2.1 2 Translation - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... Translation is the assembly of polypeptides (proteins) at ribosomes. ...
... Translation is the assembly of polypeptides (proteins) at ribosomes. ...
Transcription and Translation
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
... Remember: MR CATAP (mRNA, ribosome, codon, anticodon, tRNA, amino acid, polypeptide) • mRNA binds to a ribosome which initiates translation • The mRNA is read in codons (from start codon = AUG) • Anticodons on tRNA align opposite appropriate codons ...
LEARNING GOALS - PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Main Idea
... direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. Examples include o Addition of a poly-A tail o Addition of a GTP cap o Excision of intron ...
... direction and synthesizes complementary mRNA molecules that determine the order of amino acids in the polypeptide. 2. In eukaryotic cells the mRNA transcript undergoes a series of enzymeregulated modifications. Examples include o Addition of a poly-A tail o Addition of a GTP cap o Excision of intron ...
File
... 1. The 1st codon of the mRNA strand attaches to the ribosome. The tRNA approaches the ribosome, the anticodon from tRNA binds w/the codon on mRNA. 2. The first codon of mRNA is AUG (start codon for protein synthesis), mRNA slides along the ribosome to the next codon 3. A new tRNA carrying an amino a ...
... 1. The 1st codon of the mRNA strand attaches to the ribosome. The tRNA approaches the ribosome, the anticodon from tRNA binds w/the codon on mRNA. 2. The first codon of mRNA is AUG (start codon for protein synthesis), mRNA slides along the ribosome to the next codon 3. A new tRNA carrying an amino a ...
RNA, Protein Synthesis, Transcription, and Translation
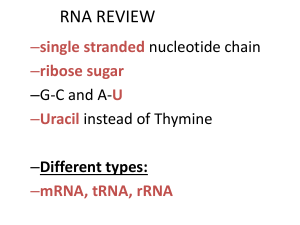
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
... • When mRNA is produced. • Part of a DNA nucleotide sequence is copied. • Starts at places called promoter. • Stops when a specific code is given. • Occurs in the nucleus of the cell • Purpose – copy instructions onto mRNA ...
RNA and protein synthesis
... • Code for ALL life! • Code is redundant – several codons for each amino acid ...
... • Code for ALL life! • Code is redundant – several codons for each amino acid ...
Translation and the Genetic Code
... 1.____ has an anticodon at one end and a binding site for an amino acid at the other. 2.____ forms part of the ribosome. 3.____ serves as a template for protein synthesis. 4.____ is synthesized from a DNA template in the nucleus. 5.____ carries the code for a particular protein to the ribosome Defin ...
... 1.____ has an anticodon at one end and a binding site for an amino acid at the other. 2.____ forms part of the ribosome. 3.____ serves as a template for protein synthesis. 4.____ is synthesized from a DNA template in the nucleus. 5.____ carries the code for a particular protein to the ribosome Defin ...
No Slide Title
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
... Transfer RNA (tRNA) leaves the nucleus, binds to the amino acid specified by it’s anticodon and transfers it to the ribisome where it meets up with mRNA to assemble a protein. ...
Plasma membrane
... proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temperature change). As a phospholipid bilayer, the lipid portion of the outer membrane is impermeable to charged molecules. However, channels called porins are present ...
... proportions of these fatty acids can be modulated by the bacterium to maintain the optimum fluidity of the membrane (e.g. following temperature change). As a phospholipid bilayer, the lipid portion of the outer membrane is impermeable to charged molecules. However, channels called porins are present ...
TRANSCRIPTION TRANSLATION
... (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
... (i) charging of the tRNA with the specific amino acids and (ii) synthesis of polypeptide chain by the ribosomes. ...
Gene Action
... 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases called an anticodon. – The anticodon pairs with the complementatry ...
... 2. The large ribosomal subunit attaches to the small subunit, creating a functional ribosome – The initiator tRNA binds to the start codon – One end of the tRNA carries a specific amino acid, the other consists of a triplet of bases called an anticodon. – The anticodon pairs with the complementatry ...
