Anhydrides, Esters and Amides
... • In practice what occurs if the two are mixed is an acidbase reaction to form an ammonium salt. • If this salt is heated to a high enough temperature, water is eliminated and an amide forms. O CH3 C-OH + H2 NCH2 CH3 ...
... • In practice what occurs if the two are mixed is an acidbase reaction to form an ammonium salt. • If this salt is heated to a high enough temperature, water is eliminated and an amide forms. O CH3 C-OH + H2 NCH2 CH3 ...
MS PowerPoint
... Protic solvent improves the reaction towards 13PD by facilitating proton transfer from solid acid to secondary alcohol by stabilizing a charged intermediate. Additives improving the conversion and selctivity towards 13PD ...
... Protic solvent improves the reaction towards 13PD by facilitating proton transfer from solid acid to secondary alcohol by stabilizing a charged intermediate. Additives improving the conversion and selctivity towards 13PD ...
05.Antibiotics of the aromatic and heterocyclic rows
... Streptomyces venezuelae on the medium (broth, glycerol, molasses and mineral salts) at 23-27 °С and strong aeration for 89 hours. After the filtering of the mycelium fungus antibiotic is extracted and purified by the chromatographic. Laevomycetin - the first antibiotic, which began to obtain by the ...
... Streptomyces venezuelae on the medium (broth, glycerol, molasses and mineral salts) at 23-27 °С and strong aeration for 89 hours. After the filtering of the mycelium fungus antibiotic is extracted and purified by the chromatographic. Laevomycetin - the first antibiotic, which began to obtain by the ...
CHAPTER 12 Study Guide
... 41. a. 11.3 mol CO, 22.5 mol H2 b. 112 g CO, 16.0 g H2 c. 11.4 g H2 42. a. 372 g F2 b. 1.32 g NH3 c. 123 g N2F4 43. The coefficients indicate the relative number of moles (or particles) of reactants and products. 44. a. 51.2 g H2O b. 5.71 × 1023 molecules NH3 c. 23.2 g Li3N 45. The amount of the lim ...
... 41. a. 11.3 mol CO, 22.5 mol H2 b. 112 g CO, 16.0 g H2 c. 11.4 g H2 42. a. 372 g F2 b. 1.32 g NH3 c. 123 g N2F4 43. The coefficients indicate the relative number of moles (or particles) of reactants and products. 44. a. 51.2 g H2O b. 5.71 × 1023 molecules NH3 c. 23.2 g Li3N 45. The amount of the lim ...
Copper perchlorate: Efficient acetylation catalyst
... ing agent i.e. acetic anhydride, the reactions proceeded slightly faster. In the absence of catalyst at room temperature the reactions are unfinished even after longer time like 24 h. Refluxing at 85 ◦ C drives the reaction faster but requires about 2 h for heteroatoms [2d]. For benzaldehyde refluxi ...
... ing agent i.e. acetic anhydride, the reactions proceeded slightly faster. In the absence of catalyst at room temperature the reactions are unfinished even after longer time like 24 h. Refluxing at 85 ◦ C drives the reaction faster but requires about 2 h for heteroatoms [2d]. For benzaldehyde refluxi ...
Organic Chemistry
... different functional group atoms in molecules • Electron-rich atom react with electron-poor atoms. – Nucleophile – electron rich (lone pair; d-) and “nucleusloving”. Donate electron pair to form bond. – Electrophile – electron poor (d+) and “electron-loving”. ...
... different functional group atoms in molecules • Electron-rich atom react with electron-poor atoms. – Nucleophile – electron rich (lone pair; d-) and “nucleusloving”. Donate electron pair to form bond. – Electrophile – electron poor (d+) and “electron-loving”. ...
Reactions of Alkenes and Alkynes
... • A reaction that results in a loss of electron density by carbon ...
... • A reaction that results in a loss of electron density by carbon ...
Kinetics and mechanism of oxidation of alcohols
... CH2Cl2 to give 97 % yield of nonhygroscopic, homogeneous material identified by its 1H NMR spectrum. Product analysis The product analysis was carried out under kinetic conditions, i.e., with excess substrate over the oxidant. The products of oxidation were the corresponding aldehydes and ketones an ...
... CH2Cl2 to give 97 % yield of nonhygroscopic, homogeneous material identified by its 1H NMR spectrum. Product analysis The product analysis was carried out under kinetic conditions, i.e., with excess substrate over the oxidant. The products of oxidation were the corresponding aldehydes and ketones an ...
