A Guide to Space - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... Earth’s equator would be the celestial equator. Earth’s North Pole would be the North Celestial Pole and Earth’s South Pole would be the South Celestial Pole. If you stand in a flat area at night, you will see a one-half of the celestial sphere in the sky. You can think of the celestial sphere as th ...
... Earth’s equator would be the celestial equator. Earth’s North Pole would be the North Celestial Pole and Earth’s South Pole would be the South Celestial Pole. If you stand in a flat area at night, you will see a one-half of the celestial sphere in the sky. You can think of the celestial sphere as th ...
Become a Member - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... and the Sun were substantially identical. Russell wrote [2] “The agreement of the solar and terrestrial lists is such as to confirm very strongly Rowland’s opinion that, if the Earth’s crust should be raised to the temperature of the Sun’s atmosphere, it would give a very similar absorption spectrum ...
... and the Sun were substantially identical. Russell wrote [2] “The agreement of the solar and terrestrial lists is such as to confirm very strongly Rowland’s opinion that, if the Earth’s crust should be raised to the temperature of the Sun’s atmosphere, it would give a very similar absorption spectrum ...
1 Kepler`s Laws of Planetary Motion
... were made possible by planetary data of unprecedented accuracy collected by Tycho Brahe. The laws were both a radical departure from the astronomical prejudices of the time and profound tools for predicting planetary motion with great accuracy. Kepler, however, was not able to describe in a signific ...
... were made possible by planetary data of unprecedented accuracy collected by Tycho Brahe. The laws were both a radical departure from the astronomical prejudices of the time and profound tools for predicting planetary motion with great accuracy. Kepler, however, was not able to describe in a signific ...
PHYS103 Hour Exam No. 1 Page: 1 1 Which of the following
... 24 A sidereal day is the time it takes for a. the Sun to come back to the same position in the sky. b. the Moon to come back to the same positions in the sky. c. the stars to come back to the same positions in the sky. ...
... 24 A sidereal day is the time it takes for a. the Sun to come back to the same position in the sky. b. the Moon to come back to the same positions in the sky. c. the stars to come back to the same positions in the sky. ...
Definition of a Graha - Saptarishis Astrology
... Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. This definition does not recognize the Moon, Sun, Rahu and Ketu as planets while Earth is a planet. The I.A.U has now defined a planet as a celestial body that:a) is in orbit around the Sun; b) has sufficient mass for its self- ...
... Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. This definition does not recognize the Moon, Sun, Rahu and Ketu as planets while Earth is a planet. The I.A.U has now defined a planet as a celestial body that:a) is in orbit around the Sun; b) has sufficient mass for its self- ...
For Creative Minds - Arbordale Publishing
... We used to think there was a 9th planet named Pluto, but it’s actually one of more than 40 “dwarf planets” that orbit our sun. An asteroid belt, the dwarf planets, and comets also orbit the sun. Most meteors are “space dust” from the comet tails. We have 24 hours in a day because it takes the Earth ...
... We used to think there was a 9th planet named Pluto, but it’s actually one of more than 40 “dwarf planets” that orbit our sun. An asteroid belt, the dwarf planets, and comets also orbit the sun. Most meteors are “space dust” from the comet tails. We have 24 hours in a day because it takes the Earth ...
IS Chapter 14 Notes
... tides – rise and fall of ocean water that goes through a cycle every 12.5 hours rising for approximately 6 hours and falling for approximately 6 hours - caused by the difference in pull of gravity from the moon and sun with Earth -at any one time on Earth, 2 places have high tides and 2 places have ...
... tides – rise and fall of ocean water that goes through a cycle every 12.5 hours rising for approximately 6 hours and falling for approximately 6 hours - caused by the difference in pull of gravity from the moon and sun with Earth -at any one time on Earth, 2 places have high tides and 2 places have ...
AE Module 5 Presentation
... Helium, methane, and ammonia are also present. Jupiter’s cloud tops are extremely dynamic and have very high winds and some of the biggest storms in the solar system. The biggest storm right now is the Great Red Spot – which is about 30,000 miles long and 10,000 miles wide, making it about the size ...
... Helium, methane, and ammonia are also present. Jupiter’s cloud tops are extremely dynamic and have very high winds and some of the biggest storms in the solar system. The biggest storm right now is the Great Red Spot – which is about 30,000 miles long and 10,000 miles wide, making it about the size ...
