Structure and assembly of the spliceosomal small nuclear
... used to investigate pairwise interactions of the Sm proteins [33•,34•]. Kambach et al. [32••] have been able to arrange all seven Sm proteins within a seven-membered ring (Figure 1d) in a manner that is consistent with all the known pairwise interactions [33•,34•]. The heptameric ring is the only co ...
... used to investigate pairwise interactions of the Sm proteins [33•,34•]. Kambach et al. [32••] have been able to arrange all seven Sm proteins within a seven-membered ring (Figure 1d) in a manner that is consistent with all the known pairwise interactions [33•,34•]. The heptameric ring is the only co ...
- Wiley Online Library
... Thus far, C-to-U editing has only been observed in eukaryotes, but not in bacteria and archaea. C-toU editing is highly prominent in plants. With only few exceptions, the mitochondrial and plastid mRNAs of all land plants show editing.37 C-to-U editing is certainly not restricted to the coding seque ...
... Thus far, C-to-U editing has only been observed in eukaryotes, but not in bacteria and archaea. C-toU editing is highly prominent in plants. With only few exceptions, the mitochondrial and plastid mRNAs of all land plants show editing.37 C-to-U editing is certainly not restricted to the coding seque ...
International Journal on New Trends in Education and Their
... stopper codon. mRNA slips. tRNAs are synthesized through mRNAs. Afterwards, a peptide bond is created between tRNAs. Considering the expression of the pre-service teacher, it can be inferred that he/she assumes tRNAs are interconnected via peptide bonds. CONCLUSIONS AND DISCUSSION In consequence of ...
... stopper codon. mRNA slips. tRNAs are synthesized through mRNAs. Afterwards, a peptide bond is created between tRNAs. Considering the expression of the pre-service teacher, it can be inferred that he/she assumes tRNAs are interconnected via peptide bonds. CONCLUSIONS AND DISCUSSION In consequence of ...
Strategies in the interfield discovery of the mechanism of protein
... bonds. Zamecnik and his colleagues, especially Mahlon Hoagland, sought to understand energetic intermediates between free amino acids and their linkage in polypeptides (recalled in Zamecnik, 1962a, 1969; Hoagland, 1990, 1996). They were thus working backward from peptide bonds to the mechanisms of p ...
... bonds. Zamecnik and his colleagues, especially Mahlon Hoagland, sought to understand energetic intermediates between free amino acids and their linkage in polypeptides (recalled in Zamecnik, 1962a, 1969; Hoagland, 1990, 1996). They were thus working backward from peptide bonds to the mechanisms of p ...
Accuracy of initial codon selection by aminoacyl
... provided that discarding of noncognate substrate in the proofreading steps is driven by free energy dissipation (10, 14). Another case is Ninio’s explanation (15) of error prone (ram) and hyperaccurate (strA) ribosomal mutants (16) as caused by varying utilization, αd, of the d values of aa-tRNA sel ...
... provided that discarding of noncognate substrate in the proofreading steps is driven by free energy dissipation (10, 14). Another case is Ninio’s explanation (15) of error prone (ram) and hyperaccurate (strA) ribosomal mutants (16) as caused by varying utilization, αd, of the d values of aa-tRNA sel ...
1-Tubulin mRNAs Are Specified by the First 13
... increases in the tubulin subunit concentration result in rapid and specific degradation of tubulin mRNAs. We have now determined that the sequences that are necessary and sufficient to specify mouse I-tubulin mRNAs as substrates for this autoregulated instability reside within the first 13 translate ...
... increases in the tubulin subunit concentration result in rapid and specific degradation of tubulin mRNAs. We have now determined that the sequences that are necessary and sufficient to specify mouse I-tubulin mRNAs as substrates for this autoregulated instability reside within the first 13 translate ...
Egg Microinjection Technique and Morpholinos
... 1. Clean the calibration micrometer slide with EtOH and put a drop of halocarbon oil on it. 2. Put calibration slide on upside-down petrie dish lid, so that you do not have to adjust the micromanipulator position before and after, or change greatly the focal plane from that used for injection. Focus ...
... 1. Clean the calibration micrometer slide with EtOH and put a drop of halocarbon oil on it. 2. Put calibration slide on upside-down petrie dish lid, so that you do not have to adjust the micromanipulator position before and after, or change greatly the focal plane from that used for injection. Focus ...
Cells_Review_Game_wi..
... Is this active or passive transport? Transport – Goes against concentration gradient and requires energy. ...
