Ligand Control of the Metal Coordination Sphere: Structures
... which functions as acceptor in the former and both a donor and an acceptor in the latter, are noteworthy and emphasize the need for detailed structural investigations to identify the occurrence and consequences of subtle substituent effects. These results triggered a theoretical structure-reactivity ...
... which functions as acceptor in the former and both a donor and an acceptor in the latter, are noteworthy and emphasize the need for detailed structural investigations to identify the occurrence and consequences of subtle substituent effects. These results triggered a theoretical structure-reactivity ...
Chapter 19
... b) sodium hexacyanocobaltate(III) b) bis(ethylenediamine)dinitroiron(III) chloride d) tetraamminediiodoplatinum(IV) tetraiodoplatinate(II) Note: The oxidation numbers of platinum where determined by looking at the possible oxidation numbers for platinum, these can be found in slide 7 of your cla ...
... b) sodium hexacyanocobaltate(III) b) bis(ethylenediamine)dinitroiron(III) chloride d) tetraamminediiodoplatinum(IV) tetraiodoplatinate(II) Note: The oxidation numbers of platinum where determined by looking at the possible oxidation numbers for platinum, these can be found in slide 7 of your cla ...
Electronic Decomposition Analysis of Substituted Metal Alkene and
... Gold is known for its interactions with carbon‐carbon π bonds. ◦ It activates alkenes and alkynes within reactions. ◦ When using gold as a catalyst with molecules with multiple alkenes or alkynes it is important to know which one will become activated. ...
... Gold is known for its interactions with carbon‐carbon π bonds. ◦ It activates alkenes and alkynes within reactions. ◦ When using gold as a catalyst with molecules with multiple alkenes or alkynes it is important to know which one will become activated. ...
Module 9 : Complexes of π −bound ligands Lecture 2 : Metal allyl
... Of particular interest are the molecular orbitals namely Ψ 1 , Ψ 2 and Ψ 3 of the allyl ligand that interact with the metal in a metal allyl complex. The energy of these molecular orbitals increase with the increase in the number of nodes. Of the three, the Ψ 1 and Ψ 2 orbitals usually engage in lig ...
... Of particular interest are the molecular orbitals namely Ψ 1 , Ψ 2 and Ψ 3 of the allyl ligand that interact with the metal in a metal allyl complex. The energy of these molecular orbitals increase with the increase in the number of nodes. Of the three, the Ψ 1 and Ψ 2 orbitals usually engage in lig ...
molybdenum(O)
... to the olefinic carbon atoms and the other two are due to the nitrile carbon atoms. This unequivocally indicates that the FN ligand is coordinated to the M (CO)5 moiety through one nitrile nitrogen atom. A symmetric coordination of FN would give only two 13C NMR signals, one for the olefinic and one ...
... to the olefinic carbon atoms and the other two are due to the nitrile carbon atoms. This unequivocally indicates that the FN ligand is coordinated to the M (CO)5 moiety through one nitrile nitrogen atom. A symmetric coordination of FN would give only two 13C NMR signals, one for the olefinic and one ...
Fall 05
... Aqueous solutions of [V(H2O)6]3+ show absorptions at 17200 and 25600 cm–1 which are assigned to the transitions: 3T2g ← 3T1g(F) and 3T1g(P) ← 3T1g(F). a) (1 marks) How many absorptions would you expect to observe, and why might they not all be ...
... Aqueous solutions of [V(H2O)6]3+ show absorptions at 17200 and 25600 cm–1 which are assigned to the transitions: 3T2g ← 3T1g(F) and 3T1g(P) ← 3T1g(F). a) (1 marks) How many absorptions would you expect to observe, and why might they not all be ...
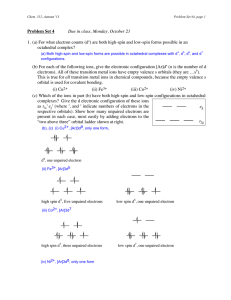
[E]ven the most difficult problems in chemical experimentation can
... is commonly called the \18-electron rule" and the \16-electron rule" for octahedral and square planar type structures, respectively. B) Explain why Cr(NO)4 is an electronically stable molecule, and propose an oxidation state and a valence number for the Cr center. ...
... is commonly called the \18-electron rule" and the \16-electron rule" for octahedral and square planar type structures, respectively. B) Explain why Cr(NO)4 is an electronically stable molecule, and propose an oxidation state and a valence number for the Cr center. ...
Electronic Spectroscopy
... empty 3d orbitals are more easily accessible than 4d or 5d from the ligand orbitals (such as 2p in O2‐) – Relates to reduction potential! 3d metals are easier to reduce. Therefore, the chemistry of 4d and 5d metals is dominated by their highest possible O.S. Consider Fe triad… only Os can achie ...
... empty 3d orbitals are more easily accessible than 4d or 5d from the ligand orbitals (such as 2p in O2‐) – Relates to reduction potential! 3d metals are easier to reduce. Therefore, the chemistry of 4d and 5d metals is dominated by their highest possible O.S. Consider Fe triad… only Os can achie ...
Lecture19_Ch19_11140..
... The color that we see is the color that is not absorbed, but is transmitted. The transmitted light is the complement of the absorbed light. ...
... The color that we see is the color that is not absorbed, but is transmitted. The transmitted light is the complement of the absorbed light. ...
5 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... 5.1 Compounds of transition elements. Most transition metal compounds contain covalent bonds between ligands and central metal atom. Some are simple polyatomic ions, e.g. permanganate [MnO4]-, a polar covalent compound. Electrons - shared between central Mn and O ligands. However most are "complex ...
