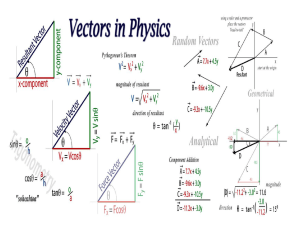
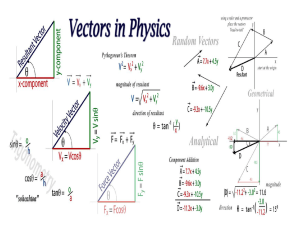
Chap. 14
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. r r • Although f ij and f ji are equal and opposite, the work of these forces will not, in general, cancel out. • If t ...
... • Principle of work and energy can be applied to the entire system by adding the kinetic energies of all particles and considering the work done by all external and internal forces. r r • Although f ij and f ji are equal and opposite, the work of these forces will not, in general, cancel out. • If t ...
Version PREVIEW – Practice 8 – carroll – (11108) 1 This print
... If the disk is released from rest in the position shown by the solid circle, what is the speed of its center of mass when the disk reaches the position indicated by the dashed circle? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . Correct answer: 9.4608 m/s. ...
... If the disk is released from rest in the position shown by the solid circle, what is the speed of its center of mass when the disk reaches the position indicated by the dashed circle? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . Correct answer: 9.4608 m/s. ...