Solar Images Taken with Calcium K
... images to the Alachua Astronomy Club’s website as he did at the beginning of 2014 January. However, these images may appear alien compared with pictures we often associate with the Sun. (See Howard’s images at http://tiny.cc/vs0f9w.) ...
... images to the Alachua Astronomy Club’s website as he did at the beginning of 2014 January. However, these images may appear alien compared with pictures we often associate with the Sun. (See Howard’s images at http://tiny.cc/vs0f9w.) ...
m03a01
... The period of rotation of the Earth itself (the “day”) depends on whether one defines it as relative to the position of the Sun or relative to the fixed stars. The time interval between when any particular (far distant) star is on the celestial meridian, from one day to the next, is the sidereal day ...
... The period of rotation of the Earth itself (the “day”) depends on whether one defines it as relative to the position of the Sun or relative to the fixed stars. The time interval between when any particular (far distant) star is on the celestial meridian, from one day to the next, is the sidereal day ...
The Milky Way
... *a. High-density materials sink toward the center and lowdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. b. Low-density materials sink toward the center and highdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. c. Only rocky materials can condense close to the Sun, whereas both ...
... *a. High-density materials sink toward the center and lowdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. b. Low-density materials sink toward the center and highdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. c. Only rocky materials can condense close to the Sun, whereas both ...
Chapter 19
... a. High-density materials sink toward the center and lowdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. b. Low-density materials sink toward the center and highdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. c. Only rocky materials can condense close to the Sun, whereas both ...
... a. High-density materials sink toward the center and lowdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. b. Low-density materials sink toward the center and highdensity materials rise toward the surface of a molten body. c. Only rocky materials can condense close to the Sun, whereas both ...
Name
... What type of geomagnetic storm has the highest probability in the next 24 hours (0-24) for the: Mid-Latitudes = ___________________ High-Latitudes = __________________ ...
... What type of geomagnetic storm has the highest probability in the next 24 hours (0-24) for the: Mid-Latitudes = ___________________ High-Latitudes = __________________ ...
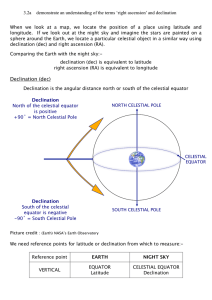
3.2a Right Ascension and Declination
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
... If a person was able to see the night sky shown above for a full day, the full band of stars would pass in front of them, moving steadily towards the right. The longitude reference point was more difficult. Many countries have laid claim to the Prime Meridian – the Chinese once used a gate from the ...
Gravity: Motivation • An initial theory describing the nature of the
... In addition to being the only body visited by humans, it is also the only object from which physical sample have been brought back to Earth (Radioactive dating found the youngest rocks formed 3 .1 billion years ago and the oldest formed 4.4 billion years ago). In addition to centuries of Earth bound ...
... In addition to being the only body visited by humans, it is also the only object from which physical sample have been brought back to Earth (Radioactive dating found the youngest rocks formed 3 .1 billion years ago and the oldest formed 4.4 billion years ago). In addition to centuries of Earth bound ...
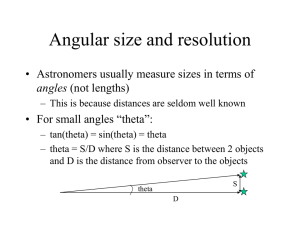
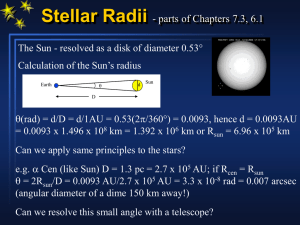
angles_telescopes
... surface (angular sizes of a few arc minutes) • To increase Moon from “actual size” to “fist size” requires magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small ...
... surface (angular sizes of a few arc minutes) • To increase Moon from “actual size” to “fist size” requires magnification of 10 (typical of binoculars) – with binoculars, can easily see shapes/shading on Moon’s surface (angular sizes of 10’s of arcseconds) • To see further detail you can use a small ...
Opposition of Saturn - Hong Kong Observatory
... Saturn revolves around the Sun with a period of about 29.5 years. Opposition of Saturn will occur about once every 378 days. The last Saturn opposition occurred on 18 December 2002 and the next occurrence will be on 1 January 2004. As Saturn has just passed the perihelion of its orbit in July 2003 ...
