Document
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
... A friction force between two objects in contact opposes the sliding of one object over the surface of the adjacent one. It is tangent to the surface of the adjacent object and opposite in direction to the velocity of the moving object. The magnitude of the frictional force is assumed to be proportio ...
Force and Motion - Rockaway Township School District
... The performance expectations in the topic Forces and Interactions focus on helping students understand ideas related to why some objects will keep moving, why objects fall to the ground and why some materials are attracted to each other while others are not. Students answer the question, “How can on ...
... The performance expectations in the topic Forces and Interactions focus on helping students understand ideas related to why some objects will keep moving, why objects fall to the ground and why some materials are attracted to each other while others are not. Students answer the question, “How can on ...
Applying Newton`s Laws
... ** Note: The value of the acceleration depends on the frame of reference. Newton’s Laws are only valid when frame is an inertial reference frame. Technically a set of axes fixed to the Earth is not an inertial reference frame due to the rotation of the Earth, but the Earth’s rotation is very slow th ...
... ** Note: The value of the acceleration depends on the frame of reference. Newton’s Laws are only valid when frame is an inertial reference frame. Technically a set of axes fixed to the Earth is not an inertial reference frame due to the rotation of the Earth, but the Earth’s rotation is very slow th ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... direction.1 For the body to constantly change direction, rotate around an axis, and keep a constant speed the force must also be perpendicular to the direction of the velocity at all times.1 The forces direction must be towards the axis, essentially pulling the body inwards. As the velocity is alway ...
... direction.1 For the body to constantly change direction, rotate around an axis, and keep a constant speed the force must also be perpendicular to the direction of the velocity at all times.1 The forces direction must be towards the axis, essentially pulling the body inwards. As the velocity is alway ...
Gravity-centripetal acceleration
... The force is brought about by the tires pushing on the racetrack. The friction between the road and the tire is very important, so race tires are designed to maximize friction. What is the source of the centripetal force required to make the earth revolve around the sun? This is where the apple fall ...
... The force is brought about by the tires pushing on the racetrack. The friction between the road and the tire is very important, so race tires are designed to maximize friction. What is the source of the centripetal force required to make the earth revolve around the sun? This is where the apple fall ...
Chapter 5
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 50.0 kg·m2. The crate weighs 4420 N. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of the dual Pulley (radius-1 = 0.600m, radius-2 = 0.200 m). ...
... The combined moment of inertia of the dual pulley is 50.0 kg·m2. The crate weighs 4420 N. A tension of 2150 N is maintained in the cable attached to the motor. Find the angular acceleration of the dual Pulley (radius-1 = 0.600m, radius-2 = 0.200 m). ...
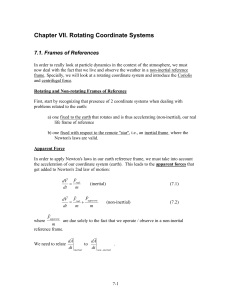
Chapter VII. Rotating Coordinate Systems
... fine the components of Fcor = −2Ω × V in a chosen Cartesian coordinate system. We can also obtain them in a more physical way. Let's do it in the physical way first. Consider first the situation where we have a particle of unit mass moving freely on the frictionless surface of the rotating earth if ...
... fine the components of Fcor = −2Ω × V in a chosen Cartesian coordinate system. We can also obtain them in a more physical way. Let's do it in the physical way first. Consider first the situation where we have a particle of unit mass moving freely on the frictionless surface of the rotating earth if ...
lectures 2014
... State the parallel and perpendicular axis theorems. (a) Calculate the moment of inertia of a uniform square plate of side a and mass m about an axis through its centre and parallel to a side. (b) Use the perpendicular axis theorem to find the moment of inertia through the centre and perpendicular to ...
... State the parallel and perpendicular axis theorems. (a) Calculate the moment of inertia of a uniform square plate of side a and mass m about an axis through its centre and parallel to a side. (b) Use the perpendicular axis theorem to find the moment of inertia through the centre and perpendicular to ...
Chapter 5 Lecture
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
... Any reference frame that moves with constant velocity relative to an inertial frame is itself an inertial frame. If you accelerate relative to an object in an inertial frame, you are observing the object from a non-inertial reference frame. A reference frame that moves with constant velocity relativ ...
Chapter 5 Notes (PowerPoint)
... • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... • Newton’s first law: if the net force on an object is zero, its velocity is constant • Inertial frame of reference: one in which the first law holds • Newton’s second law: • Free-body diagram: a sketch showing all the forces on an object Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
motion - Images
... • Suppose you pull a 10kg sled so that the net force on the sled is 5N. What is the acceleration of the sled? A = 5N ÷ 10kg = 0.5m/s2 • You throw a baseball with a mass of 10kg so it has an acceleration of 40m/s2. How much force did you exert on the baseball? Answer: 400N • Making a connection: Expl ...
... • Suppose you pull a 10kg sled so that the net force on the sled is 5N. What is the acceleration of the sled? A = 5N ÷ 10kg = 0.5m/s2 • You throw a baseball with a mass of 10kg so it has an acceleration of 40m/s2. How much force did you exert on the baseball? Answer: 400N • Making a connection: Expl ...
force - My CCSD
... Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they move. Galileo stated that ev ...
... Inertia Galileo came up with the definitions of FORCE and FRICTION. Force is any push or pull. Friction is the name given to the force that acts between materials that touch as they move past each other. Galileo was concerned with how things move rather than why they move. Galileo stated that ev ...