Alkenes—The Products of Elimination
... General Features of Elimination • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
... General Features of Elimination • Removal of the elements HX is called dehydrohalogenation. • Dehydrohalogenation is an example of elimination. • The curved arrow formalism shown below illustrates how four bonds are broken or formed in the process. ...
Chem 231 Exam #3 Study Guide
... Know what the free energy diagram looks like for an SN1 versus an SN2 reaction and be able to label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states Know the factors that effect SN2, SN1, E1, and E2 reactions Know the order of substrate reactivities for the different reactions Know how ...
... Know what the free energy diagram looks like for an SN1 versus an SN2 reaction and be able to label the reactants, products, intermediates, and transition states Know the factors that effect SN2, SN1, E1, and E2 reactions Know the order of substrate reactivities for the different reactions Know how ...
Alkanes
... What is the general formula for a dihalogenation reaction? CnH2n+2 + 2X2 CnH2nX2 + 2HX ...
... What is the general formula for a dihalogenation reaction? CnH2n+2 + 2X2 CnH2nX2 + 2HX ...
The Other Side of NHCs: NHCs in Transition Metal Catalysis
... •Employing NHCs as ligands for palladium in the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions has several benefits. •The electron donating properties of NHCs aids oxidative addition. •NHC-palladium complexes can catalyzed the coupling of unactivated aryl chlorides and or sterically encumbered coupling partners. ...
... •Employing NHCs as ligands for palladium in the Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions has several benefits. •The electron donating properties of NHCs aids oxidative addition. •NHC-palladium complexes can catalyzed the coupling of unactivated aryl chlorides and or sterically encumbered coupling partners. ...
Reductive etherification of substituted cyclohexanones with
... biporous zeolite.1 It has been shown that it contains two independent pore systems,2,3 one defined by sinusoidal 10-membered ring channels extended in two dimensions, and the other by large 12-membered ring supercages (7.1 3 7.1 3 18.1 Å) connected by 10-membered ring channels. The material has a hi ...
... biporous zeolite.1 It has been shown that it contains two independent pore systems,2,3 one defined by sinusoidal 10-membered ring channels extended in two dimensions, and the other by large 12-membered ring supercages (7.1 3 7.1 3 18.1 Å) connected by 10-membered ring channels. The material has a hi ...
Seminar_1 1. Classification and nomenclature of organic
... Reactions of organic compounds always involve the making and breaking of covalent bonds. A covalent bond may break in two fundamentally different ways. The bond may break so that one fragment takes away both electrons of the bond, leaving the other fragment with an empty orbital. This kind of cleava ...
... Reactions of organic compounds always involve the making and breaking of covalent bonds. A covalent bond may break in two fundamentally different ways. The bond may break so that one fragment takes away both electrons of the bond, leaving the other fragment with an empty orbital. This kind of cleava ...
The Chemistry of Alkyl Halides - Welcome to people.pharmacy
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
... In a stereospecific reaction with a given stereochemistry—anti-elimination, in this case—a diastereomeric product requires a diastereomeric starting material (either enantiomer). The easiest path to the answer is to convert the starting material in Eq. 9.40a into its diastereomer by the interchange ...
Octenes from E1 versus E2 Eliminations
... Fill a 10 x 100 mm reaction tube to the 0.5 mL mark with 1-octanol (n-octyl alcohol) and insert a 1/2-inch stir bar. Add 5 drops of conc. sulfuric acid. While stirring, heat the reaction for 20 to 30 minutes. At first you will see water droplets and a cloudy liquid condensing on the walls of the rea ...
... Fill a 10 x 100 mm reaction tube to the 0.5 mL mark with 1-octanol (n-octyl alcohol) and insert a 1/2-inch stir bar. Add 5 drops of conc. sulfuric acid. While stirring, heat the reaction for 20 to 30 minutes. At first you will see water droplets and a cloudy liquid condensing on the walls of the rea ...
Chapter 20 Amines-part 2
... Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of Diazonium Ion by Cl, Br or CN t Mechanism of the Sandmeyer reaction is not well -understood but is thought to occur via radicals ...
... Sandmeyer Reaction: Replacement of Diazonium Ion by Cl, Br or CN t Mechanism of the Sandmeyer reaction is not well -understood but is thought to occur via radicals ...
