Document
... • Formation of chelate ring ⇒ reaction proceeds in forward direction & the product is stable. This stability is purely kinetic in nature. This is known as chelate effect. • ΔG = ΔH - TΔS ...
... • Formation of chelate ring ⇒ reaction proceeds in forward direction & the product is stable. This stability is purely kinetic in nature. This is known as chelate effect. • ΔG = ΔH - TΔS ...
Crystal Field Theory
... The UV-Vis absorption spectrum reveals that this transition occurs with a maximum at 20300 cm-1 which corresponds to ∆o 243 kJ/mol. (1000 cm-1 = 11.96 kJ/mol or 2.86 kcal/mol or 0.124 eV.) ...
... The UV-Vis absorption spectrum reveals that this transition occurs with a maximum at 20300 cm-1 which corresponds to ∆o 243 kJ/mol. (1000 cm-1 = 11.96 kJ/mol or 2.86 kcal/mol or 0.124 eV.) ...
Lecture 15 16 - TAMU Chemistry
... The cis-dibromo-cis-diammine-cis-diaquacobalt(III) geometric isomer exists in two forms that bear the same relationship to each other as left and right handed isomers. They are non-superimposable mirror images of each other and are called optical isomers or enantiomers. Optical isomers have identica ...
... The cis-dibromo-cis-diammine-cis-diaquacobalt(III) geometric isomer exists in two forms that bear the same relationship to each other as left and right handed isomers. They are non-superimposable mirror images of each other and are called optical isomers or enantiomers. Optical isomers have identica ...
TM shape and colour
... SPLITTING OF 3d ORBITALS Placing ligands around a central ion causes the energies of the d orbitals to change Some of the d orbitals gain energy and some lose energy In an octahedral complex, two (z2 and x2-y2) go higher and three go lower In a tetrahedral complex, three (xy, xz and yz) go higher a ...
... SPLITTING OF 3d ORBITALS Placing ligands around a central ion causes the energies of the d orbitals to change Some of the d orbitals gain energy and some lose energy In an octahedral complex, two (z2 and x2-y2) go higher and three go lower In a tetrahedral complex, three (xy, xz and yz) go higher a ...
Chapter 24 Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... • How do we think about transition metals binding to other atoms? • What do those d orbitals do? • We call them, coordination compounds. ...
... • How do we think about transition metals binding to other atoms? • What do those d orbitals do? • We call them, coordination compounds. ...
Thermodynamics and Further Inorganic Chemistry
... Boiling points start high because of the strong ionic forces but become higher in the middle oxides have mixed ionic covalent nature but still form giant lattices so have high boiling points. The latter few elements form simple molecules and so have relatively low boiling points. – With water the me ...
... Boiling points start high because of the strong ionic forces but become higher in the middle oxides have mixed ionic covalent nature but still form giant lattices so have high boiling points. The latter few elements form simple molecules and so have relatively low boiling points. – With water the me ...
Lecture Notes 14 - La Salle University
... = 77 pm and rM ~120 pm. Realize that the first row transition metals are smaller, so any M-X bond distance will usually be smaller by 10-20 pm or so. ...
... = 77 pm and rM ~120 pm. Realize that the first row transition metals are smaller, so any M-X bond distance will usually be smaller by 10-20 pm or so. ...
Bis(phosphinimino)methanides as Ligands in Rare Earth, Heavy
... The contracting nature of the 4f-orbitals and the concomitant poor overlap with the ligand orbitals contribute to the predominantly ionic character of organolanthanide complexes. Normally metal ligand interactions are determined by electrostatic factors. According to the HSAB classification of Pears ...
... The contracting nature of the 4f-orbitals and the concomitant poor overlap with the ligand orbitals contribute to the predominantly ionic character of organolanthanide complexes. Normally metal ligand interactions are determined by electrostatic factors. According to the HSAB classification of Pears ...
Nomenclature for d-block complexes Writing chemical names
... Same as for neutral, but use square brackets to enclose ions. For complete complexes (in which both cation and anion are shown), cation(s) comes first followed by anion(s). If only one of the two ions is “complex”, that ion can be shown by itself with charge indicated (and the understanding that the ...
... Same as for neutral, but use square brackets to enclose ions. For complete complexes (in which both cation and anion are shown), cation(s) comes first followed by anion(s). If only one of the two ions is “complex”, that ion can be shown by itself with charge indicated (and the understanding that the ...
Metal Complexes
... • Ligands that bind to a metal cation via: – one donor atom are called monodentate ligands • Cl-, NH3, CN-, H2O (donor atoms are, respectively, Cl, N, C (or N!), O ...
... • Ligands that bind to a metal cation via: – one donor atom are called monodentate ligands • Cl-, NH3, CN-, H2O (donor atoms are, respectively, Cl, N, C (or N!), O ...
1 [L 5 FeO 2 ] - physics.muni.cz
... triplet state. The overwhelming majority of organic molecules (such as glucose or n-hexane) have all electrons paired and occur therefore in the singlet state. The products of oxidation of organic molecules, CO2 and H2O, are also in singlet states. According to the so-called Wigner-rule, processes i ...
