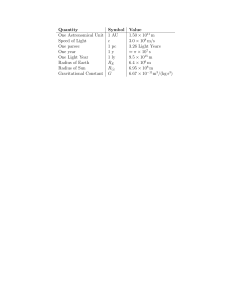
Quantity Symbol Value One Astronomical Unit 1 AU 1.50 × 10
... Part I. 1. Describe qualitatively the funny way that the planets move in the sky relative to the stars. Give a qualitative explanation as to why they move this way. 2. Draw a set of pictures approximately to scale showing the sun, the earth, the moon, α-centauri, and the milky way and the spacing b ...
... Part I. 1. Describe qualitatively the funny way that the planets move in the sky relative to the stars. Give a qualitative explanation as to why they move this way. 2. Draw a set of pictures approximately to scale showing the sun, the earth, the moon, α-centauri, and the milky way and the spacing b ...
The Sun*s
... May be viewed as an extension of the outer atmosphere of the Sun (the corona) into interplanetary space. Computer image ...
... May be viewed as an extension of the outer atmosphere of the Sun (the corona) into interplanetary space. Computer image ...
ppt document - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955) Theory of Relativity (1905 and following) predicted that different observers will measure different times, distances and masses based on the observers’ relative speeds. In particular, lifetimes and masses of particles differ if they are stationary compared to when they ...
... Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955) Theory of Relativity (1905 and following) predicted that different observers will measure different times, distances and masses based on the observers’ relative speeds. In particular, lifetimes and masses of particles differ if they are stationary compared to when they ...
Who am I? - Denton ISD
... The motion of traveling around another object in space. • Earth revolves around the Sun once a year (365 days) ...
... The motion of traveling around another object in space. • Earth revolves around the Sun once a year (365 days) ...
Document
... them together in the same constellation. b) The stars all have nearly the same parallax since they are moving together through space. c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure ...
... them together in the same constellation. b) The stars all have nearly the same parallax since they are moving together through space. c) None of them has a measurable parallax since they are mostly within our own Solar System. d) They may have significantly different parallaxes. e) We cannot measure ...
The Big Bang Demonstration
... and warmth on the planets come from the sun. The Sun get most gets its energy from nuclear reactions, which release vast quantities of energy; and these same nuclear reactions created smaller clumps of matter that became the planets, moons, comets, and asteroids. How the solar system was formed is a ...
... and warmth on the planets come from the sun. The Sun get most gets its energy from nuclear reactions, which release vast quantities of energy; and these same nuclear reactions created smaller clumps of matter that became the planets, moons, comets, and asteroids. How the solar system was formed is a ...
Dead Earth – Lesson 2 – Solar System
... distance from the Sun, and what other objects exist in the Solar system I will be successful if I can : Explain how the conditions on a planet change as the distance from the Sun increases ...
... distance from the Sun, and what other objects exist in the Solar system I will be successful if I can : Explain how the conditions on a planet change as the distance from the Sun increases ...
The Roots of Astronomy Stonehenge
... Mars is created by the fact that the earth passes Mars. This occurs every 26 months. ...
... Mars is created by the fact that the earth passes Mars. This occurs every 26 months. ...
hw4
... direction of motion and stellar velocity is found. Magnetic effects reveal themselves through a splitting of spectral lines—analyze spectrum for the Zeeman effect. Stellar rotation can be measured from the broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect. Color of the star can be determined by ...
... direction of motion and stellar velocity is found. Magnetic effects reveal themselves through a splitting of spectral lines—analyze spectrum for the Zeeman effect. Stellar rotation can be measured from the broadening of spectral lines due to the Doppler effect. Color of the star can be determined by ...
Why the sun is important too!
... Plants have specific organs in their cells that convert sunlight to food energy through a process known as photosynthesis. A plant will capture the sun’s rays in a chloroplast through a chemical reaction and this conversion gives plants the ability to supply calories to all of life. Cows eat plants, ...
... Plants have specific organs in their cells that convert sunlight to food energy through a process known as photosynthesis. A plant will capture the sun’s rays in a chloroplast through a chemical reaction and this conversion gives plants the ability to supply calories to all of life. Cows eat plants, ...
Unit 2 Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... 4. Definition of AU:Astronomical Unit is distance between Earth and Sun (93 million miles / 150 million kilometers). 5. What planet is closest to Earth in size and mass? Venus 6. List the gas giants in our solar system? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune 7. What is in the rings that surround many ...