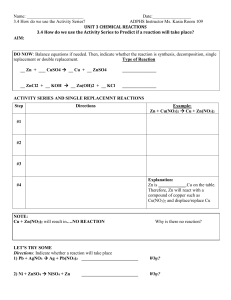
3.4 How do we use the Activity Series
... 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? ...
... 1. What is the most reactive nonmetal according to the table?___________________________________ 2. ______________________will react with anything below it 3. Will the above reaction take place?_____________________________________________________ 4. Will the reverse reaction take place, Cl2 + 2NaF? ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... attached to an arene ring, it is an aryl halide. Common names of halocarbons begin with the name of the alkyl or aryl group and end with the name of the halogen with an -ide ending. ...
... attached to an arene ring, it is an aryl halide. Common names of halocarbons begin with the name of the alkyl or aryl group and end with the name of the halogen with an -ide ending. ...
Catalytic Synthesis of Organophosphorus Compounds from
... and commercial interests have prompted us to investigate “chlorine free” protocols for the direct conversion of a various low-valent phosphorus-containing compounds (including elemental (white and red) phosphorus and such a waste from phosphorus industry as an effluent phosphine- and phosphorus cont ...
... and commercial interests have prompted us to investigate “chlorine free” protocols for the direct conversion of a various low-valent phosphorus-containing compounds (including elemental (white and red) phosphorus and such a waste from phosphorus industry as an effluent phosphine- and phosphorus cont ...
Experiment 7 — Nucleophilic Substitution
... about 3 minutes, warm the tube(s) to 40-50°C and record the time required for precipitation. If no reaction is visible after about 10 min, give up — we'll call that unreactive. On the other hand, if you want to compare reactions that appear to be instantaneous at room temperature, you'll need to slo ...
... about 3 minutes, warm the tube(s) to 40-50°C and record the time required for precipitation. If no reaction is visible after about 10 min, give up — we'll call that unreactive. On the other hand, if you want to compare reactions that appear to be instantaneous at room temperature, you'll need to slo ...
Exam 3 Review
... Describe hydrogen bonding in alcohols, and compare alcohol polarity to ether polarity. What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synt ...
... Describe hydrogen bonding in alcohols, and compare alcohol polarity to ether polarity. What are the acid/base properties of alcohols? Rank these compounds in order of acidity. How are Grignard reagents prepared? Describe their bond polarity. How do organolithiums react? Use the Williamson ether synt ...
Slide 1 - Mrs. Reed Science Classes
... After calculating the amount of reactant B required to completely react with A, then comparing that amount with the amount of B available, one can determine the a. limiting reactant. b. rate of the reaction. c. energy released in the reaction. d. pathway of the reaction. ...
... After calculating the amount of reactant B required to completely react with A, then comparing that amount with the amount of B available, one can determine the a. limiting reactant. b. rate of the reaction. c. energy released in the reaction. d. pathway of the reaction. ...
organic synthesis
... Which of the following produce a mixture of alcohols when treated with OH¯(aq)? • C2H5CHBrCH3 ...
... Which of the following produce a mixture of alcohols when treated with OH¯(aq)? • C2H5CHBrCH3 ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... a) Inert does’t mean unreactive; Inert doesn’t mean thermodynamically stable b) Inert does mean slow to react (also known as Robust) [Fe((H2O)5F]2+ = labile, but it is very thermodynamically stable [Co(NH3)6]3+ = inert, but thermodynamically unstable c) Inert complexes react slowly, so their product ...
... a) Inert does’t mean unreactive; Inert doesn’t mean thermodynamically stable b) Inert does mean slow to react (also known as Robust) [Fe((H2O)5F]2+ = labile, but it is very thermodynamically stable [Co(NH3)6]3+ = inert, but thermodynamically unstable c) Inert complexes react slowly, so their product ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Swapping
... Note: NaOH or KOH, NaCN etc is the source of The OH¯ , and CN¯ above as they are ionic But we can ignore the metals as spectators NaOH ---> Na⁺ + OH⁻ ...
... Note: NaOH or KOH, NaCN etc is the source of The OH¯ , and CN¯ above as they are ionic But we can ignore the metals as spectators NaOH ---> Na⁺ + OH⁻ ...
Arenes test - A-Level Chemistry
... In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
... In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of scientific terms. Describe how benzene could be converted into nitrobenzene. State the reagents and conditions, give a balanced equation for each stage and show the structure of the product. ...