... 5.1 Compounds of transition elements. Most transition metal compounds contain covalent bonds between ligands and central metal atom. Some are simple polyatomic ions, e.g. permanganate [MnO4]-, a polar covalent compound. Electrons - shared between central Mn and O ligands. However most are "complex ...
problem set 3 2016
... 8. Three electrochemical cells were connected in series so that the same quantity of electrical current passes through all three cells. In the first cell, 1.15 g chromium metal was deposited from a chromium(III) nitrate solution. In the second cell, 3.15 g osmium was deposited from a solution made ...
... 8. Three electrochemical cells were connected in series so that the same quantity of electrical current passes through all three cells. In the first cell, 1.15 g chromium metal was deposited from a chromium(III) nitrate solution. In the second cell, 3.15 g osmium was deposited from a solution made ...
Chem312 Au03 Problem Set 4
... of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energ ...
... of one electron from the t2g set of orbitals to the t2g eg set. In a diagram like the one at right, add ground state excited state electrons to represent the ground state and the lowest energy excited state. When you put the electrons in, you should follow Hund’s rule, that a state is lower in energ ...
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Research Background
... Nowadays, NHC-based ligands show a very important role in organometallic chemistry, because of their distinctive complexation behaviours, synthetic versatilities, and vastly tuneable characteristics. These ligands show a high tendency to act as wonderful σ-donor ligands and to make more stable metal ...
... Nowadays, NHC-based ligands show a very important role in organometallic chemistry, because of their distinctive complexation behaviours, synthetic versatilities, and vastly tuneable characteristics. These ligands show a high tendency to act as wonderful σ-donor ligands and to make more stable metal ...
Group 14 - University of Ottawa
... Triorganoarsines are generally stable at room temperature but the stability of triorganobismuthines varies with structure. e.g. 3 Me2BiAr → 2 Me3Bi + BiAr3 R3E are readily oxidized to give R3MO (M = As, Sb) and R2BiOR aryl compounds less sensitive ...
... Triorganoarsines are generally stable at room temperature but the stability of triorganobismuthines varies with structure. e.g. 3 Me2BiAr → 2 Me3Bi + BiAr3 R3E are readily oxidized to give R3MO (M = As, Sb) and R2BiOR aryl compounds less sensitive ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... EXAMPLE: H2O à this is one molecule of water What is a DIATOMIC MOLECULE? Provide an example from your notes. A diatomic molecule is always made up of pairs of the same kind of atom. ...
... EXAMPLE: H2O à this is one molecule of water What is a DIATOMIC MOLECULE? Provide an example from your notes. A diatomic molecule is always made up of pairs of the same kind of atom. ...
Review of Basic Principles: The following was adapted from The
... the CO-to-metal electron donation that constitutes the σ bond. One of the most direct arguments is structural. The M=C bond in metal carbonyls is usually substantially shorter than an M-C single bond. This is easiest to test when both types of bond are present in the same complex, such as CpMo(CO) 3 ...
... the CO-to-metal electron donation that constitutes the σ bond. One of the most direct arguments is structural. The M=C bond in metal carbonyls is usually substantially shorter than an M-C single bond. This is easiest to test when both types of bond are present in the same complex, such as CpMo(CO) 3 ...
Synthesis and characterization of transition metal coordination
... M = Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II); BDC = 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate; azoles = 2-aminobenzothiazole, 2aminothiazole, and 2-amino-4-methyl-thiazole; m = 0 or 1; and x = 1 or 2) were prepared and characterized. The complexes were characterized based on elemental analysis, infrared and electronic spectral st ...
... M = Co(II), Ni(II), and Cu(II); BDC = 1,4-benzenedicarboxylate; azoles = 2-aminobenzothiazole, 2aminothiazole, and 2-amino-4-methyl-thiazole; m = 0 or 1; and x = 1 or 2) were prepared and characterized. The complexes were characterized based on elemental analysis, infrared and electronic spectral st ...
ADVANCED INORGANIC CHEMISTRY December 6, 2006 QUIZ 4
... Structural Isomer types Ionization – Interchange of an anionic ligand bound to the central metal with in one in the crystal Hydration – Interchange of a water molecule bound to the central metal with another ligand in the crystal Coordination – Both cation and anoin are complex ions. The two metals ...
... Structural Isomer types Ionization – Interchange of an anionic ligand bound to the central metal with in one in the crystal Hydration – Interchange of a water molecule bound to the central metal with another ligand in the crystal Coordination – Both cation and anoin are complex ions. The two metals ...
this PDF file
... A possible explanation for the instability of the Co (II) complexes might be described in terms of the crystal field theory. The Co might favor a more stable d 6 (Co+ 3 ) low spin state to a less stable d7 (Co+ 2 ) high spin state due to the larger crystal field produced by the ligand than by the wa ...
... A possible explanation for the instability of the Co (II) complexes might be described in terms of the crystal field theory. The Co might favor a more stable d 6 (Co+ 3 ) low spin state to a less stable d7 (Co+ 2 ) high spin state due to the larger crystal field produced by the ligand than by the wa ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSRJAC)
... analysis, magnetic measurements and spectral studies. The complexes were found to have composition ML 2, where L = Ethyl-α-Isonitrosoacetoacetate and M = Cu (II), Ni (II) and Co (II). On the basis of elemental and spectral studies six coordinated octahedral geometry assign for Co (II), Ni (II) and s ...
... analysis, magnetic measurements and spectral studies. The complexes were found to have composition ML 2, where L = Ethyl-α-Isonitrosoacetoacetate and M = Cu (II), Ni (II) and Co (II). On the basis of elemental and spectral studies six coordinated octahedral geometry assign for Co (II), Ni (II) and s ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.






![[E]ven the most difficult problems in chemical experimentation can](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/006510251_1-96239c5b6e245cee1be60ed8e0730b48-300x300.png)