... Saturn revolves around the Sun with a period of about 29.5 years. Opposition of Saturn will occur about once every 378 days. The last Saturn opposition occurred on 18 December 2002 and the next occurrence will be on 1 January 2004. As Saturn has just passed the perihelion of its orbit in July 2003 ...
Distortion of Indian History For Muslim Appeasement, Part 6E
... Vedas was spoiled and derailed in the confused and fanciful Puranas. That is at any rate the case in the calendar, where two co-existing logical Vedic calendars (the tropical cycle of 12 half-seasons and the solilunar cycle of 12 or 13 lunar months) were replaced with a solilunar-sidereal calendar t ...
... Vedas was spoiled and derailed in the confused and fanciful Puranas. That is at any rate the case in the calendar, where two co-existing logical Vedic calendars (the tropical cycle of 12 half-seasons and the solilunar cycle of 12 or 13 lunar months) were replaced with a solilunar-sidereal calendar t ...
Episode 24 - Vigyan Prasar
... shadow of another moon. A binary star system can also produce eclipses if the plane of their orbit intersects the position of the observer. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon enters Earth’s shadow. If the moon becomes completely immersed in the umbra, the dark shadow, the eclipse is termed total. ...
... shadow of another moon. A binary star system can also produce eclipses if the plane of their orbit intersects the position of the observer. A lunar eclipse occurs when the moon enters Earth’s shadow. If the moon becomes completely immersed in the umbra, the dark shadow, the eclipse is termed total. ...
The Orrery - Eli Whitney Museum
... Textbooks usually describe the periods of rotation and revolution for the planets and the moon, but rarely do they identify the direction of movement. Can you make observations or plan experiments to determine which way the moon orbits the Earth? .... which way the Earth orbits the Sun? You can dete ...
... Textbooks usually describe the periods of rotation and revolution for the planets and the moon, but rarely do they identify the direction of movement. Can you make observations or plan experiments to determine which way the moon orbits the Earth? .... which way the Earth orbits the Sun? You can dete ...
Venus Transit and the Astronomical Unit
... Since A and B differ 9 in latitude and the circumference of Earth is given by 2r, the distance AB is given by AB = (2r/360) × 9 where r is the radius of Earth. Similarly, since the distance CD is 1/5 the solar diameter and the Sun subtends an angle of 30' or 0.5 at Earth, the angle is 0.1, wh ...
... Since A and B differ 9 in latitude and the circumference of Earth is given by 2r, the distance AB is given by AB = (2r/360) × 9 where r is the radius of Earth. Similarly, since the distance CD is 1/5 the solar diameter and the Sun subtends an angle of 30' or 0.5 at Earth, the angle is 0.1, wh ...
Bonus Article: Get Real About Astrology
... When astrology was becoming established in the form as we know it today, it drew on the twelve constellations lying within the ecliptic belt – with each constellation covering 30 degrees of the 360 degree circle. The beginning of the constellation of Aries (first point of Aries) was established as t ...
... When astrology was becoming established in the form as we know it today, it drew on the twelve constellations lying within the ecliptic belt – with each constellation covering 30 degrees of the 360 degree circle. The beginning of the constellation of Aries (first point of Aries) was established as t ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank, Manual Solution, Solution Manual
... What causes the seasons? The rotation of the Earth on its axis produces the cycle of day and night, and the revolution of the Earth around the sun produces the cycle of the year. Because Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to move eastward along the ecliptic through the constellations, completing ...
... What causes the seasons? The rotation of the Earth on its axis produces the cycle of day and night, and the revolution of the Earth around the sun produces the cycle of the year. Because Earth orbits the sun, the sun appears to move eastward along the ecliptic through the constellations, completing ...
The Planets Part 1
... This symbol in the Western world shows two semi-circles joined by horizontal line surmounting a circle. The centre is known as the starting point for path of expansion. The direction is established by the vertical line. This symbol indicates a deliberately creative individuality that knows what to a ...
... This symbol in the Western world shows two semi-circles joined by horizontal line surmounting a circle. The centre is known as the starting point for path of expansion. The direction is established by the vertical line. This symbol indicates a deliberately creative individuality that knows what to a ...