to earth Zs = the earth fault loop impedance and : Zs = Ze + (R1 + R2) Ze = the external earth fault loop impedance of the supply cable Zs = the earth fault loop impendence of the Internal current carrying circuit. R1+R2 = the su ...
Overview - Pi Speakers
... dB = 20logX/Y; 12 = 20 log (2.5/10) So this circuit provides 12dB attenuation. Notice that attenuation is the same as a single 25 ohm resistor, but the source impedance of the L-Pad is 8 ohms and the source impedance of the 12dB series attenuator is 33 ohms. More importantly, the damping of componen ...
... dB = 20logX/Y; 12 = 20 log (2.5/10) So this circuit provides 12dB attenuation. Notice that attenuation is the same as a single 25 ohm resistor, but the source impedance of the L-Pad is 8 ohms and the source impedance of the 12dB series attenuator is 33 ohms. More importantly, the damping of componen ...
Two wires made of the same material have the same lengths
... A R 1 = 3.00 Ohm and a R 2 = 1.50 Ohm resistor are wired in parallel and the combination is wired in series to a R 3 = 4.00 Ohm resistor and a 10.0 V emf device . The potential difference across the R 1 resistor is: R1 ...
... A R 1 = 3.00 Ohm and a R 2 = 1.50 Ohm resistor are wired in parallel and the combination is wired in series to a R 3 = 4.00 Ohm resistor and a 10.0 V emf device . The potential difference across the R 1 resistor is: R1 ...
Operational amplifier
... • As the frequency of the processed signals increases, the effects of parasitic capacitance in (BJT/MOS) transistors start to manifest • The gain of the amplifier circuits is frequency dependent, usually decrease with the frequency increase of the input signals • Computing by hand the exact frequenc ...
... • As the frequency of the processed signals increases, the effects of parasitic capacitance in (BJT/MOS) transistors start to manifest • The gain of the amplifier circuits is frequency dependent, usually decrease with the frequency increase of the input signals • Computing by hand the exact frequenc ...
10 Electricity Trend setter Questions
... Electric current indicates electric charges in motion. Dynamics deals with bodies in motion. The science of electricity in motion is known as electrodynamics The voltmeter is a high-resistance galvanometer used to measure voltage. It measures the potential difference across any two points in an elec ...
... Electric current indicates electric charges in motion. Dynamics deals with bodies in motion. The science of electricity in motion is known as electrodynamics The voltmeter is a high-resistance galvanometer used to measure voltage. It measures the potential difference across any two points in an elec ...
Lab 25 Electrical Resistance - Series
... An electric current is a flow of charge (electrons). For Direct Current (DC) charge always flows in the same direction. In Alternating Current (AC) the charge changes direction by moving back and forth at a frequency (cycles per second) of the electrical system. Nearly all substances fall into one o ...
... An electric current is a flow of charge (electrons). For Direct Current (DC) charge always flows in the same direction. In Alternating Current (AC) the charge changes direction by moving back and forth at a frequency (cycles per second) of the electrical system. Nearly all substances fall into one o ...
Resonance - India Study Channel
... The frequency response curve of a parallel resonant circuit is as shown in figure above. From the figure, we find that the current is minimum at resonance. Hence, impedance of the circuit is maximum at resonance. Since the current at resonance is minimum, the parallel circuit at resonance is called ...
... The frequency response curve of a parallel resonant circuit is as shown in figure above. From the figure, we find that the current is minimum at resonance. Hence, impedance of the circuit is maximum at resonance. Since the current at resonance is minimum, the parallel circuit at resonance is called ...
S1 Unit One Science in Everyday Life Revision notes
... Household appliances that are connected to parallel circuits can be switched on and off separately ...
... Household appliances that are connected to parallel circuits can be switched on and off separately ...
LAB - ECE233
... When we want to measure the potential difference between any two points we use voltmeters. Hence at each situation where voltmeter is used, we made a parallel connection to some circuit portion. This parallel connection causes a kind o voltage drop over that circuit portion. Generally Voltmeters hav ...
... When we want to measure the potential difference between any two points we use voltmeters. Hence at each situation where voltmeter is used, we made a parallel connection to some circuit portion. This parallel connection causes a kind o voltage drop over that circuit portion. Generally Voltmeters hav ...
