Osukuuni Exam I - Clayton State University
... on earth, but all other aspects of the atoms are the same. In this universe, you find that the first (lowest energy) orbital is filled with three electrons and the second orbital can hold a maximum of nine electrons. You discover an element Z that has five electrons in its atom. Would you expect Z t ...
... on earth, but all other aspects of the atoms are the same. In this universe, you find that the first (lowest energy) orbital is filled with three electrons and the second orbital can hold a maximum of nine electrons. You discover an element Z that has five electrons in its atom. Would you expect Z t ...
Word - chemmybear.com
... These are usually formed from a transition metal atoms surrounded by ligands (polar molecules or negative ions). As a "rule of thumb" you place twice the number of ligands around an ion as the charge on the ion... Examples: dark blue Cu(NH3)42+ and Ag(NH3)2+. (Note: Ammonia is used as a test for Cu2 ...
... These are usually formed from a transition metal atoms surrounded by ligands (polar molecules or negative ions). As a "rule of thumb" you place twice the number of ligands around an ion as the charge on the ion... Examples: dark blue Cu(NH3)42+ and Ag(NH3)2+. (Note: Ammonia is used as a test for Cu2 ...
Document
... Each complex has a geometry, which, depending on the symmetry elements repeating atoms or group of atoms, corresponds to a given symmetry pointgroup. Each pointgroup has specific irreducible representations which are conveniently listed in the character table. By using this table, it is relatively e ...
... Each complex has a geometry, which, depending on the symmetry elements repeating atoms or group of atoms, corresponds to a given symmetry pointgroup. Each pointgroup has specific irreducible representations which are conveniently listed in the character table. By using this table, it is relatively e ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... Stability of complexes The substitution of monodentate ligand with a bidentate or a multidentate ligand leads to a more stable complex. This is called the chelate effect This chelate effect can be explained in terms of a positive entropy change in these reactions as more molecules of products than ...
... Stability of complexes The substitution of monodentate ligand with a bidentate or a multidentate ligand leads to a more stable complex. This is called the chelate effect This chelate effect can be explained in terms of a positive entropy change in these reactions as more molecules of products than ...
Ligand field theory
... electronic structure of transition metal compounds, all of which can be considered coordination complexes. CFT successfully accounts for some magnetic properties, colours, hydration enthalpies, and spinel structures of transition metal complexes, but it does not attempt to describe bonding. CFT was ...
... electronic structure of transition metal compounds, all of which can be considered coordination complexes. CFT successfully accounts for some magnetic properties, colours, hydration enthalpies, and spinel structures of transition metal complexes, but it does not attempt to describe bonding. CFT was ...
pdf notes
... • The number of contributed electrons • The symmetry of the skeletal orbitals • The energy of skeletal orbitals Calculations of the frontier orbitals of different fragments can allow the prediction of unknown cluster compounds. This leads to the idea of isolobal fragments; fragments that share orbit ...
... • The number of contributed electrons • The symmetry of the skeletal orbitals • The energy of skeletal orbitals Calculations of the frontier orbitals of different fragments can allow the prediction of unknown cluster compounds. This leads to the idea of isolobal fragments; fragments that share orbit ...
Basic Chemistry notes
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
... ______________________—two or more like atoms combined chemically ______________________—two or more different atoms combined chemically ...
Angular Overlap
... Second and third transition series form lowspin more easily than metals form the first transition series -The greater overlap between the larger 4d and 5d orbitals and the ligand orbitals -A decreased pairing energy due to the larger volume available for electrons ...
... Second and third transition series form lowspin more easily than metals form the first transition series -The greater overlap between the larger 4d and 5d orbitals and the ligand orbitals -A decreased pairing energy due to the larger volume available for electrons ...
5.3 Chemical Formulas - Merrell Science Room
... Molecular Elements- do not normally exist in nature as single atoms instead they exist as diatomic molecules this mean two. H2 O2 Cl2 Molecular Compounds- are compounds formed between two or more nonmetals. H2O CO2 C3H6O ...