... 4. Definition of AU:Astronomical Unit is distance between Earth and Sun (93 million miles / 150 million kilometers). 5. What planet is closest to Earth in size and mass? Venus 6. List the gas giants in our solar system? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune 7. What is in the rings that surround many ...
Astronomy from the ancients to the Renaissance
... However, in a way, Ptolemy can be considered a plagiarist. He probably did not reobserve the 1000 brightest stars visible from Alexandra. He simple took the star catalogue of Hipparchus and precessed the coordinates for precession by adding the same angular value to the celestial longitudes of thos ...
... However, in a way, Ptolemy can be considered a plagiarist. He probably did not reobserve the 1000 brightest stars visible from Alexandra. He simple took the star catalogue of Hipparchus and precessed the coordinates for precession by adding the same angular value to the celestial longitudes of thos ...
File
... separate from matter, and universe bursts forth with light (This liberation of photons is what we observe today as the 3K background radiation permeating the universe) ...
... separate from matter, and universe bursts forth with light (This liberation of photons is what we observe today as the 3K background radiation permeating the universe) ...
File - Prairie Science
... full moons (29.5 days). ◦ However, now a year is just broken into 12 months (number of full moons in a year not always a whole number) ...
... full moons (29.5 days). ◦ However, now a year is just broken into 12 months (number of full moons in a year not always a whole number) ...
ASTR2050 Intro A&A NAMES: ____________________ ____________________ Work sheet
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
... Build a scale model of the solar system, including the sizes and orbital radii of the sun and planets. Most of the data you need can be found in Kutner, Appendices B and D, and Figure 17.3. Show the units in the following lists. 1. What celestial object did you use to set the scale, and what did you ...
Lecture04
... Earth’s rotation • Responsible for our familiar calendar “day”. • Period (of rotation) = 24 hours = (24 hours)x(60 min/hr)x(60s/min) =86,400 s • Astronomers refer to this 24 hour period as a mean solar day (§2-7), implying that this time period is measured with respect to the Sun’s position on the ...
... Earth’s rotation • Responsible for our familiar calendar “day”. • Period (of rotation) = 24 hours = (24 hours)x(60 min/hr)x(60s/min) =86,400 s • Astronomers refer to this 24 hour period as a mean solar day (§2-7), implying that this time period is measured with respect to the Sun’s position on the ...
Astronomy II (ASTR-1020) — Homework 1
... b) The hypothesis is debated by scientists, and if debated successfully, becomes a theory. c) The hypothesis is tested through repeated experimentation and/or observations. d) If the hypothesis passes these experiments/observations, it becomes a theory. e) None of these are part of the scientific me ...
... b) The hypothesis is debated by scientists, and if debated successfully, becomes a theory. c) The hypothesis is tested through repeated experimentation and/or observations. d) If the hypothesis passes these experiments/observations, it becomes a theory. e) None of these are part of the scientific me ...
Ch. 28 Sec. 1
... orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more ...
... orbits a point between it and the Sun called the center of mass. Just as the balance point on a seesaw is closer to the heavier box, the center of mass between two orbiting bodies is closer to the more ...
Earth Science Chapter Two: What Makes Up the Solar System
... Lesson One: Investigation-No test questions from this lesson Lesson Two: Stars and Galaxies 1. What is formed from a huge cloud of dust and gas called a nebula? 2. How long does the average star live? 3. The sun is part of a galaxy. How would you describe a galaxy? Lesson Three: Constellations 1. Wh ...
... Lesson One: Investigation-No test questions from this lesson Lesson Two: Stars and Galaxies 1. What is formed from a huge cloud of dust and gas called a nebula? 2. How long does the average star live? 3. The sun is part of a galaxy. How would you describe a galaxy? Lesson Three: Constellations 1. Wh ...
mike-ken_transit
... What is a Planet? What’s the problem with Pluto? Pluto is now known as a “dwarf planet” The new definition of planet: 1 Round (not potato-shaped) ...
... What is a Planet? What’s the problem with Pluto? Pluto is now known as a “dwarf planet” The new definition of planet: 1 Round (not potato-shaped) ...
Chapter 16: The Origin of the Solar System RQ 16
... Q: How does the solar nebula theory explain the dramatic density difference between the terrestrial and Jovian planets? A: The difference in the density of terrestrial and Jovian planets can be explained by the different ability of materials (elements, molecules) to condense at a certain temperature ...
... Q: How does the solar nebula theory explain the dramatic density difference between the terrestrial and Jovian planets? A: The difference in the density of terrestrial and Jovian planets can be explained by the different ability of materials (elements, molecules) to condense at a certain temperature ...























