LB145-lecture16
... tRNA is a translator/transfers amino acids (Multiple types of RNA) Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase (Charging enzyme loads aas on tRNAs) ...
... tRNA is a translator/transfers amino acids (Multiple types of RNA) Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase (Charging enzyme loads aas on tRNAs) ...
Cell Organelles - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... carry materials through the cytoplasm. “Rough” (have ribosomes attached, “smooth” do not. -Proteins are stored here. Also puts proteins into packages called vesicles, which carry the protein to the surface of the cell. -Patrol the cytoplasm. Contain special proteins that break down molecules and cle ...
... carry materials through the cytoplasm. “Rough” (have ribosomes attached, “smooth” do not. -Proteins are stored here. Also puts proteins into packages called vesicles, which carry the protein to the surface of the cell. -Patrol the cytoplasm. Contain special proteins that break down molecules and cle ...
Ch. 10: Presentation Slides
... • tRNAs are covalently attached to specific amino acids by aminoacyl- synthetases and contain anti-codon complementary to the mRNA codon • Base pairing between the tRNA anti-codon and the mRNA codon on the ribosome places amino acids in the correct linear sequence in translation ...
... • tRNAs are covalently attached to specific amino acids by aminoacyl- synthetases and contain anti-codon complementary to the mRNA codon • Base pairing between the tRNA anti-codon and the mRNA codon on the ribosome places amino acids in the correct linear sequence in translation ...
Proteins
... different monomers in order to make the polymers it requires! The food we eat must be broken down so that it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to ...
... different monomers in order to make the polymers it requires! The food we eat must be broken down so that it is small enough to fit through the cell membrane… THEN, the cell uses those micromolecules to ...
Lecture20_Translation
... The ribosome enhances the rate of peptide bond formation by properly positioning and orienting the substrates and/or excluding water from the active site rather than by chemical ...
... The ribosome enhances the rate of peptide bond formation by properly positioning and orienting the substrates and/or excluding water from the active site rather than by chemical ...
DRAW ENDOSYMBIOTIC THEORY
... 3. Only organelles besides nucleus with double membranes inner cristae/thylakoids have phospholipids like bacteria outer membrane has phospholipids like plasma membrane ...
... 3. Only organelles besides nucleus with double membranes inner cristae/thylakoids have phospholipids like bacteria outer membrane has phospholipids like plasma membrane ...
Protein Synthesis Notes
... between the nitrogen bases are broken by the enzyme. 3. Free RNA nucleotides match the complimentary DNA bases. 4. The phosphate of one RNA nucleotide bonds to the ribose of the next RNA nucleotide. 5. The RNA molecule leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. 6. DNA zips back up- The DNA nitroge ...
... between the nitrogen bases are broken by the enzyme. 3. Free RNA nucleotides match the complimentary DNA bases. 4. The phosphate of one RNA nucleotide bonds to the ribose of the next RNA nucleotide. 5. The RNA molecule leaves the nucleus and goes to the ribosome. 6. DNA zips back up- The DNA nitroge ...
Translation
... • All eukaryotic proteins start translation at AUG, the codon for methionine. This initial methionine is removed after translation in many proteins. There are also methionines coded by AUG in the middle of most proteins. AUG is the only methionine codon. • In addition to AUG, bacteria use GUG and UU ...
... • All eukaryotic proteins start translation at AUG, the codon for methionine. This initial methionine is removed after translation in many proteins. There are also methionines coded by AUG in the middle of most proteins. AUG is the only methionine codon. • In addition to AUG, bacteria use GUG and UU ...
Class11 POGIL Translation Full Win17 all pages
... 11. a. The ribosome contains a small segment of RNA that binds loosely to the ribosome binding site (RBS) in the mRNA. Complementary sequence in the ribosome is not exact, but is a pyrimidine-rich region. Circle the likely RBS in this mRNA. a. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ ...
... 11. a. The ribosome contains a small segment of RNA that binds loosely to the ribosome binding site (RBS) in the mRNA. Complementary sequence in the ribosome is not exact, but is a pyrimidine-rich region. Circle the likely RBS in this mRNA. a. Is the RBS closer to the 5' or 3' end of the mRNA? _____ ...
Organelles Day 3 - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
... purpose that allows the cell to function. To be inducted into the biology club, you need to know all the organelles. ...
Protein Synthesis Bead Activity
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
... __________________________________ and it occurs in the ______________________ of cells. mRNA leaves the nucleus to find a _______________. Next, we start the second part of protein synthesis called _____________________________ and it happens in the _____________________ of cells. During this proce ...
Bio1A Unit 1-3 The Cell Notes File
... 3. Genetic Material: i.e.- DNA • Directs cells activity • Allows reproduction 4. Ribosomes – Protein production ...
... 3. Genetic Material: i.e.- DNA • Directs cells activity • Allows reproduction 4. Ribosomes – Protein production ...