Exam 3 - Napa Valley College
... 4) Please give the complete mechanism for the cleavage of the ester, ethyl acetate, with H+ and water. Note: Some people try to draw the forward reaction (making of the ester) and then draw all the arrows backwards. Please refrain from doing so. Besides, it ...
... 4) Please give the complete mechanism for the cleavage of the ester, ethyl acetate, with H+ and water. Note: Some people try to draw the forward reaction (making of the ester) and then draw all the arrows backwards. Please refrain from doing so. Besides, it ...
Poly(ethylene glycol)-supported a,a,a
... be a useful new tool in the synthetic chemistry toolbox. Along this line, it is interesting to note that in the synthesis of epothilones by Ley and coworkers in which all steps were carried out using polymer-supported reagents, the final conversion of epothilone C to epoxide containing epothilone A w ...
... be a useful new tool in the synthetic chemistry toolbox. Along this line, it is interesting to note that in the synthesis of epothilones by Ley and coworkers in which all steps were carried out using polymer-supported reagents, the final conversion of epothilone C to epoxide containing epothilone A w ...
Alcohols and Phenols
... A positively polarized OH hydrogen atom from one molecule is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on a negatively polarized oxygen atom of another molecule. This produces a force that holds the two molecules together These intermolecular attractions are present in solution but not in the gas phase ...
... A positively polarized OH hydrogen atom from one molecule is attracted to a lone pair of electrons on a negatively polarized oxygen atom of another molecule. This produces a force that holds the two molecules together These intermolecular attractions are present in solution but not in the gas phase ...
Salame - The City College of New York
... The CCNY policy on academic integrity will be followed in this course. The document can be found through the CCNY website by clicking on Current Students Academic Services Policy on Academic Integrity. All students must read the details regarding plagiarism and cheating in order to be familiar w ...
... The CCNY policy on academic integrity will be followed in this course. The document can be found through the CCNY website by clicking on Current Students Academic Services Policy on Academic Integrity. All students must read the details regarding plagiarism and cheating in order to be familiar w ...
Amide bond formation and peptide coupling
... thermodynamics as the equilibrium shown in Scheme 1 and lies on the side of hydrolysis rather than synthesis.3 The direct condensation of the salt can be achieved at high temperature (160–180 8C),4 which is usually quite incompatible with the presence of other functionalities (see also Section 2.6.3 ...
... thermodynamics as the equilibrium shown in Scheme 1 and lies on the side of hydrolysis rather than synthesis.3 The direct condensation of the salt can be achieved at high temperature (160–180 8C),4 which is usually quite incompatible with the presence of other functionalities (see also Section 2.6.3 ...
Ch 10 Haloalkanes n haloarenes
... Cl bond in tert-butyl chloride gives 3 carbocation which is highly stable and favourable for SN¹ mechanism. Moreover, tert-butyl chloride (3°) bring a bulky molecule has steric hindrance which will not allow SN² mechanism to take place. Hence only SN1 mechanism can occur in tert-butyl chloride. Howe ...
... Cl bond in tert-butyl chloride gives 3 carbocation which is highly stable and favourable for SN¹ mechanism. Moreover, tert-butyl chloride (3°) bring a bulky molecule has steric hindrance which will not allow SN² mechanism to take place. Hence only SN1 mechanism can occur in tert-butyl chloride. Howe ...
10. Alkyl Halides
... If the concentration of alkyl halide is doubled, halfed or quadrupled the reaction rate will double, half or quadruple. If, on the other hand, the concentration of nucleophile is changed the reaction rate will be unaffected If the rate of this reaction does not depend upon the concentration of t ...
... If the concentration of alkyl halide is doubled, halfed or quadrupled the reaction rate will double, half or quadruple. If, on the other hand, the concentration of nucleophile is changed the reaction rate will be unaffected If the rate of this reaction does not depend upon the concentration of t ...
reactions of the conjugated dienes butadiene and isoprene alone
... that the reactions often take place under somewhat milder conditions than are usually employed (see, e.g., Adams et al., 1982c; Ballantine et al., 1981a). The reactions of monoalkenes over acidic montmorillonite catalysts have been extensively studied, both alone and in the presence ofnucleophiles, ...
... that the reactions often take place under somewhat milder conditions than are usually employed (see, e.g., Adams et al., 1982c; Ballantine et al., 1981a). The reactions of monoalkenes over acidic montmorillonite catalysts have been extensively studied, both alone and in the presence ofnucleophiles, ...