UNIT 12
... feedback conditions are met. Feedback occurs by the sinusoidal oscillatory current in L 1 inducing, by transformer action, a voltage of the same frequency in L2 (coupled magnetically to L1). This is applied to the base of Tr1 as the input and is amplified to cause a larger oscillatory current L1 and ...
... feedback conditions are met. Feedback occurs by the sinusoidal oscillatory current in L 1 inducing, by transformer action, a voltage of the same frequency in L2 (coupled magnetically to L1). This is applied to the base of Tr1 as the input and is amplified to cause a larger oscillatory current L1 and ...
Component7 - Glow Blogs
... Capacitors are electronic components that store electricity for short periods of time within electronic circuits or networks. They are made from two metal plates or films separated by an insulator. In many capacitors, film is used so that the layers of metal film and insulator can be wound into a cy ...
... Capacitors are electronic components that store electricity for short periods of time within electronic circuits or networks. They are made from two metal plates or films separated by an insulator. In many capacitors, film is used so that the layers of metal film and insulator can be wound into a cy ...
Hearing Science
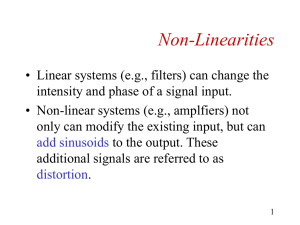
... intensity and phase of a signal input. • Non-linear systems (e.g., amplfiers) not only can modify the existing input, but can add sinusoids to the output. These additional signals are referred to as ...
... intensity and phase of a signal input. • Non-linear systems (e.g., amplfiers) not only can modify the existing input, but can add sinusoids to the output. These additional signals are referred to as ...
FIRST ORDER CIRCUITS Introduction
... At arbitrary time t, the current flows over the inductor is defined by Equation 5 given below. Is is the maximum current of the circuit, which depends on the resistance. One can see the similarity between Equation 5 and Equation 2. This similarity suggest that more than the half of the maximum curre ...
... At arbitrary time t, the current flows over the inductor is defined by Equation 5 given below. Is is the maximum current of the circuit, which depends on the resistance. One can see the similarity between Equation 5 and Equation 2. This similarity suggest that more than the half of the maximum curre ...
06_PhETPower wo kirchoff
... Record the Voltage, Current, and Power values for each bulb in the series-parallel circuit in the table below ...
... Record the Voltage, Current, and Power values for each bulb in the series-parallel circuit in the table below ...
Lecture 30 Chapter 33 EM Oscillations and AC
... Current angle φ Relation Resistance VR=IRR R In phase ...
... Current angle φ Relation Resistance VR=IRR R In phase ...
RLC circuit

A RLC circuit is an electrical circuit consisting of a resistor (R), an inductor (L), and a capacitor (C), connected in series or in parallel. The name of the circuit is derived from the letters that are used to denote the constituent components of this circuit, where the sequence of the components may vary from RLC.The circuit forms a harmonic oscillator for current, and resonates in a similar way as an LC circuit. Introducing the resistor increases the decay of these oscillations, which is also known as damping. The resistor also reduces the peak resonant frequency. Some resistance is unavoidable in real circuits even if a resistor is not specifically included as a component. An ideal, pure LC circuit is an abstraction used in theoretical considerations.RLC circuits have many applications as oscillator circuits. Radio receivers and television sets use them for tuning to select a narrow frequency range from ambient radio waves. In this role the circuit is often referred to as a tuned circuit. An RLC circuit can be used as a band-pass filter, band-stop filter, low-pass filter or high-pass filter. The tuning application, for instance, is an example of band-pass filtering. The RLC filter is described as a second-order circuit, meaning that any voltage or current in the circuit can be described by a second-order differential equation in circuit analysis.The three circuit elements, R,L and C can be combined in a number of different topologies. All three elements in series or all three elements in parallel are the simplest in concept and the most straightforward to analyse. There are, however, other arrangements, some with practical importance in real circuits. One issue often encountered is the need to take into account inductor resistance. Inductors are typically constructed from coils of wire, the resistance of which is not usually desirable, but it often has a significant effect on the circuit.