U - Lakewood City Schools
... Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
... Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
Translational Initiation in Eukaryotes
... Observation: Some viral mRNAs (such as Polio virus) are not capped, yet are preferentially translated. Some are also translated via internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) (apparently without scanning to them). Mechanism: Viral protease clips off N-terminus of eIF4G, so it can’t bind eIF4E. eIF4G bind ...
... Observation: Some viral mRNAs (such as Polio virus) are not capped, yet are preferentially translated. Some are also translated via internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) (apparently without scanning to them). Mechanism: Viral protease clips off N-terminus of eIF4G, so it can’t bind eIF4E. eIF4G bind ...
From DNA to Protein: Transcription and Translation
... Another Translation Video with Ribosomes click once on image to start ...
... Another Translation Video with Ribosomes click once on image to start ...
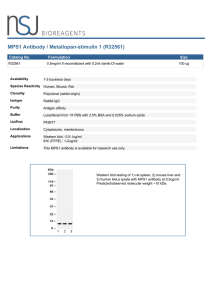
MPS1 Antibody / Metallopan-stimulin 1 (R32561)
... 40S ribosomal protein S27, also known as Metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species ...
... 40S ribosomal protein S27, also known as Metallopan-stimulin 1 or MPS-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS27 gene. Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species ...
Ch.4 Cell Notes - Milan Area Schools
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
... Puts finishing touches on proteins and lipids that arrive from ER Packages finished material for shipment to ...
Unit 7 Preparation
... ribosomes required by the cell. Ribosomes are tiny organelles that are the sites of protein synthesis in cells. Ribosomes are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotes, ribosomes are 20 nm to 30 nm in diameter; they are slightly smaller in prokaryotes. In both types of cells, rib ...
... ribosomes required by the cell. Ribosomes are tiny organelles that are the sites of protein synthesis in cells. Ribosomes are found in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. In eukaryotes, ribosomes are 20 nm to 30 nm in diameter; they are slightly smaller in prokaryotes. In both types of cells, rib ...
Ch - cloudfront.net
... the codons represent the different amino acids: _______ - ________ - ________ (use fig. 12-17) • _______ amino acids can be specified by _______ than one ________ • there is one codon _____ that can either specify the amino acid ___________ or serve as a “_______” codon for protein synthesis • there ...
... the codons represent the different amino acids: _______ - ________ - ________ (use fig. 12-17) • _______ amino acids can be specified by _______ than one ________ • there is one codon _____ that can either specify the amino acid ___________ or serve as a “_______” codon for protein synthesis • there ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... • Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
... • Proteins, however, are made in the cytosol of cells by organelles called ribosomes • Ribosomes may be free in the cytosol or attached to the surface of rough ER ...
Protein synthesis - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Elongation: The ribosome moves along the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. Each triplet is the code for a specific amino acid. This is called the reading frame. The tRNA delivers the appropriate amino acid and the polypeptide elongates. The 1st codon is the START codon AUG. AUG is the code for the a ...
... Elongation: The ribosome moves along the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. Each triplet is the code for a specific amino acid. This is called the reading frame. The tRNA delivers the appropriate amino acid and the polypeptide elongates. The 1st codon is the START codon AUG. AUG is the code for the a ...
Animation Script for Translation
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
Ribosome

The ribosome (/ˈraɪbɵˌzoʊm/) is a large and complex molecular machine, found within all living cells, that serves as the site of biological protein synthesis (translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules. Ribosomes consist of two major components: the small ribosomal subunit, which reads the RNA, and the large subunit, which joins amino acids to form a polypeptide chain. Each subunit is composed of one or more ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules and a variety of proteins. The ribosomes and associated molecules are also known as the translational apparatus.The sequence of DNA encoding for a protein may be copied many times into RNA chains of a similar sequence. Ribosomes can bind to an RNA chain and use it as a template for determining the correct sequence of amino acids in a particular protein. Amino acids are selected, collected and carried to the ribosome by transfer RNA (tRNA molecules), which enter one part of the ribosome and bind to the messenger RNA chain. The attached amino acids are then linked together by another part of the ribosome. Once the protein is produced, it can then fold to produce a specific functional three-dimensional structure.A ribosome is made from complexes of RNAs and proteins and is therefore a ribonucleoprotein. Each ribosome is divided into two subunits: 1. a smaller subunit which binds to a larger subunit and the mRNA pattern, and 2. a larger subunit which binds to the tRNA, the amino acids, and the smaller subunit. When a ribosome finishes reading an mRNA molecule, these two subunits split apart. Ribosomes are ribozymes, because the catalytic peptidyl transferase activity that links amino acids together is performed by the ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are often embedded in the intercellular membranes that make up the rough endoplasmic reticulum.Ribosomes from bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes (the three domains of life on Earth) differ in their size, sequence, structure, and the ratio of protein to RNA. The differences in structure allow some antibiotics to kill bacteria by inhibiting their ribosomes, while leaving human ribosomes unaffected. In bacteria and archaea, more than one ribosome may move along a single mRNA chain at one time, each ""reading"" its sequence and producing a corresponding protein molecule. The ribosomes in the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells functionally resemble many features of those in bacteria, reflecting the likely evolutionary origin of mitochondria.