Proteins – where do they come from?
... • The mRNA is either read by another ribosome or it is recycled so its nucleotides can be used again. • The ribosome large and small subunit falls apart from each other ...
... • The mRNA is either read by another ribosome or it is recycled so its nucleotides can be used again. • The ribosome large and small subunit falls apart from each other ...
DNA to Eye Color? Just How does it Happen?
... particular amino acid. •20 amino acids make up all proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
... particular amino acid. •20 amino acids make up all proteins for life •Since codons are 3 bases, there are 64 different codon sequences -Some amino acids have two or more codons. ...
Protein Synthesis PPT
... • There are four DNA bases • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
... • There are four DNA bases • They code for 20 amino acids • If two bases coded for one amino acid, there wouldn’t be enough, only 16 • Three bases coding for each amino acid is just right, 64 possible combinations. • A set of 3 DNA bases that code for one amino acid is referred to as a codon. ...
The role of the C-terminal tail of the ribosomal protein S13 in protein
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
... mRNA by transcription, and then passed onto proteins by translation. The ribosome synthesizes proteins based on the information on the mRNA sequence in the cell; like building a house using bricks according to a blueprint. Bacterial growth is determined by how fast the whole process is. The bacteria ...
Transcription and Translation
... – Structure is more like a sphere shape – Functions are typically enzymes and transport proteins Fig. 2: Representation of a hemoglobin protein responsible for transportation of oxygen in the blood stream ...
... – Structure is more like a sphere shape – Functions are typically enzymes and transport proteins Fig. 2: Representation of a hemoglobin protein responsible for transportation of oxygen in the blood stream ...
January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
... January 7, 2014 Notes Transcription: process of copying DNA into an RNA template. (Occurs in nucleus) ...
charged
... poly rAC (2:1) asparagine, threonine, glutamine Ribosomes bind to nitrocellulose filters (tRNAs do not) aminoacyl-tRNAs (labelled with radioactive amino acids) are attached to ribosomes in the presence of ribo-trinucleotides. 64 different triplets yielded the complete code library. The code is made ...
... poly rAC (2:1) asparagine, threonine, glutamine Ribosomes bind to nitrocellulose filters (tRNAs do not) aminoacyl-tRNAs (labelled with radioactive amino acids) are attached to ribosomes in the presence of ribo-trinucleotides. 64 different triplets yielded the complete code library. The code is made ...
Protein Synthesis Drawing
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
... More tRNA molecules transfer correct amino acids to the growing protein chain (by matching the anticodon on tRNA to the codons on mRNA). Remember: One tRNA only carries one kind of A.A. ...
CHEM 482
... 2. Why do oligonucleotides containing Shine-Delgarno sequences inhibit translation in prokaryotes? Why don’t they do the same thing in eukaryotes? 3. Why does m7GTP inhibit translation in eukaryotes? Why doesn’t it do so in prokaryotes? ...
... 2. Why do oligonucleotides containing Shine-Delgarno sequences inhibit translation in prokaryotes? Why don’t they do the same thing in eukaryotes? 3. Why does m7GTP inhibit translation in eukaryotes? Why doesn’t it do so in prokaryotes? ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... STEP 2: Translation A. The process of converting the info. in mRNA into a protein. - Occurs within the cytoplasm. ...
... STEP 2: Translation A. The process of converting the info. in mRNA into a protein. - Occurs within the cytoplasm. ...
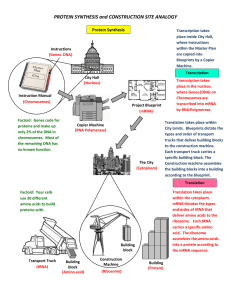
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS and CONSTRUCTION SITE ANALOGY
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
... within the Master Plan are copied into Blueprints by a Copier Machine. ...
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
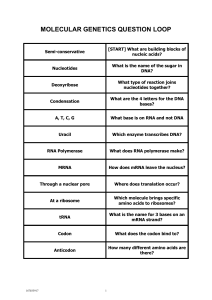
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
... 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for making proteins in cells 14. The numbe ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.