File - Mrs. Weimer`s 5th Grade Class
... High grade fever, shaking chills, severe head aches and body aches, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, chest pain, stomach pain, convulsions, coma, or hallucinations ...
... High grade fever, shaking chills, severe head aches and body aches, weakness, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, chest pain, stomach pain, convulsions, coma, or hallucinations ...
Disease Cheat Sheet
... You can get typhoid fever if you eat food or drink beverages that have been handled by a person who is shedding Salmonella Typhi or if sewage contaminated with Salmonella Typhi bacteria gets into the water you use for drinking or washing food. Therefore, typhoid fever is more common in areas of the ...
... You can get typhoid fever if you eat food or drink beverages that have been handled by a person who is shedding Salmonella Typhi or if sewage contaminated with Salmonella Typhi bacteria gets into the water you use for drinking or washing food. Therefore, typhoid fever is more common in areas of the ...
Epidemiology of Cholera
... contamination are particularly explosive. because • a water source may serve a large population. • Water dilutes gastric acid which would otherwise inactivate pathogenic agents. • Water and other beverages remain in the stomach only very briefly ...
... contamination are particularly explosive. because • a water source may serve a large population. • Water dilutes gastric acid which would otherwise inactivate pathogenic agents. • Water and other beverages remain in the stomach only very briefly ...
SEROLOGICAL DIAGNOSIS OF TYPHOID FEVER: A review of the
... The copyright of this article belongs to the Editorial Board of the Malta Medical Journal. The Malta Medical Journal’s rights in respect of this work are as defined by the Copyright Act (Chapter 415) of the Laws of Malta or as modified by any successive legislation. Users may access this full-text ...
... The copyright of this article belongs to the Editorial Board of the Malta Medical Journal. The Malta Medical Journal’s rights in respect of this work are as defined by the Copyright Act (Chapter 415) of the Laws of Malta or as modified by any successive legislation. Users may access this full-text ...
Typhoid and Paratyphoid fever ICD-10 A01.0: Typhoid Fever ICD
... ICD-10 A01.0: Typhoid Fever ICD-10 A01.1-A01.4: Paratyphoid Fever Identification ...
... ICD-10 A01.0: Typhoid Fever ICD-10 A01.1-A01.4: Paratyphoid Fever Identification ...
SALMONELLA - Nexus Academic Publishers
... – Antibiotics are not recommended for uncomplicated gastroenteritis ...
... – Antibiotics are not recommended for uncomplicated gastroenteritis ...
Who Won the Wars
... killing most of the 1839 soldiers who contracted the disease. Others were done in by malaria (362), yellow fever (143) and dengue fever (2), all vector-borne. v Emphasis on sanitation during the Civil War brought the disease vs. battle ratio down to 2:1. v Lice, ongoing problems where personnel are ...
... killing most of the 1839 soldiers who contracted the disease. Others were done in by malaria (362), yellow fever (143) and dengue fever (2), all vector-borne. v Emphasis on sanitation during the Civil War brought the disease vs. battle ratio down to 2:1. v Lice, ongoing problems where personnel are ...
doc
... Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever typhus Food Poisoning typhoid fever food poisoning dysentery Toxic shock syndrome cavities pneumonia scarlet fever rheumatic fever syphilis yaws cholera plague ...
... Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever typhus Food Poisoning typhoid fever food poisoning dysentery Toxic shock syndrome cavities pneumonia scarlet fever rheumatic fever syphilis yaws cholera plague ...
Typhoid fever Infectious Disease Deepika Gupta
... Bay, New York in 1906 who is known to have infected 53 people, 5 of whom died. 2. Later returned with false name but detained and quarantined after another typhoid outbreak. 3. She died of pneumonia after 26 years in quarantine. ...
... Bay, New York in 1906 who is known to have infected 53 people, 5 of whom died. 2. Later returned with false name but detained and quarantined after another typhoid outbreak. 3. She died of pneumonia after 26 years in quarantine. ...
Salmonella Lecture
... Clinical Syndromes- Enteric fever S. typhi causes typhoid fever S. paratyphi A, B and C cause milder form of enteric fever called paratyphoid fever Infectious dose large = 106 CFU Fecal-oral route of transmission Person-to-person spread by chronic carrier Fecally-contaminated food or wate ...
... Clinical Syndromes- Enteric fever S. typhi causes typhoid fever S. paratyphi A, B and C cause milder form of enteric fever called paratyphoid fever Infectious dose large = 106 CFU Fecal-oral route of transmission Person-to-person spread by chronic carrier Fecally-contaminated food or wate ...