... Is this active or passive transport? Transport – Goes against concentration gradient and requires energy. ...
Topological studies suggest that the pathway of the protons through
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
... TID-reactive residues in F0• The labeling profilein Fig. 58 was obtaincd after reaction with Neurospora crassa mitochondria in the presence of an oligomycin concentration 10-fold higher than necessary for maximal inhibition. The identical group of residues was TID-reactive in the presence and in the ...
Modeling tRNA*s Translator Function
... • Go to the tRNA activity page at http://pdb101.rcsb.org/learn/resource/trna-activity-page or search for “Paper Model of tRNA – RCSB Protein Data Bank”. • Scroll down to section #3 titled, “Explore Atomic Structure of tRNA” and select the “Model color scheme” option for coloring the interactive mode ...
... • Go to the tRNA activity page at http://pdb101.rcsb.org/learn/resource/trna-activity-page or search for “Paper Model of tRNA – RCSB Protein Data Bank”. • Scroll down to section #3 titled, “Explore Atomic Structure of tRNA” and select the “Model color scheme” option for coloring the interactive mode ...
The origin of the eukaryotic cell: A genomic investigation
... cholesterol, and steroids are synthesized in the smooth ER. The rough ER is so designated because it is a membrane decorated by ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized, folded, and packaged for transport to the Golgi apparatus. This relationship between the smooth and rough ER is indicative of an ...
... cholesterol, and steroids are synthesized in the smooth ER. The rough ER is so designated because it is a membrane decorated by ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized, folded, and packaged for transport to the Golgi apparatus. This relationship between the smooth and rough ER is indicative of an ...
Minimally invasive determination of mRNA
... associated signal relative to its mean (12). The relative fluctuations to the mean of the fluorescence signal are directly related to the absolute number of molecules present in the detection volume. A single FCS measurement provides the absolute concentration and the size of the diffusing fluorescent m ...
... associated signal relative to its mean (12). The relative fluctuations to the mean of the fluorescence signal are directly related to the absolute number of molecules present in the detection volume. A single FCS measurement provides the absolute concentration and the size of the diffusing fluorescent m ...
Nucleolar localization of early tRNA processing
... probe will detect intermediates both before and after 58and 38-end processing, of which the end-matured intermediates are more abundant (Lee et al. 1991). Fluorescein signal from the combined pre-tRNA intron probes (green in Fig. 2a) colocalizes almost exclusively in the single crescent-shaped nucle ...
... probe will detect intermediates both before and after 58and 38-end processing, of which the end-matured intermediates are more abundant (Lee et al. 1991). Fluorescein signal from the combined pre-tRNA intron probes (green in Fig. 2a) colocalizes almost exclusively in the single crescent-shaped nucle ...
Molecular Chaperones in the Cytosol: from Nascent Chain to Folded
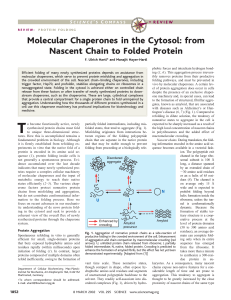
... Fig. 3. Structure and function of chaperones with the ability to bind nascent chains. (A) (Top) Structures of the ATPase domain (40) and the peptide-binding domain (38) of Hsp70 shown representatively for E. coli DnaK, generated with the program MOLSCRIPT (87). The ␣-helical latch of the peptide bin ...
... Fig. 3. Structure and function of chaperones with the ability to bind nascent chains. (A) (Top) Structures of the ATPase domain (40) and the peptide-binding domain (38) of Hsp70 shown representatively for E. coli DnaK, generated with the program MOLSCRIPT (87). The ␣-helical latch of the peptide bin ...
Diversity in P-loop Structure of A-ATP Synthase
... in ion translocation. Both of these domains are connected through the stalk part containing subunits C-F, H and a.1 Subunit A has been regarded as having catalytic function2 while subunit B plays an important role in nucleotide binding and/or regulatory function. 4-6 Crystallographic structures of t ...
... in ion translocation. Both of these domains are connected through the stalk part containing subunits C-F, H and a.1 Subunit A has been regarded as having catalytic function2 while subunit B plays an important role in nucleotide binding and/or regulatory function. 4-6 Crystallographic structures of t ...
PDF of original
... first position of synonyms, as for N-formyl-methionine. One consequence of logical degeneracy is that many single base replacements in DNA may be silent and thus not result in amino acid replacement in protein (el. Sonneborn, 1965). Also, the code is arranged so that the effects of some errors may b ...
