JMI Telescopes EZAlign Polar Alignment Scope (Starfinder Version)
... The Initial Polar Alignment — The initial polar alignment can be accomplished with the star-drift method or by using the following instructions. First, you must set the telescope at +90º declination using the mechanical setting circles or a carpenter’s square. This is a mechanical setting, placing t ...
... The Initial Polar Alignment — The initial polar alignment can be accomplished with the star-drift method or by using the following instructions. First, you must set the telescope at +90º declination using the mechanical setting circles or a carpenter’s square. This is a mechanical setting, placing t ...
Click here to view Carolyn`s poster
... The first x-ray telescopes were launched in the 1970’s and the basic theory remains the same today, all x-ray telescopes are space borne, as x-rays from space do not penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere. An x-ray telescope works on the principle of external reflection, essentially an x-ray is ‘bounced’ ...
... The first x-ray telescopes were launched in the 1970’s and the basic theory remains the same today, all x-ray telescopes are space borne, as x-rays from space do not penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere. An x-ray telescope works on the principle of external reflection, essentially an x-ray is ‘bounced’ ...
chris - ESA Earth Online
... calibration. This slightly reduces the aperture area available for useful Earth imaging. During normal Earth imaging, the solar calibration device projects very little light into the main instrument aperture. It is used for calibration when the instrument is over the Antarctic, on the dark side of t ...
... calibration. This slightly reduces the aperture area available for useful Earth imaging. During normal Earth imaging, the solar calibration device projects very little light into the main instrument aperture. It is used for calibration when the instrument is over the Antarctic, on the dark side of t ...
SunRISE Proposal
... Reconnection followed by either resubmergence or expulsion could explain the apparent cancellation of unrelated flux bundles when they are brought together by larger scale flows (such as the supergranular flow). With very high resolution time series of quantitative vector magnetic field measurements ...
... Reconnection followed by either resubmergence or expulsion could explain the apparent cancellation of unrelated flux bundles when they are brought together by larger scale flows (such as the supergranular flow). With very high resolution time series of quantitative vector magnetic field measurements ...
SPECTROHELIOSCOPE DESIGNS
... To adjust the slits, have one blade fixed. The other blade is moveable with finger pressure. Firstly close the two blades a bit tight. Hold the mounted slits up to a light bulb. Look through the closed slits towards the light. Adjust one blade until it barely lets the light through the slit. This is ...
... To adjust the slits, have one blade fixed. The other blade is moveable with finger pressure. Firstly close the two blades a bit tight. Hold the mounted slits up to a light bulb. Look through the closed slits towards the light. Adjust one blade until it barely lets the light through the slit. This is ...
Light & Telescopes
... A telescope’s most important function is to gather as much light as possible. Its second function is to reveal the observed object in as much detail as possible. Often the least important function of a telescope is to magnify objects. Reflecting telescopes, or reflectors, produce images by refle ...
... A telescope’s most important function is to gather as much light as possible. Its second function is to reveal the observed object in as much detail as possible. Often the least important function of a telescope is to magnify objects. Reflecting telescopes, or reflectors, produce images by refle ...
INTL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATIONS
... becomes necessary to guide the telescope during the image exposure. Even the finest, most expensive mounts are plagued by mechanical imperfections or alignment errors, which may produce oblong stars. In Fig. 8 and 9 two pictures of the M81 Galaxy in Ursa Major are shown. The first one is made in con ...
... becomes necessary to guide the telescope during the image exposure. Even the finest, most expensive mounts are plagued by mechanical imperfections or alignment errors, which may produce oblong stars. In Fig. 8 and 9 two pictures of the M81 Galaxy in Ursa Major are shown. The first one is made in con ...
Relating axial motion of optical elements to focal shift
... These graphs can be used to get a general idea of the amount of focal shift that will occur for a given element motion based on the element focal length, beam diameter, and entering NA. The most sensitive elements of a system can then easily be determined. As evident by the graph, elements with a la ...
... These graphs can be used to get a general idea of the amount of focal shift that will occur for a given element motion based on the element focal length, beam diameter, and entering NA. The most sensitive elements of a system can then easily be determined. As evident by the graph, elements with a la ...
Dana_Denis_talk_SDSS2013
... • Sensors are inherently insensitive to polarization. • Spectroscopy is usually considered impractical since nothing can be done post-detection, and versatile or tight pre-detection filtering is extremely hard to implement. Some attempts have been made. • Extraordinary care is required in the design ...
... • Sensors are inherently insensitive to polarization. • Spectroscopy is usually considered impractical since nothing can be done post-detection, and versatile or tight pre-detection filtering is extremely hard to implement. Some attempts have been made. • Extraordinary care is required in the design ...
The Large Binocular Telescope`s ARGOS ground
... projection. The layout is illustrated in Figure 7, where for clarity the enclosing sides of the box have been omitted. The conditioning optics impose a linear polarization on the beams whose axis is chosen to match the preferred direction of the coating on the beam splitters ahead of the science ins ...