General characteristic of intestinal infections. Typhoid fever
... the environment with feces, urine, vomits (cholera), it can cause disease in a healthy person only after ingestion with food or water. In other words, i.i. are characterized by faecal-oral mechanism of transmission. ...
... the environment with feces, urine, vomits (cholera), it can cause disease in a healthy person only after ingestion with food or water. In other words, i.i. are characterized by faecal-oral mechanism of transmission. ...
Paratyphoid Fever - Leeds, Grenville and Lanark District Health Unit
... possible, physicians should be encouraged to request antibiotic sensitivity testing due to resistant strains. With appropriate antibiotic treatment, infected individuals with typhoid or paratyphoid fever usually recover within ten to 14 days. Educate the case about transmission of infection and prop ...
... possible, physicians should be encouraged to request antibiotic sensitivity testing due to resistant strains. With appropriate antibiotic treatment, infected individuals with typhoid or paratyphoid fever usually recover within ten to 14 days. Educate the case about transmission of infection and prop ...
Infectious diseases exempt from NHS charges
... Infectious diseases exempt from NHS charges The treatment and diagnosis of certain infectious diseases is available to all patients free of charge, including overseas visitors. The conditions to which this exemption applies are: ...
... Infectious diseases exempt from NHS charges The treatment and diagnosis of certain infectious diseases is available to all patients free of charge, including overseas visitors. The conditions to which this exemption applies are: ...
Salmonella
... reaction may sometimes be of a group character since the patient's serum contains agglutinins not only to specific but also to group antigens which occur in other bacteria. In such cases the patient's blood must be sampled again in 5-6 days and the Widal reaction repeated. Increase of the agglutinin ...
... reaction may sometimes be of a group character since the patient's serum contains agglutinins not only to specific but also to group antigens which occur in other bacteria. In such cases the patient's blood must be sampled again in 5-6 days and the Widal reaction repeated. Increase of the agglutinin ...
Typhoid
... exclusively in humans. Typhoid fever is a severe multisystemic illness characterized by the classic prolonged fever, sustained bacteremia without endothelial or endocardial involvement, and bacterial invasion of and multiplication within the mononuclear phagocytic cells of the liver, spleen, lymph n ...
... exclusively in humans. Typhoid fever is a severe multisystemic illness characterized by the classic prolonged fever, sustained bacteremia without endothelial or endocardial involvement, and bacterial invasion of and multiplication within the mononuclear phagocytic cells of the liver, spleen, lymph n ...
CHOLERA
... Dehydration is the most common complication of typhoid fever, but serious intestinal & extraintestinal complications may occur. ...
... Dehydration is the most common complication of typhoid fever, but serious intestinal & extraintestinal complications may occur. ...
The Strange Case of Typhoid Mary
... they respond to pathogens, some growing well despite serious infections. The concept has begun to take root in the animal immunology world over the last 10 years or so. “We knew it happened but didn’t have a systematic way of describing this process,” Soares said. Of course, the mechanisms that Soar ...
... they respond to pathogens, some growing well despite serious infections. The concept has begun to take root in the animal immunology world over the last 10 years or so. “We knew it happened but didn’t have a systematic way of describing this process,” Soares said. Of course, the mechanisms that Soar ...
Bacterial Gastrointestinal Infection
... Serological test: Widal test is used for the diagnosis of Typhoid fever.. measures levels of antibodies against (O, H ) antigens.. Titer > 160 or rising titers.. positive (Vi ) antigen indicate S. typhi.. acute infection. ...
... Serological test: Widal test is used for the diagnosis of Typhoid fever.. measures levels of antibodies against (O, H ) antigens.. Titer > 160 or rising titers.. positive (Vi ) antigen indicate S. typhi.. acute infection. ...
Slide 1
... Blood Cultures: used to determine the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria in the blood. •A blood sample from the individual is placed in a special laboratory preparation and incubated for up to seven days. • It is important that the conditions within the environment are controlled to avoid c ...
... Blood Cultures: used to determine the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria in the blood. •A blood sample from the individual is placed in a special laboratory preparation and incubated for up to seven days. • It is important that the conditions within the environment are controlled to avoid c ...
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
... Positive Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) for Salmonella Typhi without culture confirmation ...
... Positive Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) for Salmonella Typhi without culture confirmation ...
Slide 1
... Blood Cultures: used to determine the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria in the blood. •A blood sample from the individual is placed in a special laboratory preparation and incubated for up to seven days. • It is important that the conditions within the environment are controlled to avoid c ...
... Blood Cultures: used to determine the presence of microorganisms such as bacteria in the blood. •A blood sample from the individual is placed in a special laboratory preparation and incubated for up to seven days. • It is important that the conditions within the environment are controlled to avoid c ...
