6th Grade Science
... Describe friction Describe how resistance of materials affects electrical flow Identify forces acting on objects Give examples of forces Describe gravity Compare and contrast forces and explain the causes and effects of gravity Differentiate velocity from speed Identify that velocity ...
... Describe friction Describe how resistance of materials affects electrical flow Identify forces acting on objects Give examples of forces Describe gravity Compare and contrast forces and explain the causes and effects of gravity Differentiate velocity from speed Identify that velocity ...
1-2 - Renton School District
... Friction is a force that exists between a piece of matter that is either moving or has a force applied to it and any other matter it is in contact with. Friction always acts in a direction opposite to that of the motion or the applied force. It is friction that causes a moving object that appears to ...
... Friction is a force that exists between a piece of matter that is either moving or has a force applied to it and any other matter it is in contact with. Friction always acts in a direction opposite to that of the motion or the applied force. It is friction that causes a moving object that appears to ...
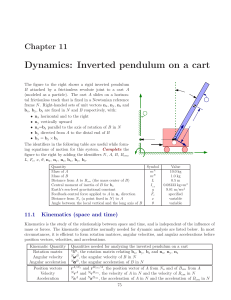
Dynamics: Inverted pendulum on a cart
... • Use the right-hand rule to determine the sign of λ . In other words, point the four fingers of your right hand in the direction of n⊥ , and then curl them in the direction of b⊥ . If you thumb points in the direction of λ , the sign of λ is positive, otherwise it is negative. ...
... • Use the right-hand rule to determine the sign of λ . In other words, point the four fingers of your right hand in the direction of n⊥ , and then curl them in the direction of b⊥ . If you thumb points in the direction of λ , the sign of λ is positive, otherwise it is negative. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Of course, you already know all about the Law of Uniform Motion since this is really just stating an observation. Consider, for example, a block placed on a table. Clearly you know that the block won’t move unless someone (or something) pushes on the ball. This is (in essence) Newton’s 1st Law: The ...
... Of course, you already know all about the Law of Uniform Motion since this is really just stating an observation. Consider, for example, a block placed on a table. Clearly you know that the block won’t move unless someone (or something) pushes on the ball. This is (in essence) Newton’s 1st Law: The ...
There are 2 types of acceleration
... Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net force causing the acceleration must also point toward the center of the circle. This net force is called the Centripetal Force because it causes the objects to move in a circle. Remember: the Centripetal Force is ALWAYS toward the c ...
... Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net force causing the acceleration must also point toward the center of the circle. This net force is called the Centripetal Force because it causes the objects to move in a circle. Remember: the Centripetal Force is ALWAYS toward the c ...
Circular Motion
... • Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net force causing the acceleration must also point toward the center of the circle. This net force is called the Centripetal Force because it causes the objects to move in a circle. Remember: the Centripetal Force is ALWAYS toward the c ...
... • Since the acceleration is toward the center on the circle the net force causing the acceleration must also point toward the center of the circle. This net force is called the Centripetal Force because it causes the objects to move in a circle. Remember: the Centripetal Force is ALWAYS toward the c ...
P1710_MWF09
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
... • Newton’s Laws of Motion are: (1) Acceleration (or deceleration) occurs if and only if there is a net external force. (2) a = F/m [Note this is a vector eqn.] (3) The force exerted by a first object on a second is always equal and opposite the the force exerted by the second on the first. F12 = ...
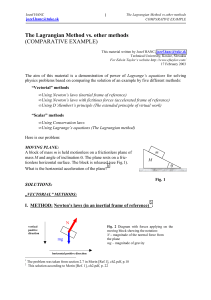
The Lagrangian Method vs
... 1) This principle uses the concept of the virtual displacement, which means, not actual small displacement, but it involves a possible, but purely mathematical experiment, so it can be applied in a certain definite time (even if such a displacement would involve physically infinite velocities). At t ...
... 1) This principle uses the concept of the virtual displacement, which means, not actual small displacement, but it involves a possible, but purely mathematical experiment, so it can be applied in a certain definite time (even if such a displacement would involve physically infinite velocities). At t ...
Chapter 5 Lectures
... “Every body continues its state of rest or uniform speed in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force acting on it.” This tendency to maintain one’s state of motion (whether actually moving or at rest) is called inertia; for this reason, the Newton’s First Law of Mo ...
... “Every body continues its state of rest or uniform speed in a straight line, unless it is compelled to change that state by a net force acting on it.” This tendency to maintain one’s state of motion (whether actually moving or at rest) is called inertia; for this reason, the Newton’s First Law of Mo ...
Physics 11 Dynamics - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... line at constant speed in the absence of outside forces; objects with greater mass have greater inertia Dynamics - the study of the motions of bodies while considering their masses and the responsible forces Mechanics - the branch of physics comprising kinematics and dynamics; simply, the how and th ...
... line at constant speed in the absence of outside forces; objects with greater mass have greater inertia Dynamics - the study of the motions of bodies while considering their masses and the responsible forces Mechanics - the branch of physics comprising kinematics and dynamics; simply, the how and th ...
Microsoft Word - Phy.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... line at constant speed in the absence of outside forces; objects with greater mass have greater inertia Dynamics - the study of the motions of bodies while considering their masses and the responsible forces Mechanics - the branch of physics comprising kinematics and dynamics; simply, the how and th ...
... line at constant speed in the absence of outside forces; objects with greater mass have greater inertia Dynamics - the study of the motions of bodies while considering their masses and the responsible forces Mechanics - the branch of physics comprising kinematics and dynamics; simply, the how and th ...
Newton`s 1st Law of Motion
... the ball to a stop. But if a ball were given a push in deep space, it would travel an exceedingly long distance before being acted on by external forces. To understand a concept like this we need to “undress nature.” We must look past superficial complexity to see the simple characteristics of natur ...
... the ball to a stop. But if a ball were given a push in deep space, it would travel an exceedingly long distance before being acted on by external forces. To understand a concept like this we need to “undress nature.” We must look past superficial complexity to see the simple characteristics of natur ...