Amino acids
... 1-Loss of biological activities of proteins 2- Permanent disorder (irreversible) in common cases (reversible in rare cases). Denaturation can be produced by: 1-Physical agents as heat, ultaviolet rays, X rays… etc 2-Chemical agents: as strong acids, alkalies, heavy metals N.B. Protreolytic enzymes ( ...
... 1-Loss of biological activities of proteins 2- Permanent disorder (irreversible) in common cases (reversible in rare cases). Denaturation can be produced by: 1-Physical agents as heat, ultaviolet rays, X rays… etc 2-Chemical agents: as strong acids, alkalies, heavy metals N.B. Protreolytic enzymes ( ...
Amino acids
... 1-Loss of biological activities of proteins 2- Permanent disorder (irreversible) in common cases (reversible in rare cases). Denaturation can be produced by: 1-Physical agents as heat, ultaviolet rays, X rays… etc 2-Chemical agents: as strong acids, alkalies, heavy metals N.B. Protreolytic enzymes ( ...
... 1-Loss of biological activities of proteins 2- Permanent disorder (irreversible) in common cases (reversible in rare cases). Denaturation can be produced by: 1-Physical agents as heat, ultaviolet rays, X rays… etc 2-Chemical agents: as strong acids, alkalies, heavy metals N.B. Protreolytic enzymes ( ...
chm238f02.exam2
... (b) Given pKas: CH3OH = 45; CH3OH = 16; H2 = 38; H2O = 16; PhOH = 10: Predict the direction and Keq of the reaction above. ...
... (b) Given pKas: CH3OH = 45; CH3OH = 16; H2 = 38; H2O = 16; PhOH = 10: Predict the direction and Keq of the reaction above. ...
Şenol, O.İ., Viljava, T.-R., Krause, AOI
... the deesterification reaction yields carboxylic acids and methanol. The water required for the reaction may be supplied by the dehydration of the alcohols in path I. The formed carboxylic acids are either reduced to alcohol releasing a mole of water or decarboxylated to alkenes followed by hydrogena ...
... the deesterification reaction yields carboxylic acids and methanol. The water required for the reaction may be supplied by the dehydration of the alcohols in path I. The formed carboxylic acids are either reduced to alcohol releasing a mole of water or decarboxylated to alkenes followed by hydrogena ...
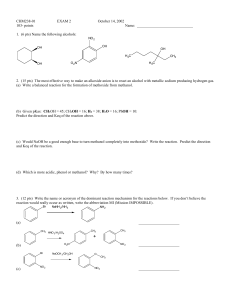
CHM238-01 EXAM 2 October 14, 2002 103
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
... 5. (12 pts) Preparation of alcohols by Grignard reagents reacted with C=O compounds is very important. (a) If the Grignard reagent were phenyl Grignard, PhMgBr, what C=O compound would be the best one to use in order to make the following alcohols. If it doesn’t work, write NR. (b) If the Grignard ...
Carbonyl α-substitution and Condensation Reactions
... Substituted arylamines can be either more basic or less basic than aniline, depending on the substituent. Electron-donating substituents, such as –CH3 and – OCH3, which increase the reactivity of an aromatic ring toward electrophilic substitution, also increase the basicity of the corresponding aryl ...
... Substituted arylamines can be either more basic or less basic than aniline, depending on the substituent. Electron-donating substituents, such as –CH3 and – OCH3, which increase the reactivity of an aromatic ring toward electrophilic substitution, also increase the basicity of the corresponding aryl ...
Petasis reaction

The Petasis reaction (alternatively called the Petasis borono–Mannich (PBM) reaction) is the chemical reaction of an amine, aldehyde, and vinyl- or aryl-boronic acid to form substituted amines.Reported in 1993 by Nicos Petasis as a practical method towards the synthesis of a geometrically pure antifungal agent, naftifine, the Petasis reaction can be described as a variation of the Mannich reaction. Rather than generating an enolate to form the substituted amine product, in the Petasis reaction, the vinyl group of the organoboronic acid serves as the nucleophile. In comparison to other methods of generating allyl amines, the Petasis reaction tolerates a multifunctional scaffold, with a variety of amines and organoboronic acids as potential starting materials. Additionally, the reaction does not require anhydrous or inert conditions. As a mild, selective synthesis, the Petasis reaction is useful in generating α-amino acids, and is utilized in combinatorial chemistry and drug discovery.