... projection. The layout is illustrated in Figure 7, where for clarity the enclosing sides of the box have been omitted. The conditioning optics impose a linear polarization on the beams whose axis is chosen to match the preferred direction of the coating on the beam splitters ahead of the science ins ...
here
... also available from Kokusai Kohki to insure always safe observation. until reticle image is sharp o r yo ur eyes can ○ Do not disassemble or otherwise tamper with this finder. Rotate lock ring to Repair of any resulting damage will incur repair fees. ① ② lock focus position ○ Grime and dirt on the o ...
... also available from Kokusai Kohki to insure always safe observation. until reticle image is sharp o r yo ur eyes can ○ Do not disassemble or otherwise tamper with this finder. Rotate lock ring to Repair of any resulting damage will incur repair fees. ① ② lock focus position ○ Grime and dirt on the o ...
PeliTalk - BiOptic Driving Network
... • Determine refraction by listening to sounds of neural activity in the cortex, monitored with intracellular electrodes, while changing lenses ...
... • Determine refraction by listening to sounds of neural activity in the cortex, monitored with intracellular electrodes, while changing lenses ...
Chapter 4 Telescope Making Basics
... focal ratio (less than f/5). The primary mirror can be of average quality (λ/4 at wavefront or λ/8 on the glass) if the desired magnifications do not exceed 1x the diameter of the instrument. In general, observation of very faint objects is done at low magnification, and the diffraction disk remains ...
... focal ratio (less than f/5). The primary mirror can be of average quality (λ/4 at wavefront or λ/8 on the glass) if the desired magnifications do not exceed 1x the diameter of the instrument. In general, observation of very faint objects is done at low magnification, and the diffraction disk remains ...
seeingandhearin5 ima..
... 1) When the object is on the same side of the reflecting or refracting surface as the incoming light the object distance s is positive, otherwise it is negative 2) When the image is on the same side of the reflecting or refracting surface as the outgoing light the image distance s’ is positive (real ...
... 1) When the object is on the same side of the reflecting or refracting surface as the incoming light the object distance s is positive, otherwise it is negative 2) When the image is on the same side of the reflecting or refracting surface as the outgoing light the image distance s’ is positive (real ...
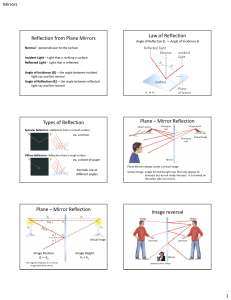
Reflection from Plane Mirrors Law of Reflection Types of Reflection
... Principle Axis – straight line perpendicular to the surface of the mirror that divides the mirror in half Focal Point (F) – Point where incident rays that are parallel to the principle axis converge after reflecting from the mirror Focal Length (f) – the position of the focal point with respect to ...
... Principle Axis – straight line perpendicular to the surface of the mirror that divides the mirror in half Focal Point (F) – Point where incident rays that are parallel to the principle axis converge after reflecting from the mirror Focal Length (f) – the position of the focal point with respect to ...
Dissecting Stereoscopic Microscope
... Types of Microscopes •Light Microscope –the models found in most schools, use compound lenses to magnify objects. The lenses bend or refract light to make the object beneath them appear closer. ...
... Types of Microscopes •Light Microscope –the models found in most schools, use compound lenses to magnify objects. The lenses bend or refract light to make the object beneath them appear closer. ...
Mirror Development for the Cherenkov Telescope Array
... Carbon fibre/epoxy based substrates have good mechanical properties and show the potential for fast and economical production in large quantities. The challenge is to produce mirrors with good surface qualities without labourintensive polishing. Currently, at SRC PAS, the sheet moulding compund (SMC ...
... Carbon fibre/epoxy based substrates have good mechanical properties and show the potential for fast and economical production in large quantities. The challenge is to produce mirrors with good surface qualities without labourintensive polishing. Currently, at SRC PAS, the sheet moulding compund (SMC ...
Organization of the project
... Requirement is : “to not be destroyed”. • Thermal cycling will be performed. No switch-ON or operations outside the nominal temperature range is foreseen. • At each deliveries and before integration will be performed an acceptance test including documentation. • A test plan will be write for the int ...
... Requirement is : “to not be destroyed”. • Thermal cycling will be performed. No switch-ON or operations outside the nominal temperature range is foreseen. • At each deliveries and before integration will be performed an acceptance test including documentation. • A test plan will be write for the int ...
Optical telescope
An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light, mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct view, or to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.There are three primary types of optical telescope: refractors, which use lenses (dioptrics) reflectors, which use mirrors (catoptrics) catadioptric telescopes, which combine lenses and mirrorsA telescope's light gathering power and ability to resolve small detail is directly related to the diameter (or aperture) of its objective (the primary lens or mirror that collects and focuses the light). The larger the objective, the more light the telescope collects and the finer detail it resolves.People use telescopes and binoculars for activities such as observational astronomy, ornithology, pilotage and reconnaissance, and watching sports or performance arts.