... Molecular Elements- do not normally exist in nature as single atoms instead they exist as diatomic molecules this mean two. H2 O2 Cl2 Molecular Compounds- are compounds formed between two or more nonmetals. H2O CO2 C3H6O ...
Chem 101 notes review
... alcohols esters ethers carbonyl groups aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids acyl chlorides organic halides amines amides resonance Arrhenius acids/bases Brönsted/Lowery acids/bases Lewis acids/bases ...
... alcohols esters ethers carbonyl groups aldehydes ketones carboxylic acids acyl chlorides organic halides amines amides resonance Arrhenius acids/bases Brönsted/Lowery acids/bases Lewis acids/bases ...
1 - shawnschmitt
... 21. When an electron in the excited state drops from n=4 to n=2, what color is the photon given off? blue light 22. How does an atom form a positive ion with a 3+ charge? anion with a 2- (two negative) charge? a 3+ charge is the result of losing 3 electrons, a 2- charge is a result of gaining 2 elec ...
... 21. When an electron in the excited state drops from n=4 to n=2, what color is the photon given off? blue light 22. How does an atom form a positive ion with a 3+ charge? anion with a 2- (two negative) charge? a 3+ charge is the result of losing 3 electrons, a 2- charge is a result of gaining 2 elec ...
Chapter 1 - DORAS
... without the related disadvantages. By substituting one or more of the 2,2-bipyridine ligands it is possible to improve the parent complex and generate a system which may undergo more efficient supramolecular processes. This substitution may have the affect of altering the energy gap between the exci ...
... without the related disadvantages. By substituting one or more of the 2,2-bipyridine ligands it is possible to improve the parent complex and generate a system which may undergo more efficient supramolecular processes. This substitution may have the affect of altering the energy gap between the exci ...
CH160 (Coordination Chemistry – APD) Tutorial
... State the dn electron configuration Sketch, label (e.g. cis, fac, etc) and name the type of isomerism (e.g. “stereoisomerism - optical isomerism”) for all possible isomers ...
... State the dn electron configuration Sketch, label (e.g. cis, fac, etc) and name the type of isomerism (e.g. “stereoisomerism - optical isomerism”) for all possible isomers ...
Complex Ion Equilibria - South Kingstown High School
... The formation constant, Kf , is the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from the aqueous metal ion and the ligands. ...
... The formation constant, Kf , is the equilibrium constant for the formation of a complex ion from the aqueous metal ion and the ligands. ...
metal ions in biological systems
... effects from metal ion binding, by V. (3. Bregadze Chapter 13" Electron transfer reactions through the DNA double helix, by T. J. Meade Chapter 14" Role of metal ions in ribozymes, by A. M. Pyle Chapter 15: Ternary metal ion-nucleic acid base-protein complexes, by M. Sabat Chapter 16 Metal-responsiv ...
... effects from metal ion binding, by V. (3. Bregadze Chapter 13" Electron transfer reactions through the DNA double helix, by T. J. Meade Chapter 14" Role of metal ions in ribozymes, by A. M. Pyle Chapter 15: Ternary metal ion-nucleic acid base-protein complexes, by M. Sabat Chapter 16 Metal-responsiv ...
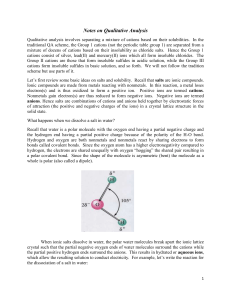
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
... Qualitative analysis involves separating a mixture of cations based on their solubilities. In the traditional QA scheme, the Group 1 cations (not the periodic table group 1) are separated from a mixture of dozens of cations based on their insolubility as chloride salts. Hence the Group 1 cations con ...
Introduction(s)
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
Memorization?
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
... and a nonmetal react. Covalent (molecular) compounds are formed when two nonmetals react. ...
Coordination complex

In chemistry, a coordination complex or metal complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the coordination centre, and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ligands or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those of transition metals, are coordination complexes.