Targeted and All-Sky Search for Nanosecond Optical Pulses at
... the target. At a range of 1000 ly, this corresponds to a proper motion uncertainty of 33 µas/year and a positional accuracy of 33 mas. The required range accuracy depends on the star’s proper motion, but not its range; for example, to target the planetary zone (say 10 AU) of a star whose transverse ...
... the target. At a range of 1000 ly, this corresponds to a proper motion uncertainty of 33 µas/year and a positional accuracy of 33 mas. The required range accuracy depends on the star’s proper motion, but not its range; for example, to target the planetary zone (say 10 AU) of a star whose transverse ...
Lecture #1 Basic Concepts and Principles of Adaptive Optics
... It needs to be bright enough so that sufficient photons are collected in order to make a good estimate of the geometry of the wavefront distortions. A natural guide star (i.e. an astronomical source), or even the science object itself, may be used as a reference star; however, if one is not availabl ...
... It needs to be bright enough so that sufficient photons are collected in order to make a good estimate of the geometry of the wavefront distortions. A natural guide star (i.e. an astronomical source), or even the science object itself, may be used as a reference star; however, if one is not availabl ...
Human Eye • Human eye is a simple single lens system • Cornea
... • Transverse Spherical Aberration across axis • These create a “circle of least confusion” at focus • Area over which different parts of image come into focus • Lenses also have aberrations due to index of refraction issues ...
... • Transverse Spherical Aberration across axis • These create a “circle of least confusion” at focus • Area over which different parts of image come into focus • Lenses also have aberrations due to index of refraction issues ...
What Makes a Failure? Designing a New National Telescope, 1975
... of a big technological project must be judged on more than whether or not it is ever actually built. Ever since astronomers began to use telescopes they have wished for bigger instruments. A bigger telescope collects more light, enabling an astronomer to observe fainter, more distant, and older cele ...
... of a big technological project must be judged on more than whether or not it is ever actually built. Ever since astronomers began to use telescopes they have wished for bigger instruments. A bigger telescope collects more light, enabling an astronomer to observe fainter, more distant, and older cele ...
The Big Eye Now and Then
... onto a domed ceiling to give the audience the illusion of being out under the night sky. Astronomers at Palomar recently made an artificial star of their own in the real sky. To make this artificial star, a laser was broadcast into the sky. This was the first step in creating a laserguide star for u ...
... onto a domed ceiling to give the audience the illusion of being out under the night sky. Astronomers at Palomar recently made an artificial star of their own in the real sky. To make this artificial star, a laser was broadcast into the sky. This was the first step in creating a laserguide star for u ...
LAB 4: THE SIMPLE MAGNIFIER EYEPIECES The Simple Magnifier:
... Plossl's incorporate at least 4 optical elements. The Plossl design is a very well designed eyepiece, I would highly recommend them if you are using a Newtonian telescope with a very short focal length. Plossl's are very costly to make and hence a lot more expensive than the other designs mentioned ...
... Plossl's incorporate at least 4 optical elements. The Plossl design is a very well designed eyepiece, I would highly recommend them if you are using a Newtonian telescope with a very short focal length. Plossl's are very costly to make and hence a lot more expensive than the other designs mentioned ...
Activity 15
... eyepiece-end of a telescope. Photographs of fainter celestial objects—planets, stars, nebulae, comets—proved more challenging. To capture their feeble light on a photographic plate required long time-exposures. This, in turn, demanded both speedier photographic processes and, to prevent night-sky ta ...
... eyepiece-end of a telescope. Photographs of fainter celestial objects—planets, stars, nebulae, comets—proved more challenging. To capture their feeble light on a photographic plate required long time-exposures. This, in turn, demanded both speedier photographic processes and, to prevent night-sky ta ...
New initiatives - Major Instrumentation
... Active and Adaptive Optics will have to be integrated into GSMT Telescope and Instrument concepts from the start ...
... Active and Adaptive Optics will have to be integrated into GSMT Telescope and Instrument concepts from the start ...
Housing Decision Information:
... Each of the two motors is operated by a dedicated power amplifier (CSR Inc.). These amplifiers are classic switching amplifiers, in that they utilize an alternating polarity square wave with an adjustable duty cycle, to control the equivalent DC current. Their switching frequency is of 20Khz. Intern ...
... Each of the two motors is operated by a dedicated power amplifier (CSR Inc.). These amplifiers are classic switching amplifiers, in that they utilize an alternating polarity square wave with an adjustable duty cycle, to control the equivalent DC current. Their switching frequency is of 20Khz. Intern ...
OverviewJuly2007 - Magdalena Ridge Observatory
... • Density: 1.9 g/cm3 (Packed more loosely than sand). • Gravity is so low (Vesc =10 cm/s), if you “shook” it gently, the pieces would fly apart. ...
... • Density: 1.9 g/cm3 (Packed more loosely than sand). • Gravity is so low (Vesc =10 cm/s), if you “shook” it gently, the pieces would fly apart. ...