... first position of synonyms, as for N-formyl-methionine. One consequence of logical degeneracy is that many single base replacements in DNA may be silent and thus not result in amino acid replacement in protein (el. Sonneborn, 1965). Also, the code is arranged so that the effects of some errors may b ...
Chapter 9: Introns and the RNA World
... RNA exons held together by self-splicing RNA introns, either group I or group II introns, both of which functions are catalyzed by RNA molecules acting as ribozymes. In this picture, the RNA genetic material would have an extended, presumably a more linear, structure adapted for copying. After the g ...
... RNA exons held together by self-splicing RNA introns, either group I or group II introns, both of which functions are catalyzed by RNA molecules acting as ribozymes. In this picture, the RNA genetic material would have an extended, presumably a more linear, structure adapted for copying. After the g ...
Functional Equivalence of Translation Factor eIF5B from Candida
... along with additional factors, and the resulting 43S complex then binds mRNA at its 5′ end, forming a 48S complex that scans to locate the AUG start codon. Basepairing between the Met-tRNA in the ribosomal complex and the AUG codon triggers GTP hydrolysis. The 48S complex joins with the large 60S ri ...
... along with additional factors, and the resulting 43S complex then binds mRNA at its 5′ end, forming a 48S complex that scans to locate the AUG start codon. Basepairing between the Met-tRNA in the ribosomal complex and the AUG codon triggers GTP hydrolysis. The 48S complex joins with the large 60S ri ...
SURVEY AND SUMMARY A profusion of upstream open reading
... all examples have two adjacent proline residues near the C-terminus. In animals belonging to six phyla the uCC ends with another proline followed by a serine—a dipeptide sequence identical to the C-terminus of the ‘short’ uORF regulating the expression of AdoMetDC in plants. The presence of the two ...
... all examples have two adjacent proline residues near the C-terminus. In animals belonging to six phyla the uCC ends with another proline followed by a serine—a dipeptide sequence identical to the C-terminus of the ‘short’ uORF regulating the expression of AdoMetDC in plants. The presence of the two ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... specificity further so that it no longer binds the stop codon with new meaning ...
... specificity further so that it no longer binds the stop codon with new meaning ...
Ribozyme catalysis: not different, just worse
... there are only a limited number of mechanisms through which a reaction can be catalyzed. The overall goal is to stabilize the transition state of the reaction relative to the ground state. To do this, the catalyst can pay for the cost of entropy lost in achieving the transition state by positioning ...
... there are only a limited number of mechanisms through which a reaction can be catalyzed. The overall goal is to stabilize the transition state of the reaction relative to the ground state. To do this, the catalyst can pay for the cost of entropy lost in achieving the transition state by positioning ...
the selective interruption of nucleolar rna synthesis in hela cells by
... From the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Biology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139 ...
... From the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Department of Biology, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02139 ...
Biology, 7e (Campbell)
... 30) Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein excretion in prokaryotic cells? A) Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to excrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system. B) The mechanism of protein excretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in ...
... 30) Which of the following statements correctly describes some aspect of protein excretion in prokaryotic cells? A) Prokaryotes are unlikely to be able to excrete proteins because they lack an endomembrane system. B) The mechanism of protein excretion in prokaryotes is probably the same as that in ...
MBch13(2008)
... The spliceosome machinery • RNA splicing is carried out by a large complex called the spliceosome • Spliceosome comprises about 150 proteins and 5 RNAs and is similar in size with ribosomes. • Many functions of spliceosome are carried out by RNAs rather by proteins. • Five RNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and ...
... The spliceosome machinery • RNA splicing is carried out by a large complex called the spliceosome • Spliceosome comprises about 150 proteins and 5 RNAs and is similar in size with ribosomes. • Many functions of spliceosome are carried out by RNAs rather by proteins. • Five RNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5 and ...
An mRNA Putatively Coding for an O
... in more mature regions of the root. The exodermis is located immediately intemal to the epidermis; eventually the epidermis sloughs away, and the exodermis functions as the bamer between the roots and the soil (Raven et al., 1992) Plant development and function are coordinately regulated through pre ...
... in more mature regions of the root. The exodermis is located immediately intemal to the epidermis; eventually the epidermis sloughs away, and the exodermis functions as the bamer between the roots and the soil (Raven et al., 1992) Plant development and function are coordinately regulated through pre ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.