PART 3 Principles and Applications of Organometallics in Catalysis
... what catalysts do and don't do The effect of a catalyst is to change the rate of conversion of a substrate into products, but they do not change the position of an equilibrium. The thermodynamics of the reaction concerned have to be favourable at the outset; catalysts can't perform the miracle of pu ...
... what catalysts do and don't do The effect of a catalyst is to change the rate of conversion of a substrate into products, but they do not change the position of an equilibrium. The thermodynamics of the reaction concerned have to be favourable at the outset; catalysts can't perform the miracle of pu ...
11.Unit 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
... Q3. When an alkyl halide is treated with ethanolic solution of KCN, the major product is alkylcyanide where as if alkyl halide is treated with AgCN, the major product is alkyl isocyanide. Ans. KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is stronger than C-N bond. So RCN is major produc ...
... Q3. When an alkyl halide is treated with ethanolic solution of KCN, the major product is alkylcyanide where as if alkyl halide is treated with AgCN, the major product is alkyl isocyanide. Ans. KCN is ionic they can attach through C or N but C-C bond is stronger than C-N bond. So RCN is major produc ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... Inorganic Oxidation and Reduction 1) Oxidation = loss of electrons: Cu+ 2) Reduction = gain of electrons: Zn2+ ...
... Inorganic Oxidation and Reduction 1) Oxidation = loss of electrons: Cu+ 2) Reduction = gain of electrons: Zn2+ ...
An Efficient Synthetic Route to Glycoamino Acid Building Blocks for
... spectrometry. Such a dimer is formed by further condensation of 2a to starting sugar. The formation of this dimer in up to 10% yield has also been observed in thermal reactions8b and has been shown not to interfere with subsequent acylations. The formation of dimer was significantly increased at hig ...
... spectrometry. Such a dimer is formed by further condensation of 2a to starting sugar. The formation of this dimer in up to 10% yield has also been observed in thermal reactions8b and has been shown not to interfere with subsequent acylations. The formation of dimer was significantly increased at hig ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... We can begin to connect this reaction type with what we have seen earlier by thinking about the mechanism. We notice that the O- end of the group (called an alkoxide) which is doing the substituting is very much like the oxygen in an OH-. Since we've seen the OH- act as a nucleophile when it attacke ...
... We can begin to connect this reaction type with what we have seen earlier by thinking about the mechanism. We notice that the O- end of the group (called an alkoxide) which is doing the substituting is very much like the oxygen in an OH-. Since we've seen the OH- act as a nucleophile when it attacke ...
Exp 19 - Diphenylacetylene_2015
... dibromide. What volume of TEG would be required? 5. The boiling point of TEG is 285 °C. Explain why it is necessary as the solvent in this experiment. Why can’t ethanol be used instead? ...
... dibromide. What volume of TEG would be required? 5. The boiling point of TEG is 285 °C. Explain why it is necessary as the solvent in this experiment. Why can’t ethanol be used instead? ...
Stille reaction

The Stille reaction, or the Migita-Kosugi-Stille coupling, is a chemical reaction widely used in organic synthesis which involves the coupling of an organotin compound (also known as organostannanes) with a variety of organic electrophiles via palladium-catalyzed coupling reaction.The R1 group attached to the trialkyltin is normally sp2-hybridized, including alkenes, and aryl groups; however, conditions have been devised to incorporate both sp3-hybridized groups, such as allylic and benzylic substituents, and sp-hybridized alkynes. These organostannanes are also stable to both air and moisture, and many of these reagents are either commercially available or can be synthesized from literature precedent. However, these tin reagents tend to be highly toxic. X is typically a halide, such as Cl, Br, I, yet pseudohalides such as triflates and sulfonates and phosphates can also be used.The groundwork for the Stille reaction was laid by Colin Eaborn, Toshihiko Migita, and Masanori Kosugi in 1976 and 1977, who explored numerous palladium catalyzed couplings involving organotin reagents. John Stille and David Milstein developed a much milder and more broadly applicable procedure in 1978. Stille’s work on this area might have earned him a share of the 2010 Nobel Prize, which was awarded to Richard Heck, Ei-ichi Negishi, and Akira Suzuki for their work on the Heck, Negishi, and Suzuki coupling reactions. However, Stille died in the plane crash of United Airlines Flight 232 in 1989.Several reviews have been published on the Stille reaction.