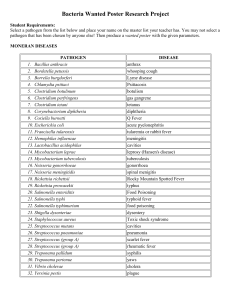
Bacteria Wanted Poster
... Bacteria Wanted Poster Select a pathogen from the list below and research it. Then produce a “wanted” poster with the following information: 1. “photo” (electron micrograph or microscopic picture/diagram) 2. Description 3. Organism’ m.o. (how the organism attacks and spreads) 4. Most common victims ...
... Bacteria Wanted Poster Select a pathogen from the list below and research it. Then produce a “wanted” poster with the following information: 1. “photo” (electron micrograph or microscopic picture/diagram) 2. Description 3. Organism’ m.o. (how the organism attacks and spreads) 4. Most common victims ...
Salmonella Typhi - faculty development
... She worked as a cook and servant throughout her life. Infected as many as 50 people, 3 of which where fatal cases. Mary Mallon was taken into custody and held in isolation until she died in 1938. ...
... She worked as a cook and servant throughout her life. Infected as many as 50 people, 3 of which where fatal cases. Mary Mallon was taken into custody and held in isolation until she died in 1938. ...
3-Epidemiology of typhoid
... • About 1–5% of people who are infected with S. typhi become asymptomatic chronic carriers. • The carrier state may follow acute or mild illness or subclinical infection. • The incidence of chronic carriage is higher among women and persons with biliary tract abnormalities. ...
... • About 1–5% of people who are infected with S. typhi become asymptomatic chronic carriers. • The carrier state may follow acute or mild illness or subclinical infection. • The incidence of chronic carriage is higher among women and persons with biliary tract abnormalities. ...
Typhoid and paratyphoid (enteric) fevers
... Transmitted by the faecal–oral route. After a few days of bacteraemia, the bacilli localise, mainly in the lymphoid tissue of the small intestine, resulting in typical lesions in the Peyer’s patches and follicles. These swell at first, then ulcerate and usually heal. After clinical recovery, about 5 ...
... Transmitted by the faecal–oral route. After a few days of bacteraemia, the bacilli localise, mainly in the lymphoid tissue of the small intestine, resulting in typical lesions in the Peyer’s patches and follicles. These swell at first, then ulcerate and usually heal. After clinical recovery, about 5 ...
Typhoid fever

Typhoid fever, also known simply as typhoid, is a symptomatic bacterial infection due to Salmonella typhi. Symptoms may vary from mild to severe and usually begin six to thirty days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several days. Weakness, abdominal pain, constipation, and headaches also commonly occur. Diarrhea and vomiting are uncommon. Some people develop a skin rash with rose colored spots. In severe cases there may be confusion. Without treatment symptoms may last weeks or months. Other people may carry the bacterium without being affected; however, they are still able to spread the disease to others. Typhoid fever is a type of enteric fever along with paratyphoid fever.The cause is the bacterium Salmonella typhi, also known as Salmonella enterica serotype typhi, growing in the intestines and blood. Typhoid is spread by eating or drinking food or water contaminated with the feces of an infected person. Risk factors include poor sanitation and poor hygiene. Those who travel to the developing world are also at risk. Humans are the only animal infected. Diagnosis is by either culturing the bacteria or detecting the bacterium's DNA in the blood, stool, or bone marrow. Culturing the bacterium can be difficult. Bone marrow testing is the most accurate. Symptoms are similar to that of many other infectious diseases. Typhus is a different disease.A typhoid vaccine can prevent about 50% to 70% of cases. The vaccine may be effective for up to seven years. It is recommended for those at high risk or people traveling to areas where the disease is common. Other efforts to prevent the disease include providing clean drinking water, better sanitation, and better handwashing. Until it has been confirmed that an individual's infection is cleared, the individual should not prepare food for others. Treatment of disease is with antibiotics such as azithromycin, fluoroquinolones or third generation cephalosporins. Resistance to these antibiotics has been developing, which has made treatment of the disease more difficult.In 2010 there were 27 million cases reported. The disease is most common in India, and children are most commonly affected. Rates of disease decreased in the developed world in the 1940s as a result of improved sanitation and use of antibiotics to treat the disease. About 400 cases are reported and the disease is estimated to occur in about 6,000 people per year in the United States. In 2013 it resulted in about 161,000 deaths – down from 181,000 in 1990 (about 0.3% of the global total). The risk of death may be as high as 25% without treatment, while with treatment it is between 1 and 4%. The name typhoid means ""resembling typhus"" due to the similarity in symptoms.