Notes for Newton
... A. Newton’s First Law 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibr ...
... A. Newton’s First Law 1. An object in motion will remain in motion, an object at rest will remain at rest unless acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibr ...
Origin of Inertial Mass
... fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gravitational mass. In addition to gravity, Newton claimed, there existed another fundamenta ...
... fundamentally different mechanisms and relate to different forces. The force of gravity is an attraction of two bodies for each other. This article is concerned with inertial mass only and does not deal with gravitational mass. In addition to gravity, Newton claimed, there existed another fundamenta ...
Newton`s 2nd Law
... In the equation for weight, g is no longer considered the acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at th ...
... In the equation for weight, g is no longer considered the acceleration due to gravity, but rather the gravitational field strength, with units of newtons/kilogram. Inertial and gravitational masses have been tested and are believed to always be equal in amount. This is why all objects freefall at th ...
Lect-7
... This can be extended to other planets, but the value of g varies from planet to planet, so the object’s weight will vary from planet to planet ...
... This can be extended to other planets, but the value of g varies from planet to planet, so the object’s weight will vary from planet to planet ...
Class Exercise - Career Launcher
... Centrifugal Force in Circular Motion P is at rest with respect to itself. A pseudo force Fpseudo to be added as frame is non inertial. So in frame of P; F Fcp Fpseudo 0. Fcp ...
... Centrifugal Force in Circular Motion P is at rest with respect to itself. A pseudo force Fpseudo to be added as frame is non inertial. So in frame of P; F Fcp Fpseudo 0. Fcp ...
Ezio Fornero, Space and Motion as Problems of
... rule: when we say “the speed of a car is 50 km/h”, we refer to Earth’s surface, without asking what “real” velocity is with respect to a some hypothetic “absolute space”, at all needless in such a context. Really, the history of Astronomy contradicts such a thesis: if all motions are relative and th ...
... rule: when we say “the speed of a car is 50 km/h”, we refer to Earth’s surface, without asking what “real” velocity is with respect to a some hypothetic “absolute space”, at all needless in such a context. Really, the history of Astronomy contradicts such a thesis: if all motions are relative and th ...
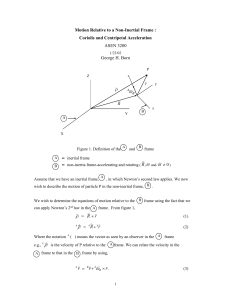
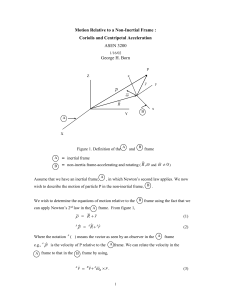
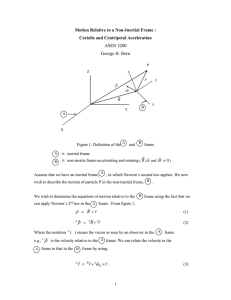
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Anisotropy of Inertia from the CMB Anisotropy
... describes its response to external forces as well as the motion of that body in the absence of forces (and, perhaps more importantly, its motion in the presence and in the absence of other bodies). Here the history of inertia in physical theory will be briefly considered with an emphasis on its rela ...
... describes its response to external forces as well as the motion of that body in the absence of forces (and, perhaps more importantly, its motion in the presence and in the absence of other bodies). Here the history of inertia in physical theory will be briefly considered with an emphasis on its rela ...