File
... energy in the bond with the amino acid attached which will be used to form the peptide bond. There are three binding sites on the large subunit of the ribosome, but only two can contain tRNA molecules at a time. ...
... energy in the bond with the amino acid attached which will be used to form the peptide bond. There are three binding sites on the large subunit of the ribosome, but only two can contain tRNA molecules at a time. ...
protein synthesis - Science with Mrs Beggs
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
... information • tRNA has an anti-codon which matches a specific codon of mRNA • Each tRNA attaches to a specific amino acid that compliments its anti-codon • There are 20 different tRNA types (one for each type of amino acid) ...
6.3 Protein Synthesis Translation
... The ribosome has 2 sites for the tRNA’s to “lock” into for translation. They are the A (acceptor) site and the P (peptide) site. The process begins with the tRNA carrying methionine locking into the P site. The next tRNA carrying the corresponding amino acid enters A site and the methonine forms a p ...
... The ribosome has 2 sites for the tRNA’s to “lock” into for translation. They are the A (acceptor) site and the P (peptide) site. The process begins with the tRNA carrying methionine locking into the P site. The next tRNA carrying the corresponding amino acid enters A site and the methonine forms a p ...
Packet 9: Transcription and Translation Name: Hour: _____ Notes
... In addition to an amino acid, each ______ molecule has three unpaired bases. These bases, called the ______________, are complementary to one mRNA codon. ...
... In addition to an amino acid, each ______ molecule has three unpaired bases. These bases, called the ______________, are complementary to one mRNA codon. ...
Gene expression PPT
... RNA Processing •5’ GTP cap – G-P-P-P – protects mRNA from degradation and serves as an “attach here” sign for ribosomes •3’ PolyA tail – A-A-A-A-A – inhibits degradation and stabilizes mRNA as it moves out of nucleus ...
... RNA Processing •5’ GTP cap – G-P-P-P – protects mRNA from degradation and serves as an “attach here” sign for ribosomes •3’ PolyA tail – A-A-A-A-A – inhibits degradation and stabilizes mRNA as it moves out of nucleus ...
Protein Synthesis
... Purpose: To create a fictional protein, illustrated by a chain of colorful beads. 1. Imagine that the following string of letters are nitrogen bases on one side of a DNA molecule. The DNA molecule has opened to this particular section of itself (called a gene) to allow a messenger RNA to be formed f ...
... Purpose: To create a fictional protein, illustrated by a chain of colorful beads. 1. Imagine that the following string of letters are nitrogen bases on one side of a DNA molecule. The DNA molecule has opened to this particular section of itself (called a gene) to allow a messenger RNA to be formed f ...
8.5
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
... are made up of twenty types of amino acids. The mRNA message is read as a series of non-overlapping codons, a sequence of three nucleotides that code for an amino acid. Many amino acids are coded for by more than one codon. In general, codons that code for the same amino acid share the same first tw ...
Sept10
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
... rRNA and ribosomes provide the decoder. Ribosomes bring together mRNA and tRNA, and catalyze the translation of an mRNA into a polypeptide chain. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis. Ribosomes create peptide bonds between amino acids to create proteins ...
Reading the Blueprint of Life Chromosome DNA Gene Transcription
... Reading the Blueprint of Life: Translation 1. mRNA must be decoded by the ribosome Message from DNA the Gene! Instructions to ribosome on how to assemble a protein mRNA Code words are called Codons Codons are 3 base pairs long Every message has a start codon Every message has a stop cod ...
... Reading the Blueprint of Life: Translation 1. mRNA must be decoded by the ribosome Message from DNA the Gene! Instructions to ribosome on how to assemble a protein mRNA Code words are called Codons Codons are 3 base pairs long Every message has a start codon Every message has a stop cod ...
Protein Synthesis A gene is a segment of DNA that is located on a
... Cells have three major types of RNA. Each plays a different role in protein synthesis. 1. messenger RNA (mRNA)- a single stranded molecule that carries the instructions from a gene to make a protein. It carries the genetic message from DNA to the ribosomes. 2. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)- It is part of the ...
... Cells have three major types of RNA. Each plays a different role in protein synthesis. 1. messenger RNA (mRNA)- a single stranded molecule that carries the instructions from a gene to make a protein. It carries the genetic message from DNA to the ribosomes. 2. ribosomal RNA (rRNA)- It is part of the ...
RNA & Protein Synthesis
... 1) Title (reflects main concept of poem) 2 ) Minimum 2 stanzas 4 lines each (grouping of lines, set off by a space, that usually has a set pattern of meter and rhyme) ...
... 1) Title (reflects main concept of poem) 2 ) Minimum 2 stanzas 4 lines each (grouping of lines, set off by a space, that usually has a set pattern of meter and rhyme) ...
