Astronomy
... orbits of stars. One example of this was found at Building J at Monte Alban, it was constructed in an arrow shape, so that the five brightest stars of that time would set at the point of the arrow. A line drawn perpendicular to the front steps on the building showed that it would point directly to t ...
... orbits of stars. One example of this was found at Building J at Monte Alban, it was constructed in an arrow shape, so that the five brightest stars of that time would set at the point of the arrow. A line drawn perpendicular to the front steps on the building showed that it would point directly to t ...
16 October 2006
... spectral lines, indicating wobble due to the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet. ...
... spectral lines, indicating wobble due to the gravitational pull of an orbiting planet. ...
The Solar System - Junta de Andalucía
... The Earth revolves around the Sun in orbit, at the same time that it rotates on its axis. It takes one year and six hours for the Earth to complete its orbit around the Sun. As a result, every four years we have an extra day in February. This year is called a leap year. The Earth’s revolution causes ...
... The Earth revolves around the Sun in orbit, at the same time that it rotates on its axis. It takes one year and six hours for the Earth to complete its orbit around the Sun. As a result, every four years we have an extra day in February. This year is called a leap year. The Earth’s revolution causes ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
... Luminosity = (energy radiated per cm2 per sec) x (area of surface in cm2) So: Luminosity (temperature) 4 x (surface area) Determine luminosity from apparent brightness and distance, determine temperature from spectrum (black-body curve or spectral lines), then find surface area, then find radius ( ...
Garden-Variety Star - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Flares last from a few minutes to a few hours A lot of ionized material is ejected in a flare Unlike the material in prominences, the solar-flare material moves with enough energy to escape the Sun's gravity When such a burst of ions reaches the Earth, it interferes with radio communication Sometime ...
... Flares last from a few minutes to a few hours A lot of ionized material is ejected in a flare Unlike the material in prominences, the solar-flare material moves with enough energy to escape the Sun's gravity When such a burst of ions reaches the Earth, it interferes with radio communication Sometime ...
Locating Geographic Coordinates Using Observations over the Sun
... A device of this type was used for short term observations (within a few hours) in my second experiment described in Section 3. However, for longer term observations within months, I needed a more stable, stationary instrument which could not be affected by wind, birds, etc. Preferably, it would all ...
... A device of this type was used for short term observations (within a few hours) in my second experiment described in Section 3. However, for longer term observations within months, I needed a more stable, stationary instrument which could not be affected by wind, birds, etc. Preferably, it would all ...
Unit 6
... watts are spread out over a larger area on the ground, and each square meter of the Earth’s surface receives only a fraction as much energy. You take advantage of this effect instinctively when you warm your hands at a fire by holding your palms flat toward the fire. You also may have experienced th ...
... watts are spread out over a larger area on the ground, and each square meter of the Earth’s surface receives only a fraction as much energy. You take advantage of this effect instinctively when you warm your hands at a fire by holding your palms flat toward the fire. You also may have experienced th ...
SOLAR ECLIPSES
... Retina’s exposure to intense visible light also results in the destruction of its cells by a photo-oxidation process. This destructive process, called photochemical retinopathy takes place especially due to the radiation between 380 nm and 500 nm. By watching the Sun without any special filters, the ...
... Retina’s exposure to intense visible light also results in the destruction of its cells by a photo-oxidation process. This destructive process, called photochemical retinopathy takes place especially due to the radiation between 380 nm and 500 nm. By watching the Sun without any special filters, the ...
PLANETARY MOTIONS
... which moved with respect to the “fixed stars.” There were seven known planets in ancient times: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, the Sun, and the Moon. All other celestial objects were fixed stars and moved together - their positions with respect to one another did not change. Planetary motion ...
... which moved with respect to the “fixed stars.” There were seven known planets in ancient times: Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, the Sun, and the Moon. All other celestial objects were fixed stars and moved together - their positions with respect to one another did not change. Planetary motion ...
Document
... First it actually gives us a very specific day - the 20th day of Taurus. In astrological terms that means exactly just that: 20 days after the sun rose for the first time in the constellation of Taurus.. No doubt about the day and period. So everyone jumped on our modern Zodiac birthdates and see "O ...
... First it actually gives us a very specific day - the 20th day of Taurus. In astrological terms that means exactly just that: 20 days after the sun rose for the first time in the constellation of Taurus.. No doubt about the day and period. So everyone jumped on our modern Zodiac birthdates and see "O ...
2 The Origin of the Seasons
... to keep track of the seasons were large stone structures (such as Stonehenge) that used the positions of the rising Sun or Moon to forecast the coming seasons. The first recognizable calendars that we know about were developed in Egypt, and appear to date from about 4,200 BC. Of course, all a calend ...
... to keep track of the seasons were large stone structures (such as Stonehenge) that used the positions of the rising Sun or Moon to forecast the coming seasons. The first recognizable calendars that we know about were developed in Egypt, and appear to date from about 4,200 BC. Of course, all a calend ...
Orbits - davis.k12.ut.us
... Kepler's second law helps us to predict the motion of planets. Because planets change speed during the course of their orbits, they do not follow simple models of motion. We have to use more complicated methods that take into account the eccentricity of the planet's orbit and its exact position alon ...
... Kepler's second law helps us to predict the motion of planets. Because planets change speed during the course of their orbits, they do not follow simple models of motion. We have to use more complicated methods that take into account the eccentricity of the planet's orbit and its exact position alon ...