... triplet state. The overwhelming majority of organic molecules (such as glucose or n-hexane) have all electrons paired and occur therefore in the singlet state. The products of oxidation of organic molecules, CO2 and H2O, are also in singlet states. According to the so-called Wigner-rule, processes i ...
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS COMPLEX
... composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules) that are formally donating electrons to the metal center ...
... composed of a metal atom or ion and one or more ligands (atoms, ions, or molecules) that are formally donating electrons to the metal center ...
ncur_powerpoint Courtney
... Typical Metal Complex: [Ni3(tris-CB-Cyclens)(OAc)3](PF6)3 ∙ 6H2O Elemental Analysis Calculated as Ni3C48H87N12O6P3F18 ∙ 6 H2O: Calc: C 35.00, H 6.06, N 10.20; Found: C 34.66, H 5.61, N 10.20 ...
... Typical Metal Complex: [Ni3(tris-CB-Cyclens)(OAc)3](PF6)3 ∙ 6H2O Elemental Analysis Calculated as Ni3C48H87N12O6P3F18 ∙ 6 H2O: Calc: C 35.00, H 6.06, N 10.20; Found: C 34.66, H 5.61, N 10.20 ...
Lecture 2
... Hexaaminecobalt(III) chloride: [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 Number of ligand indicated by prefix (di,tri,tetra or bis, tris, tetrakis if ligand in parenthesis) tris(bipyridine)iron(II) chloride: [Fe(bipy)3]Cl2 Ligands named in alphabetical order ignoring prefix Anionic ligands are given the suffix -o (chloro-, sul ...
... Hexaaminecobalt(III) chloride: [Co(NH3)6]Cl3 Number of ligand indicated by prefix (di,tri,tetra or bis, tris, tetrakis if ligand in parenthesis) tris(bipyridine)iron(II) chloride: [Fe(bipy)3]Cl2 Ligands named in alphabetical order ignoring prefix Anionic ligands are given the suffix -o (chloro-, sul ...
Coordination compounds in nature
... *In reservoirs metal ions that are available in higher percentages are ions like Na+,K+,Ca2+ *These ions are not good at making coordination compounds due to the lack of empty orbitals with comparable energy to that of the available ligand orbitals to accept lone pairs of electrons *Although some st ...
... *In reservoirs metal ions that are available in higher percentages are ions like Na+,K+,Ca2+ *These ions are not good at making coordination compounds due to the lack of empty orbitals with comparable energy to that of the available ligand orbitals to accept lone pairs of electrons *Although some st ...
Chemistry of Coordination Compounds
... • It is possible to find cis and trans isomers in octahedral complexes. • For example, cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+1 is violet. • The trans-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+1 isomer is green. • The two isomers also have different solubilities. • optical isomerism • Optical isomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. • These ar ...
... • It is possible to find cis and trans isomers in octahedral complexes. • For example, cis-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+1 is violet. • The trans-[Co(NH3)4Cl2]+1 isomer is green. • The two isomers also have different solubilities. • optical isomerism • Optical isomers are nonsuperimposable mirror images. • These ar ...
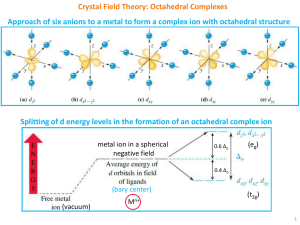
Crystal Field Theory: Octahedral Complexes
... There are only 4 ligands in the tetrahedral complex and hence the ligand field is roughly 2/3 of the octahedral field. The direction of ligand approach in tetrahedral complex does not coincide with the d-orbitals. This reduces the field by a factor of 2/3. Therefore Δt is roughly 2/3 x 2/3 = 4/9 ...
... There are only 4 ligands in the tetrahedral complex and hence the ligand field is roughly 2/3 of the octahedral field. The direction of ligand approach in tetrahedral complex does not coincide with the d-orbitals. This reduces the field by a factor of 2/3. Therefore Δt is roughly 2/3 x 2/3 = 4/9 ...
Cr2(SO4)3∙n H2O
... 4. Anions that appear more than once (have subscript number) are indicated by using the multiplicative prefixes: bis (two), tris (three), tetrakis (four), penta (five), hexa (six), hepta (seven), octa (eight), nona (nine), deca (ten) and so on. 5. Water of hydration is recognized by its position at ...
... 4. Anions that appear more than once (have subscript number) are indicated by using the multiplicative prefixes: bis (two), tris (three), tetrakis (four), penta (five), hexa (six), hepta (seven), octa (eight), nona (nine), deca (ten) and so on. 5. Water of hydration is recognized by its position at ...
Lectures 29-31
... •Where does the variety in colour come from? •Many co-ordination complexes have octahedral geometry. This means that two of the d orbitals on the transition metal point directly at ligands while the other three do not: ...
... •Where does the variety in colour come from? •Many co-ordination complexes have octahedral geometry. This means that two of the d orbitals on the transition metal point directly at ligands while the other three do not: ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.












![1 [L 5 FeO 2 ] - physics.muni.cz](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000263887_1-9a7fea8feae8a4c4c33cd53b2038de6b-300x300.png)