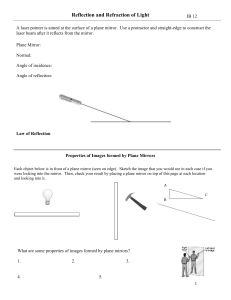
chapter26
... The rays from any point on the object diverge after reflection as though they were coming from some point behind the mirror The image is virtual because the reflected rays only appear to originate at the image point ...
... The rays from any point on the object diverge after reflection as though they were coming from some point behind the mirror The image is virtual because the reflected rays only appear to originate at the image point ...
NEW DESIGN AND NEW CHALLENGE FOR SPACE LARGE
... With this approach, adaptive optics will correct ground to flight instability and mid-term evolutions but doesn't necessitate to measure and correct very often thermoelastic deformations of the primary mirror. This approach will ensure therefore equivalent availability and reliability to those of a ...
... With this approach, adaptive optics will correct ground to flight instability and mid-term evolutions but doesn't necessitate to measure and correct very often thermoelastic deformations of the primary mirror. This approach will ensure therefore equivalent availability and reliability to those of a ...
Optical Instruments
... 3. TELEPHOTO LENS To obtain an image of the object situated at a very long distance, a convex lens of large focal length should be used. In this case, to obtain a magnified image the distance between the lens and the photographic plate should be large. Thus a magnified image requires a long camera w ...
... 3. TELEPHOTO LENS To obtain an image of the object situated at a very long distance, a convex lens of large focal length should be used. In this case, to obtain a magnified image the distance between the lens and the photographic plate should be large. Thus a magnified image requires a long camera w ...
unit 9: imaging
... Reflecting Telescopes Reflecting telescopes use mirrors rather than the lenses of refracting telescopes. The largest telescopes used are reflecting. Advantages: 1) To see distant faint objects requires large lenses (to collect more light); but large lenses are hard to make and can only be supported ...
... Reflecting Telescopes Reflecting telescopes use mirrors rather than the lenses of refracting telescopes. The largest telescopes used are reflecting. Advantages: 1) To see distant faint objects requires large lenses (to collect more light); but large lenses are hard to make and can only be supported ...
ppt document
... Types of Telescopes The type of telescope we have looked at so far, and the type we have or will have made in the lab is called a refracting telescope, since it uses the refraction of light going from air to glass and back to air. This is the type used by Galileo. There is a second type of telescop ...
... Types of Telescopes The type of telescope we have looked at so far, and the type we have or will have made in the lab is called a refracting telescope, since it uses the refraction of light going from air to glass and back to air. This is the type used by Galileo. There is a second type of telescop ...
Quantification of Distant Luminous Objects
... twice as much atmosphere is traversed by the light path, causing a 0.48 mag loss, or a 63% loss of photons. 15 degrees from the horizon is 3 atmospheres (0.72 mag), and 10 degrees from the horizon is 4 atmospheres or 0.96 mag (~ 1 complete magnitude) lost, which is a loss of 2.5 photons for every on ...
... twice as much atmosphere is traversed by the light path, causing a 0.48 mag loss, or a 63% loss of photons. 15 degrees from the horizon is 3 atmospheres (0.72 mag), and 10 degrees from the horizon is 4 atmospheres or 0.96 mag (~ 1 complete magnitude) lost, which is a loss of 2.5 photons for every on ...
microscope, telescope
... Making an image of an image with 2 lenses: The first lens the light goes through makes the first image. ...
... Making an image of an image with 2 lenses: The first lens the light goes through makes the first image. ...
p30opticsS
... concave lens to diverge the light entering the eye b. concave lens to converge the light entering the eye c. convex lens to diverge the light entering the eye d. convex lens to converge the light entering the eye ...
... concave lens to diverge the light entering the eye b. concave lens to converge the light entering the eye c. convex lens to diverge the light entering the eye d. convex lens to converge the light entering the eye ...
Exploring Chile, the Astronomy Capital of the World
... with lower resolution, while the others are constantly moved around to image a smaller area with astounding resolution. There are over 60 antennas that can be moved into arrays as large as 10 miles across. The wider their separation, the more detailed their measurements. The ALMA detectors are looki ...
... with lower resolution, while the others are constantly moved around to image a smaller area with astounding resolution. There are over 60 antennas that can be moved into arrays as large as 10 miles across. The wider their separation, the more detailed their measurements. The ALMA detectors are looki ...
Light Rays FACILITATOR NOTES
... source where they will be in full view of the class. Both the robot and the light source should be below eye level to avoid shining the light into anyone’s eyes. Both the light source and the robot should be centered as shown. The angular distance from center to edge across the target is not critica ...
... source where they will be in full view of the class. Both the robot and the light source should be below eye level to avoid shining the light into anyone’s eyes. Both the light source and the robot should be centered as shown. The angular distance from center to edge across the target is not critica ...
Stop Faking It! Light
... Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through Translucent: letting light through but scattering it Opaque: materials that do not let light through Transmit: to send (as in sound or light). It also means light passing through an object. ...
... Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through Translucent: letting light through but scattering it Opaque: materials that do not let light through Transmit: to send (as in sound or light). It also means light passing through an object. ...
Reflecting telescope

A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is an optical telescope which uses a single or combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Reflecting telescopes come in many design variations and may employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a ""catoptric"" telescope.