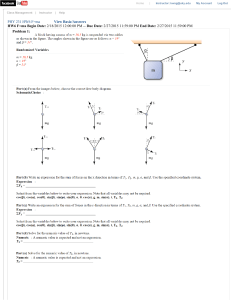
Angle Relationships in Polygons
... The average of 6 numbers is 31. When a new number is introduced, the average is now 33. What is the new number? ...
... The average of 6 numbers is 31. When a new number is introduced, the average is now 33. What is the new number? ...
PHY 231 HW6 F=ma View Basic/Answers HW6 F=ma Begin Date: 2
... Problem 7: Full solution not currently available at this time. Cranes use a system of two pulleys to provide mechanical advantage, which reduces the force they need to apply to lift a particular weight (two such possible configurations are shown in the figure). A crane is attempting to lift a com ...
... Problem 7: Full solution not currently available at this time. Cranes use a system of two pulleys to provide mechanical advantage, which reduces the force they need to apply to lift a particular weight (two such possible configurations are shown in the figure). A crane is attempting to lift a com ...
Problem Set #5
... round-robin tournament, the total number of wins by all teams equals the total number of losses – do you see why? Once you do, determine the total number of wins if n teams are involved. Problem 2: As a follow-up to Problem 1, can you show that for any roundrobin tournament, the sum of the squares o ...
... round-robin tournament, the total number of wins by all teams equals the total number of losses – do you see why? Once you do, determine the total number of wins if n teams are involved. Problem 2: As a follow-up to Problem 1, can you show that for any roundrobin tournament, the sum of the squares o ...
The Niels Henrik Abel mathematics competition 2015–2016
... Do not turn the page until told to by your teacher! The first round of the Abel competition consists of 20 multiple choice problems to be solved in 100 minutes. Only one of the five alternatives is correct. Write your answers in the lower left hand side of the form. You get 5 points for each correct ...
... Do not turn the page until told to by your teacher! The first round of the Abel competition consists of 20 multiple choice problems to be solved in 100 minutes. Only one of the five alternatives is correct. Write your answers in the lower left hand side of the form. You get 5 points for each correct ...
Weber problem

In geometry, the Weber problem, named after Alfred Weber, is one of the most famous problems in location theory. It requires finding a point in the plane that minimizes the sum of the transportation costs from this point to n destination points, where different destination points are associated with different costs per unit distance.The Weber problem generalizes the geometric median, which assumes transportation costs per unit distance are the same for all destination points, and the problem of computing the Fermat point, the geometric median of three points. For this reason it is sometimes called the Fermat–Weber problem, although the same name has also been used for the unweighted geometric median problem. The Weber problem is in turn generalized by the attraction–repulsion problem, which allows some of the costs to be negative, so that greater distance from some points is better.