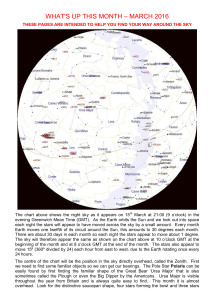
what`s up this month – march 2016
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
... The night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 on 15 thMarch The chart above shows the night sky looking to the south at about 21:00 (9 o’clock in the evening) on 15th March (around the middle of the month). The sky will appear very much the same an hour later at the beginning of the month and an ...
cards for each vacation stop - Morehead Planetarium and Science
... 4. The weather is terrible, too. Jupiter has a storm, the Great Red Spot, that’s been observed for more than 300 years and is larger than Earth. 5. Your days on Jupiter would whiz by, since each one lasts only 10 hours. 6. But the years are long. The farther away planets are from the Sun, the longer ...
... 4. The weather is terrible, too. Jupiter has a storm, the Great Red Spot, that’s been observed for more than 300 years and is larger than Earth. 5. Your days on Jupiter would whiz by, since each one lasts only 10 hours. 6. But the years are long. The farther away planets are from the Sun, the longer ...
File - Mr. Catt`s Class
... southernmost positions, respectively. 9. The vernal and autumnal equinoxes are the points on the celestial sphere where the Sun crosses the celestial equator while moving north and south, respectively. © 2007 Jones and Bartlett Publishers ...
... southernmost positions, respectively. 9. The vernal and autumnal equinoxes are the points on the celestial sphere where the Sun crosses the celestial equator while moving north and south, respectively. © 2007 Jones and Bartlett Publishers ...
cosmo ca greeks and middle ages
... which joins the positions of a given planet everyday at midnight (a ``join the dots'' game); see, for example Fig 2.13. Most of the planets move in one direction, but Mars does not, its motion over several months is seen sometimes to backtrack (the same behavior would have been observed for other ce ...
... which joins the positions of a given planet everyday at midnight (a ``join the dots'' game); see, for example Fig 2.13. Most of the planets move in one direction, but Mars does not, its motion over several months is seen sometimes to backtrack (the same behavior would have been observed for other ce ...
Detection of the Rossiter–McLaughlin effect in
... The Venus transit as seen from the Moon has a slightly different timing and projection on the solar disc from what is seen from the Earth. The Moon was 95 per cent illuminated and about 8◦ ahead the Earth, and Venus reached the Sun–Moon alignment with a delay of about 2 h. As seen from the Moon cent ...
... The Venus transit as seen from the Moon has a slightly different timing and projection on the solar disc from what is seen from the Earth. The Moon was 95 per cent illuminated and about 8◦ ahead the Earth, and Venus reached the Sun–Moon alignment with a delay of about 2 h. As seen from the Moon cent ...
Algebra I Study Guide 7-1 to 7-5
... 52. When t = 0, the value of the expression is 80 g. This is the initial quantity of strontium-90. When t = 28, the value of the expression is 40 g. This is the amount of strontium-90 remaining after 28 years i.e., after 1 half-life. When t = 56, the value of the expression is 20 g. This is the amou ...
... 52. When t = 0, the value of the expression is 80 g. This is the initial quantity of strontium-90. When t = 28, the value of the expression is 40 g. This is the amount of strontium-90 remaining after 28 years i.e., after 1 half-life. When t = 56, the value of the expression is 20 g. This is the amou ...
The Earth`s orbit and an exoplanetary orbit 1 Creating the objects 2
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
Printable Version of this information
... What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a dry season. People have paid attention to seasons ...
... What are seasons? While we might think there is a "correct" answer to this question, in actuality it is a vague question. In addition to winter, spring, summer and fall, here we also have hurricane season. Tropical climates typically have a wet and a dry season. People have paid attention to seasons ...
The Earth`s orbit and an exoplanetary orbit 1 Creating
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
... What happens if you aim the objects straight away from each other? With large or small initial speeds? What happens if you aim the objects straight toward each other? (When the objects get very close, the force changes rapidly with distance, so the calculations become increasingly inaccurate and the ...
Solutions
... mass must go up. (The reason fusion is faster in the core is that it has become compressed relative to the core of the main sequence star; the hotter and denser core allows for faster fusion.) Note: a few of you in your argument mentioned that the sun would be “more massive” as a red giant. This is ...
... mass must go up. (The reason fusion is faster in the core is that it has become compressed relative to the core of the main sequence star; the hotter and denser core allows for faster fusion.) Note: a few of you in your argument mentioned that the sun would be “more massive” as a red giant. This is ...
How the Earth Moves Transcript
... stars – in reality the stars are widely separated in their distance away from Earth, and only appear to be close as they lie in the same direction when viewed from our vantage point. However, that wasn’t clear to most ancient civilisation, who (quite reasonably) believed that all the stars were loc ...
... stars – in reality the stars are widely separated in their distance away from Earth, and only appear to be close as they lie in the same direction when viewed from our vantage point. However, that wasn’t clear to most ancient civilisation, who (quite reasonably) believed that all the stars were loc ...
Moon Obs #1 Due!
... All of the planets orbit the Sun in the same direction. The orbits of all of the planets lie near the ecliptic plane. The outer planets have compositions similar to the Sun. Most of the moons in our solar system belong to the Jovian planets. ...
... All of the planets orbit the Sun in the same direction. The orbits of all of the planets lie near the ecliptic plane. The outer planets have compositions similar to the Sun. Most of the moons in our solar system belong to the Jovian planets. ...
Life of the Sun—16 Oct
... between gravity and pressure. How does the sun adjust? • Without burning fuel to keep temperature up, pressure (PV=nRT) would fall and gravity would win. • Core shrinks, gets hotter • H→He in the a shell surrounding inert core • Balance restored. ...
... between gravity and pressure. How does the sun adjust? • Without burning fuel to keep temperature up, pressure (PV=nRT) would fall and gravity would win. • Core shrinks, gets hotter • H→He in the a shell surrounding inert core • Balance restored. ...