Chapter 6 The Sum of Ranks Test
... the Skeptic is correct then the two sets of data in the clone-enhanced study will be identical, which implies that ρ1 = ρ2 . Although I won’t give you details (and, thus, don’t worry about it) it is possible for the Skeptic to be incorrect and yet ρ1 = ρ2 . For the clone-enhanced data in Table 6.3 w ...
... the Skeptic is correct then the two sets of data in the clone-enhanced study will be identical, which implies that ρ1 = ρ2 . Although I won’t give you details (and, thus, don’t worry about it) it is possible for the Skeptic to be incorrect and yet ρ1 = ρ2 . For the clone-enhanced data in Table 6.3 w ...
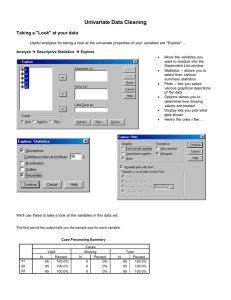
Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the
... Background: In systematic reviews and meta-analysis, researchers often pool the results of the sample mean and standard deviation from a set of similar clinical trials. A number of the trials, however, reported the study using the median, the minimum and maximum values, and/or the first and third qu ...
... Background: In systematic reviews and meta-analysis, researchers often pool the results of the sample mean and standard deviation from a set of similar clinical trials. A number of the trials, however, reported the study using the median, the minimum and maximum values, and/or the first and third qu ...
Statistics: Informed Decisions Using Data, 4e (Sullivan)
... 4) A survey claims that 9 out of 10 doctors (i.e., 90%) recommend brand Z for their patients who have children. To test this claim against the alternative that the actual proportion of doctors who recommend brand Z is less than 90%, a random sample of 100 doctors results in 83 who indicate that the ...
... 4) A survey claims that 9 out of 10 doctors (i.e., 90%) recommend brand Z for their patients who have children. To test this claim against the alternative that the actual proportion of doctors who recommend brand Z is less than 90%, a random sample of 100 doctors results in 83 who indicate that the ...
Lecture Slides for Elementary Statistics: Looking at the Big Picture
... Solution Method: Assume (temporarily) that population proportion is 0.10, find probability of sample proportion as high as 0.13. If it’s too improbable, we won’t believe population proportion is 0.10. ©2011 Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning ...
... Solution Method: Assume (temporarily) that population proportion is 0.10, find probability of sample proportion as high as 0.13. If it’s too improbable, we won’t believe population proportion is 0.10. ©2011 Brooks/Cole, Cengage Learning ...