Mutation
... • Purpose is sometimes to allow for promiscuous basepairing: Inosine in the 1st “wobble” position of anticodon can bind to 3rd U, C or A in codon. • This means that fewer different tRNAs are required. • Others play a structural role. ...
... • Purpose is sometimes to allow for promiscuous basepairing: Inosine in the 1st “wobble” position of anticodon can bind to 3rd U, C or A in codon. • This means that fewer different tRNAs are required. • Others play a structural role. ...
CENTRAL DOGMA AND GENE REGULATION
... 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and requires mRNA, tRNA and rRNA. Each plays a different role. mRNA has the codon (a string of three b ...
... 3. A cap is added at the start site and a poly A++ tail is added at to the termination site. 4. The resulting mRNA is called “transcript”. Translation occurs in the cytoplasm on the ribosomes (rER) and requires mRNA, tRNA and rRNA. Each plays a different role. mRNA has the codon (a string of three b ...
Poster
... Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are major targets of antibiotics. While translation is a universally conserved cellular process, the ability of drugs to target prokaryotic ribosomes depends on subtle variations from eukaryotic ribosomes. The ribosome is composed of ribosomal RNA ...
... Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are major targets of antibiotics. While translation is a universally conserved cellular process, the ability of drugs to target prokaryotic ribosomes depends on subtle variations from eukaryotic ribosomes. The ribosome is composed of ribosomal RNA ...
Protein Synthesis
... mRNA is short and disposable (more can easily be made), so it is perfect for traveling out into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. CAGUCUAGG UCCAUGAAG UGACCCUGA ...
... mRNA is short and disposable (more can easily be made), so it is perfect for traveling out into the cytoplasm to the ribosomes. CAGUCUAGG UCCAUGAAG UGACCCUGA ...
Mock Exam 2BY330 Summer 2014 Assume that 4 molecules of
... 19. Eukaryotic ribosomal subunits are assembled in the _______________________ region of the ______________________. Each subunit is made up of some combination of 4 _________ molecules and about ________ proteins. _________________ ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the __________________ region of th ...
... 19. Eukaryotic ribosomal subunits are assembled in the _______________________ region of the ______________________. Each subunit is made up of some combination of 4 _________ molecules and about ________ proteins. _________________ ribosomal RNA is synthesized in the __________________ region of th ...
Ribosomes (20-30nm)
... Ribosomes (20-30nm) Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into p ...
... Ribosomes (20-30nm) Small organelles often attached to the ER but also found in the cytoplasm Large (protein) and small (rRNA) subunits form the functional ribosome o Subunits bind with mRNA in the cytoplasm o This starts translation of mRNA for protein synthesise (assembly of amino acids into p ...
Sex linked inheritance, sex linkage in Drosophila and man, XO, XY
... Amino Acids Are First Activated by ATP and then transfer to tRNA to produce aminoacyl-tRNA (aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase). The activated tRNA is bound in the P site on the ribosome. ...
... Amino Acids Are First Activated by ATP and then transfer to tRNA to produce aminoacyl-tRNA (aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase). The activated tRNA is bound in the P site on the ribosome. ...
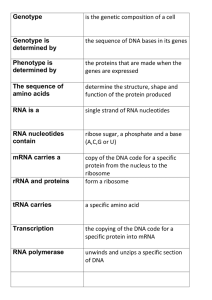
The sequence of amino acids
... copy of the DNA code for a specific protein from the nucleus to the ...
... copy of the DNA code for a specific protein from the nucleus to the ...
Translation: A Four
... • In short, it takes LOTS of energy to synthesize proteins. • A portion of that energy has to do with how the proteins are sequentially synthesized: once 25 amino acids (more or less) are linked by peptide bonds during translation, the AUG site is available/exposed for binding by ANOTHER 70S ribosom ...
... • In short, it takes LOTS of energy to synthesize proteins. • A portion of that energy has to do with how the proteins are sequentially synthesized: once 25 amino acids (more or less) are linked by peptide bonds during translation, the AUG site is available/exposed for binding by ANOTHER 70S ribosom ...
bio12_sm_07_3
... simulation. Both experiences merge to build a fuller understanding of how proteins are synthesized. 7.3 Section Questions, page 331 1. In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the key steps in the initiation of translation are the association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. ...
... simulation. Both experiences merge to build a fuller understanding of how proteins are synthesized. 7.3 Section Questions, page 331 1. In both eukaryotes and prokaryotes, the key steps in the initiation of translation are the association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. ...
Translation - Genes to proteins
... synthesized, but how is the information in the mRNA molecule used to direct the assembly of amino acids into a protein? The primary structure of a protein is the number and order of amino acids; there are 20 amino acids that can be found in proteins, but there are only four nitrogenous bases used in ...
... synthesized, but how is the information in the mRNA molecule used to direct the assembly of amino acids into a protein? The primary structure of a protein is the number and order of amino acids; there are 20 amino acids that can be found in proteins, but there are only four nitrogenous bases used in ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.